
Sea slug is a common name for some marine invertebrates with varying levels of resemblance to terrestrial slugs. Most creatures known as sea slugs are actually gastropods, i.e. they are sea snails that over evolutionary time have either completely lost their shells, or have seemingly lost their shells due to having a greatly reduced or internal shell. The name "sea slug" is most often applied to nudibranchs, as well as to a paraphyletic set of other marine gastropods without obvious shells.
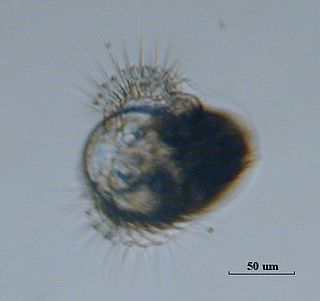
A veliger is the planktonic larva of many kinds of sea snails and freshwater snails, as well as most bivalve molluscs (clams) and tusk shells.
Elysia subornata is a species of small sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusk in the family Plakobranchidae.

Elysia chlorotica is a small-to-medium-sized species of green sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusc. This sea slug superficially resembles a nudibranch, yet it does not belong to that clade of gastropods. Instead it is a member of the clade Sacoglossa, the sap-sucking sea slugs. Some members of this group use chloroplasts from the algae they eat for photosynthesis, a phenomenon known as kleptoplasty. Elysia chlorotica is one of these "solar-powered sea slugs". It lives in a subcellular endosymbiotic relationship with chloroplasts of the marine heterokont alga Vaucheria litorea.

Elysia is a genus of sea slugs, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Plakobranchidae. These animals are colorful sea slugs, and they can superficially resemble nudibranchs, but are not very closely related to them. Instead they are sacoglossans, commonly known as sap-sucking slugs.

Elysia ornata, commonly known as ornate elysia or ornate leaf slug, is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusk. This sea slug superficially resembles a nudibranch, yet it does not belong to that suborder of gastropods. Instead it is a member of the closely related clade Sacoglossa, the "sap-sucking" sea slugs.

Peltodoris atromaculata, more commonly known as the dotted sea slug or sea cow, is a species of sea slug, a dorid nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Discodorididae. It dwells in salt water up to the depth of 40m. It is exclusively found in precorralligene and coralligene communities and is very common in such communities.

Tritonicula hamnerorum is a species of dendronotid nudibranch. It is a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Tritoniidae. A number of Caribbean species of Tritonia were moved to a new genus Tritonicula in 2020 as a result of an integrative taxonomic study of the family Tritoniidae.

Elysia gordanae is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc.
Elysia lobata is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. This sea slug resembles a nudibranch, but it is not closely related to that order of gastropods, instead it is a sacoglossan.

Elysia obtusa is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. This sea slug resembles a nudibranch but is not closely related to that order of gastropods, instead it is a sacoglossan.

Elysia diomedea is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae.
Elysia trisinuata is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. This sea slug resembles a nudibranch but is not closely related to that order of gastropods, instead belonging to another clade, Sacoglossa, the "sap-sucking" sea slugs.
Elysia rufescens is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. This sea slug resembles a nudibranch but is not classified in that order of gastropods, instead belonging to a closely related clade, Sacoglossa, the "sap-sucking" sea slugs. This species was first described by Pease from Tahiti in 1871.
Halophila engelmannii is a species of seagrass in the Hydrocharitaceae family. It is referred to by the common names star grass and Engelmann's seagrass and grows underwater on shallow sandy or muddy sea floors. It is native to the Bahamas, the Cayman Islands, Costa Rica, Cuba, the Gulf Coast of the United States, the Gulf Coast of Mexico, Puerto Rico, and Trinidad and Tobago.
Elysia serca, the seagrass elysia or Caribbean seagrass elysia, is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae. Although this sea slug resembles a nudibranch, it is not a nudibranch; it belongs to the clade, Sacoglossa, the "sap-sucking" sea slugs. It was first described by Marcus in 1955 from specimens found in Brazil.

Okenia zoobotryon is a species of sea slug, a dorid nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Goniodorididae. It is normally found on the colonial bryozoan Zoobotryon verticillatum on which it lives and feeds.

Berghia stephanieae is a species of sea slug, an aeolid nudibranch. It is a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Aeolidiidae. It was previously known as Aeolidiella stephanieae.

Elysia grandifolia is a species of sea slug, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae native to the waters off southern India and Sri Lanka. It has colonised the waters of the eastern Mediterranean Sea.

Electra posidoniae is a species of bryozoan in the family Electridae. It is endemic to the Mediterranean Sea, and is commonly known as the Neptune-grass bryozoan because it is exclusively found growing on seagrasses, usually on Neptune grass, but occasionally on eelgrass.














