
Kottayam is one of 14 districts in the Indian state of Kerala. Kottayam district comprises six municipal towns: Kottayam, Changanassery, Pala, Erattupetta, Ettumanoor, and Vaikom. It is the only district in Kerala that does not border either the Arabian Sea or another Indian state.

Kodungallur is a historically significant town situated on the banks of river Periyar on the Malabar Coast in Thrissur district of Kerala, India. It is 29 kilometres (18 mi) north of Kochi (Cochin) by National Highway 66 and 38 km (24 mi) from Thrissur. Kodungallur, being a port city at the northern end of the Kerala lagoons, was a strategic entry point for the naval fleets to the extensive Kerala backwaters.

Valluvanad was an independent chiefdom in present-day central Kerala that held power from the early 12th century to the end of the 18th century. Prior to that, and since the late 10th century, Valluvanad existed as an autonomous chiefdom within the kingdom of the Chera Perumals. The disintegration of the Chera Perumal kingdom in early 12th century led to the independence of the various autonomous chiefdoms of the kingdom, Valluvanad being one of them.

The Kingdom of Cochin, also known as the Kingdom of Kochi or later as Cochin State, named after its capital in the city of Kochi (Cochin), was an Indian Hindu kingdom in the central part of present-day Kerala state. It commenced at the early part of the 12th century and continued to rule until its accession to the Dominion of India in 1949.

Kolattunādu (Kola Swarupam, as Kingdom of Cannanore in foreign accounts, Chirakkal (Chericul) in later times) was one of the four most powerful kingdoms on the Malabar Coast during the arrival of the Portuguese Armadas in India, along with Zamorin, the Kingdom of Cochin and Quilon. Kolattunādu had its capital at Ezhimala and was ruled by the Kolattiri royal family and roughly comprised the North Malabar region of Kerala state in India. Traditionally, Kolattunādu is described as the land lying between the Chandragiri river in the north and the Korappuzha river in the south. The Kolathunadu (Kannur) Kingdom at the peak of its power, reportedly extended from the Netravati River (Mangalore) in the north to Korapuzha (Kozhikode) in the south with the Arabian Sea on the west and Kodagu hills on the eastern boundary, also including the isolated islands of Lakshadweep in the Arabian Sea.

Edappally is a ward of Kochi, Kerala. The name is also used to refer to adjacent wards of Kalamassery and Thrikkakkara municipalities. Edappally is a major commercial centre as well as a prominent residential region. Edappally junction is one of the busiest junctions in the city.
Azhvanchery Thamprakkal or Azhvanchery Samrāṭ is the title of the senior-most male member of the Nambudiri Brahmin feudal lords of Azhvanchery Mana in Athavanad, Kerala, South India. They had the right over Guruvayur, and were the titular head of all Nambudiri Brahmins of Kerala. The Lord of Azhvanchery based at Athavanad and the Lord of Kalpakanchery based at neighbouring Kalpakanchery were usually present at the coronation of a new Zamorin of Kozhikode. Kalpakanchery Thamprakkals were related to the Nambudiris of Panniyoor while Azhvanchery Thamprakkals to those of Chowwara.
Jenmi or Janmi, plural Jenmimar, is the Malayalam term used to refer to the landed aristocracy of Kerala who traditionally held their lands as absolute and allodial owners, with such lands known as Jenmom or Janmam. They formed the landowning nobility as well as the landed gentry of the region in colonial times, and the majority of the estates and feudal properties were owned by this community. They predominantly belonged to the Nambudiri and Nair castes.

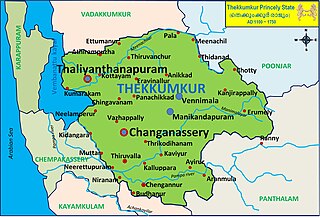
The Kingdom of Thekkumkur was an independent kingdom in the southern part of Kerala in India from 1103 CE until 1750 CE. It was ruled by the Thekkumkur Royal Family. Thekkumkur lies between the Meenachil River and the Pamba River, from the Western Ghats to the Vembanad Kayal. Thekkumkur emerges as a result of administrative changes in the princely states at the end of the Chera Kulasekhara dynasty of Mahodayapuram. The literal meaning of the title is the southern regent and the attribute southern distinguished them from another kingdom known as Vadakkumkur which bordered it in the northern side. The royal household, Thekkumkur Kovilakam, were at Vennimala and Manikandapuram near Puthuppally, later it shifted to Neerazhi Palace at Puzhavathu of Changanassery and Thalilkotta at Thaliyanthanapuram (Kottayam).

This article lists the various old and ancient churches that exist among the Saint Thomas Christians in Kerala.

The Samoothiri was the title of the erstwhile ruler and monarch of the Kingdom of Kozhikode (Calicut) in the South Malabar region of India. Originating from the former feudal kingdom of Nediyiruppu Swaroopam, the Samoothiris and their vassal kings from Nilambur Kovilakam established Calicut as one of the most important trading ports on the southwest coast of India. At the peak of their reign, they ruled over a region extending from Kozhikode Kollam to the forested borders of Panthalayini Kollam (Koyilandy). The Samoothiris belonged to the Eradi subcaste of the Samantan community of colonial Kerala, and were originally the ruling chiefs of Eranad. The final Zamorin of Calicut committed suicide by setting fire to his palace and burning himself alive inside it, upon learning that Hyder Ali had captured the neighboring country of Chirackal in Kannur.

The Kavalappara is an princely Indian Nair tharavad or swaroopam, whose estates and powers vested in the matrilineally-mediated succession to and from each Kavalappara Nair, who headed the family and held the rank of Moopil Nair. In medieval Kerala, they served as part of the jenmi, or allodially landed nobility, and were sworn to the service of the rajas of the area, first that of Palghat and then later that of Cochin. Based at Kavalappara Desam in Karakkat, Valluvanada, their holdings extended to areas such as Kailiad and Panayur, ultimately compassing some 155,358 acres of jenmom estates, and ranking preeminent among the jenmimars of Malabar.

Thiruvarkadu Bhagavathi Temple is the mother temple of all Bhadrakali shrines of Kerala. The deity is the Fierce form of Bhadrakali. The Bhagavathy is addressed by tantrics in the vicinity as Tiruvarkkad Achchi due to this. The temple administration is Malabar Devaswom Board. The temple is a revered shrine of Chirakkal Royal Family and a shrine of Chirakkal devaswom before. The temple is situated in Madayi, Payangadi, hence prominently known as Madayi Kavu.
Kallooppara is a village near Thiruvalla in Pathanamthitta district in the state of Kerala, India. It is part of the Thiruvalla constituency.
The Kingdom of Tanur was one of the numerous feudal principalities on the Malabar Coast of the Indian subcontinent during the Middle Ages. It was ruled by a Hindu dynasty, claiming kshatriya status, known as the Tanur dynasty. The kingdom comprised parts of the coastal Taluks of Tirurangadi, Tirur, and Ponnani taluks in present-day Malappuram district and included places such as Tanur, Tirur (Trikkandiyur) and Chaliyam. The coastal villages of Kadalundi and Chaliyam in the southernmost area of Kozhikode district was also under Tanur Swaroopam.

Sree Valayanad Devi Temple dedicated to Bhagavathy, is situated in Valayanad near Kozhikode in North Kerala, India.
Poonjar dynasty was one of the royal dynasties in medieval Kerala descended from the Pandya kings of Madurai. History has it that Manavikrama Kulasekara Perumal, a Pandya king as the sole founder of the dynasty. It was a minor principality in the central Travancore region which covered the parts of present-day Dindigul, Cumbum, Kudallor, Bodinayakkanur, Vandiperiyar, Peerumedu and Kannan Devan hills.
Kaviyoor is a village located in Thiruvalla Sub-District & Taluk In Pathanamthitta district of Kerala State,India, situated on the western bank of the Manimala River.It Is Located Adjoining Thiruvalla Municipal Town.
The Battle of Changanacherry was a battle between the kingdoms of Thekkumkur and Travancore in September 1749. Defeat in this decisive battle led to Thekkumkur losing its dominance and expanding the Tranvancore empire to the southern border of the river Meenachilar.

Lakshmipuram Palace is the royal palace of the Parappanad royal families at Changanassery. Palace is located at Puzhavathu near to Kavil Bhagavathy Temple. The Lakshmipuram Palace was built in 1811 AD by Travancore ruler Maharani Ayilyom Thirunal Gouri Lakshmi Bayi (1791–1815) on behalf of the family of her husband Raja Raja Varma Valiya Koil Thampuran. Until then, the royal family at the Neerazhi Palace in Changanacherry had been moved to newly built Lakshmipuram Palace. It was the seat of the royal family of Koi thampurans and has produced many illustrious writers such as Raja Raja Varma Koil Thampuran, Kerala Varma Valiya Koil Thampuran and A. R. Raja Raja Varma. Noted Malayalam singer and classical musician L. P. R. Varma also hails from this palace.














