
The Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS) is an American partnership of federal agencies designed to provide consistent and reliable information on the taxonomy of biological species. ITIS was originally formed in 1996 as an interagency group within the US federal government, involving several US federal agencies, and has now become an international body, with Canadian and Mexican government agencies participating. The database draws from a large community of taxonomic experts. Primary content staff are housed at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History and IT services are provided by a US Geological Survey facility in Denver. The primary focus of ITIS is North American species, but many biological groups exist worldwide and ITIS collaborates with other agencies to increase its global coverage.

Whiteleg shrimp, also known as Pacific white shrimp or King prawn, is a species of prawn of the eastern Pacific Ocean commonly caught or farmed for food.
Palibythus magnificus, sometimes called the musical furry lobster, is a species of furry lobster found in Polynesia. It is generally included in the family Palinuridae, although it has also been separated from that family with the genus Palinurellus to form the family Synaxidae in the past. The species is known in Samoan as ula moana, a name which also covers the deep-water shrimp Heterocarpus laevigatus.

Shrimpfish, also called razorfish, are five small species of marine fishes in the subfamily Centriscinae of the family Centriscidae. The species in the genera Aeoliscus and Centriscus are found in relatively shallow tropical parts of the Indo-Pacific, while the banded bellowsfish, which often is placed in the subfamily Macroramphosinae instead, is restricted to deeper southern oceans.

The leatherjacket fish, also known as leather jack, is a species of jack in the family Carangidae. Leather jack may also refer to other members of the Carangidae, such as the pilot fish. The largest are about a foot long.

Snipe eels are a family, Nemichthyidae, of eels that consists of nine species in three genera. They are pelagic fishes, found in every ocean, mostly at depths of 300–600 m (980–1,970 ft) but sometimes as deep as 4,000 m (13,000 ft). Depending on the species, adults may reach 1–2 m (39–79 in) in length, yet they weigh only 80–400 g (2.8–14.1 oz). They are distinguished by their very slender jaws that separate toward the tips as the upper jaw curves upward. The jaws appear similar to the beak of the bird called the snipe. Snipe eels are oviparous, and the juveniles, called Leptocephali, do not resemble the adults but have oval, leaf-shaped and transparent bodies. Different species of snipe eel have different shapes, sizes and colors. The similarly named bobtail snipe eel is actually in a different family and represented by two species, the black Cyema atrum and the bright red Neocyema erythrosoma.

Pandalus platyceros, also called California spot prawn or Alaskan prawn, is a shrimp of the genus Pandalus.
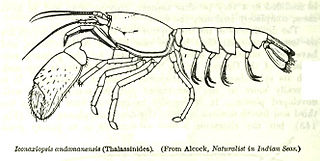
Eiconaxius andamanensis is a species in the family Axiidae. Although it is not a true lobster, is sometimes known by the common names "mud lobster" and "scorpion lobster". Its scientific name comes from the Andaman Sea, where it has been collected off the west coast of Andaman Islands at a depth of 238–290 fathoms.

Eiconaxius is a genus of mud lobster that includes the following species:

Galathea is a genus of squat lobsters in the family Galatheidae. It is one of the largest genera of squat lobsters that in 2008 contained 73 species. Most species of Galathea live in shallow waters.
Eiconaxius cristagalli is a species of mud lobster from the Pacific Ocean.

Hymenodora glacialis, commonly known as the Northern deep-sea shrimp or the Northern ambereye, is a species of pelagic shrimp in the Acanthephyridae family. It is the only known species of pelagic shrimp to inhabit the Canada Basin.

The Indian mackerel or bigmouth mackerel is a species of mackerel in the scombrid family of order Perciformes. It is commonly found in the Indian and West Pacific oceans, and their surrounding seas. It is an important food fish and is commonly used in South and South-East Asian cuisine.

Pseudosquilla ciliata, the common mantis shrimp, is a species of mantis shrimp, known by common names including rainbow mantis shrimp and false mantis shrimp. It is widespread in the tropical Indo-Pacific region and in both the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean.

Heterocarpus ensifer is a species of deep-water shrimp. The nominate subspecies is found in the Atlantic Ocean from Spain and Madeira to Angola and from North Carolina to the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea; other subspecies occur in the Pacific Ocean and around the Philippines and Indonesia. Despite being one of the most abundant shrimp in some areas, its biology is still poorly known. These deep water crustaceans are most copious between 300 and 400m. Their distribution demonstrates an ability to adapt well to distinct environments. It is generally found at depths of 200–885 m (656–2,904 ft).
Tetrasquilla is a genus of mantis shrimp containing a single species, Tetrasquilla mccullochae. It is the only known pantropical stomatopod. The specific epithet commemorates Dr. Irene A. McCulloch, professor of zoology of the University of Southern California.

Lysmata vittata, commonly known as the peppermint shrimp, is a species of shrimp, native to the Indo-Pacific from East Africa to the Philippines, Japan, Australia and New Zealand.

Clupea is genus of planktivorous bony fish belonging to the family Clupeidae, commonly known as herrings. They are found in the shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and the North Atlantic oceans, including the Baltic Sea. Two main species of Clupea are currently recognized: the Atlantic herring and the Pacific herring, which have each been divided into subspecies. Herrings are forage fish moving in vast schools, coming in spring to the shores of Europe and America, where they form important commercial fisheries.

Periclimenes, commonly known as glass shrimp or cleaner shrimp, is a commensal and often symbiotic genus of semi-transparent shrimp within the family Palaemonidae. Species of this large genus feature a wide variety of coloration and patterns, widespread distribution throughout much of the world's tropical oceans, and are often sought out for aquarium trade.
Thor manningi is a species of shrimp. The common name for this species is the Manning grass shrimp. On average the life span in this species is 4 to 5 months. The species uses drag powered swimming to move from place to place.













