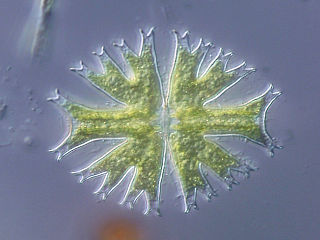
Desmidiales, commonly called the desmids, are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Desmids consist of single-celled microscopic green algae. Because desmids are highly symmetrical, attractive, and come in a diversity of forms, they are popular subjects for microscopists, both amateur and professional.

Trachelomonas is a genus of swimming, free-living euglenoids characterized by the presence of a shell-like covering called a lorica. Details of lorica structure determine the classification of distinct species in the genus. The lorica can exist in spherical, elliptical, cylindrical, and pyriform (pear-shaped) forms. The lorica surface can be smooth, punctuate or striate and range from hyaline, to yellow, or brown. These colors are due to the accumulation of ferric hydroxide and manganic oxide deposited with the mucilage and minerals that comprise the lorica. In Trachelomonas, the presence of a lorica obscures cytoplasmic details of the underlying cell. In each Trachelomonas cell, there is a gap at the apex of the lorica from which the flagellum protrudes. Thickening around this gap results in a rim-like or collar-like appearance. During asexual reproduction, the nucleus divides yielding two daughter cells one of which exits through the opening in the lorica. This new cell then synthesizes its own new lorica.
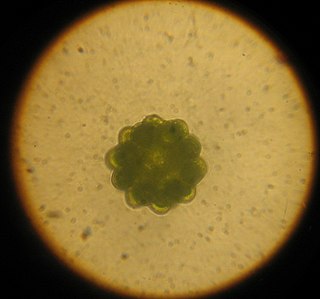
Coelastrum is a genus of green algae in the Scenedesmaceae family. It is a common component of the phytoplankton in freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, waterfalls, and temporary pools of water, particularly eutrophic ones. The genus has a more or less cosmopolitan distribution, although some species appear to have more restricted geographical distributions.
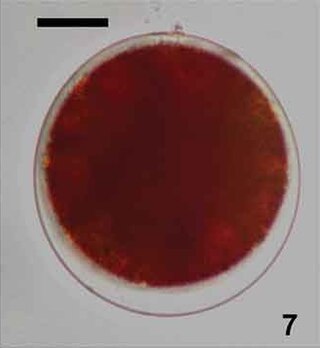
Chlainomonas is a genus of algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. They are found in freshwater habitats or on snow, where they are one of the main algae responsible for causing watermelon snow.

Chlamydocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae.
Coelastropsis is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae, containing the single species Coelastropsis costata. It is found in freshwater lakes and bogs, usually associated with mosses and filamentous algae. It has been recorded in Europe, Cuba and possibly New Zealand.

Golenkinia is a genus of green algae first described in 1894 by Robert Chodat. The genus is named for the Russian phycologist Mikhail Iljitsch Golenkin. Golenkinia species live in fresh water and are found around the world.

Hariotina is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. They are classified in the subfamily Coelastroideae.

Lagerheimia is a genus of green algae in the family Oocystaceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats all over the world, although some species are rare and have only been recorded from Europe or the United States.
Neodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae.
Palmellopsis is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Palmellopsidaceae. They are either planktonic or attached to substrates in fresh water, or in aeroterrestrial habitats.

Paulschulzia is a genus of green algae, specifically of the family Tetrasporaceae.

Planktosphaeria is a genus of Chlorophyceae of the green algae. It was first described by the phycologist Gilbert Morgan Smith in 1918, with Planktosphaeria gelatinosa as its type species. Species of Planktosphaeria are commonly found in freshwater plankton around the world.

Radiofilum is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. It is a freshwater genus; they are often found in soft, boggy or acidic waters.

Sorastrum is a genus of green algae in the family Hydrodictyaceae. It is a component of the phytoplankton of freshwater ponds, lakes, and ditches. Sorastrum is common in tropical to temperate regions of the world, but due to its small size it is often overlooked.
Spinoclosterium is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Closteriaceae. It is rare, but widely distributed in freshwater regions throughout the world.

Tetrastrum is a genus of green algae (Chlorophyta). It is a common component of the phytoplankton of freshwater habitats, particularly eutrophic and alkaline waters.
Gilbertsmithia is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae, containing the single species Gilbertsmithia grandis. It was named after the American botanist Gilbert Morgan Smith. This remarkable alga has only been recorded once from a muddy rainwater pool in Madras, India.

Chlorokybus is a multicellular (sarcinoid) genus of basal green algae or charophyte. It has been classified as the sole member of the family Chlorokybaceae, which is the sole member of the order Chlorokybales, in turn the sole member of the class Chlorokybophyceae. It grows on soil and rock surfaces, and is rare.
Pseudokirchneriella is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is found as phytoplankton in freshwater ponds, lakes, and pools. It has been reported from Europe and North America.














