| Elm | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Original author | Dave Taylor |
| Developer | Bill Pemberton |
| Initial release | 1986 |
| Stable release | 2.5.8 (August 18, 2005) [±] |
| Repository | |
| Operating system | Any Unix-like |
| Type | Email client |
| License | BSD-like |
| Website | www |
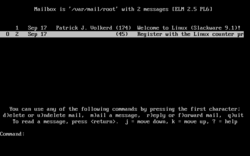
Elm is a text-based email client commonly found on Unix systems. First released in 1986, it became popular as one of the first email clients to use a text user interface, and as a utility with freely available source code. The name elm originated from the phrase ELectronic Mail. [1]
Contents
Dave Taylor (currently with Intuitive Systems) developed elm while working for Hewlett-Packard. [2] Development later passed to a team of volunteers. The latest (as of 21 May 2014 [update] ) public release was version 2.5.8 in August 2005.
Other popular text-based email readers which followed elm and took it as an inspiration include Pine (1989) and Mutt (1995). From about 1995 elm slipped in popularity and functionality, and it now sees relatively little use.
Former elm coordinators include Bill Pemberton of the University of Virginia and Sydney Weinstein from the Myxa Corporation.