This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2015) |

Minnesota Internet Users Essential Tool (Minuet) is an integrated Internet package for DOS operating systems on IBM-compatible PCs.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2015) |

Minnesota Internet Users Essential Tool (Minuet) is an integrated Internet package for DOS operating systems on IBM-compatible PCs.
Minuet was created at the University of Minnesota, in the early days of the World Wide Web (1994–1996). At that time, Internet software for MS-DOS was immature — the only programs available were NCSA Telnet and NCSA FTP. Both are glitchy, hard to configure, and TTY-oriented.
The microcomputer support department at the university decided to come up with something better. Their design goals were:
The result was "Minuet". Minuet was quite successful at its time, being used at many colleges and institutions. Its usage peaked around 1996, going down as Windows 95 and its free e-mail reader and web browser proliferated.
The program was written in Turbo Pascal, using the Turbo Vision GUI. This base is a good match for the PCs of that time. Turbo Vision in its early incarnations uses the 80×25 character text mode, meaning very speedy screen updates, even on slow PCs. Later Minuet versions - including the last one 1.0 Beta 18A - also support graphical modes up to 1600 × 1200 pixels (UXGA) while displaying up to 16.7 million colors, depending on the capabilities and VESA compatibility of the hardware used.
A homebrew multi-tasking kernel allows users to have several Minuet windows active at the same time. An FTP session could be transferring files, while in another window, the user could be composing an e-mail. All the parts of Minuet use multi-tasking, the user does not have to wait for a slow operation to complete.
Email in Minuet resembles most standard email programs — From:, To:, cc:, Bcc:, and Message body fields. Attachments use the BinHex and UUCP encoding schemes, which predated MIME and were popular in Minuet's days.
In Minuet, Newsgroups appear much like e-mail folders. An innovative concept is included — Minuet would not attempt to download the whole newsgroups file, which even then included thousands of newsgroups. Instead, a Perl server[ clarification needed ] is contacted to search for interesting newsgroups. This cuts down the newsgroup searching startup time from many minutes to a few seconds.
Minuet also comes with a built-in Gopher client.
Minuet is one of the first programs to have a graphical tree-structured approach to FTP. At the time, most FTP clients required an almost endless sequence of "cd", "ls" commands to browse servers.
In its last version 1.0 Beta 18A from 1994, Minuet also includes a WWW browser for the first time. However, it is only HTTP/1.0-compliant, renders web sites in a pre-HTML 2.0 standard and therefore comes with no web form or table support. Later common web browser features such as JavaScript, CSS or proxy server support are not present in this version either. Enabling the graphical mode, however, allows Minuet to directly render GIF and JPEG images in HTML documents, which is a superior feature compared to other DOS-based WWW browsers of the time.
At that time most PC users connected to the internet using a modem, so a robust modem-capable driver was required. Unfortunately, SLIP drivers of the time were poor — hard to configure, difficult to test, missing important features like dialing, and often not using all of the buffering features of the serial port chips. Consequently, the Minuet team developed a SLIP driver and dial-up program.

A bulletin board system (BBS), also called a computer bulletin board service (CBBS), is a computer server running software that allows users to connect to the system using a terminal program. Once logged in, the user performs functions such as uploading and downloading software and data, reading news and bulletins, and exchanging messages with other users through public message boards and sometimes via direct chatting. In the early 1980s, message networks such as FidoNet were developed to provide services such as NetMail, which is similar to internet-based email.
A file manager or file browser is a computer program that provides a user interface to manage files and folders. The most common operations performed on files or groups of files include creating, opening, renaming, copying, moving, deleting and searching for files, as well as modifying file attributes, properties and file permissions. Folders and files may be displayed in a hierarchical tree based on their directory structure.

The history of the graphical user interface, understood as the use of graphic icons and a pointing device to control a computer, covers a five-decade span of incremental refinements, built on some constant core principles. Several vendors have created their own windowing systems based on independent code, but with basic elements in common that define the WIMP "window, icon, menu and pointing device" paradigm.
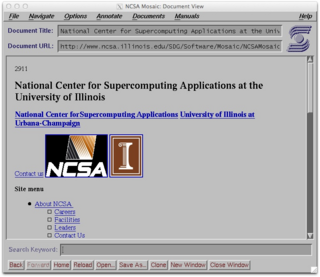
NCSA Mosaic was among the first widely available web browsers, instrumental in popularizing the World Wide Web and the general Internet by integrating multimedia such as text and graphics. Mosaic was the first browser to display images inline with text.

Cello is an early, discontinued graphical web browser for Windows 3.1; it was developed by Thomas R. Bruce of the Legal Information Institute at Cornell Law School. It was released as shareware in 1993. While other browsers ran on various Unix machines, Cello was the first web browser for Microsoft Windows, using the winsock system to access the Internet. In addition to the basic Windows, Cello worked on Windows NT 3.5 and with small modifications on OS/2.
An online service provider (OSP) can, for example, be an Internet service provider, an email provider, a news provider (press), an entertainment provider, a search engine, an e-commerce site, an online banking site, a health site, an official government site, social media, a wiki, or a Usenet newsgroup.
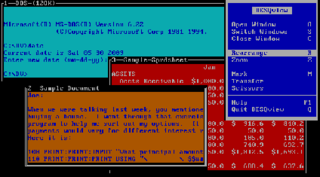
DESQview (DV) is a text mode multitasking operating environment developed by Quarterdeck Office Systems which enjoyed modest popularity in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Running on top of DOS, it allows users to run multiple programs concurrently in multiple windows.

Damn Small Linux (DSL) is a computer operating system for the x86 family of personal computers. It is free and open-source software under the terms of the GNU GPL and other free and open-source licenses. It was designed to run graphical user interface applications on older PC hardware, for example, machines with 486 and early Pentium microprocessors and very little random-access memory (RAM). DSL is a live CD with a size of 50 megabytes (MB). What originally began as an experiment to see how much software could fit in 50 MB eventually became a full Linux distribution. It can be installed on storage media with small capacities, like bootable business cards, USB flash drives, various memory cards, and Zip drives.
Windows 9x is a generic term referring to a line of discontinued Microsoft Windows operating systems from 1995 to 2000, which were based on the Windows 95 kernel and its underlying foundation of MS-DOS, both of which were updated in subsequent versions. The first version in the 9x series was Windows 95, which was succeeded by Windows 98 and then Windows Me, which was the third and last version of Windows on the 9x line, until the series was superseded by Windows XP.

DOS Shell is a file manager that debuted in MS-DOS and PC DOS version 4.0, released in June 1988. It was no longer included in MS-DOS version 6, but remained part of the Supplemental Disk. The Supplemental Disk could be ordered or could be downloaded through Microsoft's FTP server. DOS Shell was retained in PC DOS until PC DOS 2000.
The Line Mode Browser is the second web browser ever created. The browser was the first demonstrated to be portable to several different operating systems. Operated from a simple command-line interface, it could be widely used on many computers and computer terminals throughout the Internet. The browser was developed starting in 1990, and then supported by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) as an example and test application for the libwww library.
GEOS is a computer operating environment, graphical user interface (GUI), and suite of application software. Originally released as PC/GEOS, it runs on MS-DOS-based, IBM PC compatible computers. Versions for some handheld platforms were also released and licensed to some companies.
SlipKnot was one of the earliest World Wide Web browsers, available to Microsoft Windows users between November 1994 and January 1998. It was created by Peter Brooks of MicroMind, Inc. to provide a fully graphical view of the web for users without a SLIP or other TCP/IP connection to the net, hence the name – SLIP...not. SlipKnot provided a graphical web experience through what would otherwise be a text-only Unix shell account. SlipKnot version 1.0 was released on November 22, 1994, approximately 3 weeks before Netscape's Netscape Navigator version 1.0 came out. It was designed to serve a significant fraction of PC/Windows-based Internet users who could not use Mosaic or Netscape at that time.

Microsoft Internet Explorer 2 (IE2) is the second, and by now discontinued, version of Internet Explorer (IE), a graphical web browser by Microsoft. It was unveiled in October 1995, and was released on November 27, 1995, for Microsoft Windows, and on April 23, 1996, for Apple Macintosh.

Arachne is an Internet suite containing a graphical web browser, email client, and dialer. Originally, Arachne was developed by Michal Polák under his xChaos label, a name he later changed into Arachne Labs. It was written in C and compiled using Borland C++ 3.1. Arachne has since been released under the GPL as Arachne GPL.
Amiga software is computer software engineered to run on the Amiga personal computer. Amiga software covers many applications, including productivity, digital art, games, commercial, freeware and hobbyist products. The market was active in the late 1980s and early 1990s but then dwindled. Most Amiga products were originally created directly for the Amiga computer, and were not ported from other platforms.
RoboBOARD/FX was the third generation Bulletin Board System hosting package released by Hamilton TeleGraphics Inc of Canada, programmed by owner Seth Hamilton in 1993. It was the follow-up to ROBO-BOARD Pro and ROBO-BOARD Plus which first utilized groundbreaking Remote Imaging Protocol developed by TeleGrafix Communications, which was also known as RIPscrip.
A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. It further provides for the capture or input of information which may be returned to the presenting system, then stored or processed as necessary. The method of accessing a particular page or content is achieved by entering its address, known as a Uniform Resource Identifier or URI. This may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content. Hyperlinks present in resources enable users easily to navigate their browsers to related resources. A web browser can also be defined as an application software or program designed to enable users to access, retrieve and view documents and other resources on the Internet.
Emissary was a popular early commercial internet suite from Attachmate for Windows. It featured a web browser, FTP support, e-mail program, a newsreader program, and an HTML editor.

A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with a computer program by inputting lines of text called command-lines. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user-friendly alternative to the non-interactive interface available with punched cards.