
The leopard coral grouper, also known as the common coral trout, leopard coral trout, blue-dotted coral grouper or spotted coral grouper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in the Western Pacific Ocean.

Plectropomus laevis, known commonly as the black-saddled coral grouper, cluespotted coral trout, blacksaddled coral trout, blue-spot trout, Chinese footballer, footballer cod, footballer coral trout, oceanic coral trout or tiger trout, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in the Indo-Pacific region.

Pseudorhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae. The type-species of the genus is Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli .

The Diplectanidae are a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans. They are all parasitic on the gills of fish. Diplectanids are small animals, generally around 1 mm in length. As parasites, they can be extremely numerous, up to several thousand on an individual fish.
Pseudorhabdosynochus auitoe is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the Highfin grouper, Epinephelus maculatus. It was described in 2007.
Pseudorhabdosynochus buitoe is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the Highfin grouper, Epinephelus maculatus. It has been described in 2007.
Pseudorhabdosynochus duitoe is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the highfin grouper, Epinephelus maculatus. It has been described in 2007.
Pseudorhabdosynochus fuitoe is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the highfin grouper, Epinephelus maculatus. It has been described in 2007.
Pseudorhabdosynochus guitoe is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the Highfin grouper, Epinephelus maculatus. It has been described in 2007.
Pseudorhabdosynochus huitoe is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the highfin grouper, Epinephelus maculatus. It was described in 2007.

Echinoplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on the gills of fish; hosts recorded to date are all groupers, including coralgroupers and the Dusky grouper. So far, species of Echinoplectanum have been recorded only from fish caught off Australia, New Caledonia and in the Mediterranean Sea.

Echinoplectanum laeve is a species of diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the black-saddled coralgrouper, Plectropomus laevis. It has been described in 2006. E. laeve is the type-species of the genus Echinoplectanum.

Pseudorhabdosynochus dolicocolpos is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of groupers. It has been described in 2007 by Lassad Neifar & Louis Euzet. The species name refers to the size of the vagina and is derived from the Greek words “dolicos” meaning long and “colpos” vagina. The species has been redescribed by Amira Chaabane, Lassad Neifar, and Jean-Lou Justine in 2017.
Pseudorhabdosynochus chauveti is a species of diplectanid monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of the blue grouper Epinephelus cyanopodus. It was described in 2008.
Pseudorhabdosynochus dionysos is a species of diplectanid monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of the camouflage grouper Epinephelus polyphekadion. It was described in 2011.
Pseudorhabdosynochus exoticus is a species of diplectanid monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of the blue grouper Epinephelus cyanopodus. It was described in 2008.
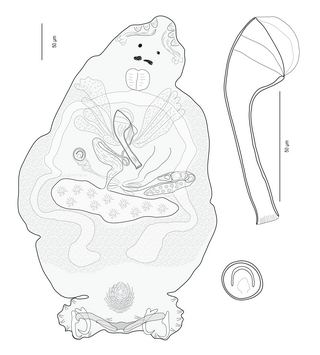
Laticola dae is a species of diplectanid monogenean. It is parasitic on the gills of the Highfin grouper, Epinephelus maculatus. It was described in 2006. The species is a member of the genus Laticola Yang, Kritsky, Sun, Zhang, Shi & Agrawal, 2006. More than 400 specimens of this parasite were studied for the description of the species, which was the most abundant monogenean species, representing about 50% of the specimens found on this fish.
Echinoplectanum leopardi is a species of diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the leopard coralgrouper, Plectropomus leopardus. It has been described in 2006.
Echinoplectanum pudicum is a species of diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the leopard coralgrouper, Plectropomus leopardus. It has been described in 2006. This species was distinguished from all other species of the genus Echinoplectanum by the shape and small size of its male copulatory organ, and the apparent absence of a sclerotised vagina.
Echinoplectanum rarum is a species of diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the leopard coralgrouper, Plectropomus leopardus. It has been described in 2006. This species is very rare and represented only 2% of the specimens of Echinoplectanum spp. found in P. leopardus. This species was distinguished from other species of the same genus by its characteristic ring-shaped sclerotised vagina.






