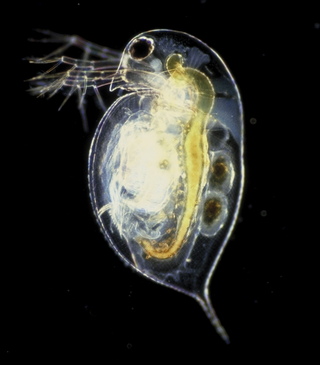
Daphnia is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, 0.2–6.0 mm (0.01–0.24 in) in length. Daphnia are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. Daphnia spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds.

Lumholtz's tree-kangaroo is a rare, long-tailed bear-like mammal found in rainforests in northeastern Australia. Like most tree-kangaroos, it lives alone in trees and feeds on plant matter. It belongs to the macropod family (Macropodidae) with kangaroos, and carries its young in a pouch like other marsupials. It is threatened by climate change and diseases, and is found in the hilly, fertile Atherton Tableland in Queensland.

The kirikuchi char, Salvelinus leucomaenis japonicus, is a freshwater fish in the family Salmonidae. It is endemic to the Kii Peninsula of central Honshu in Japan. It is the southernmost population of the char genus Salvelinus and is considered a relict in its region. It is usually considered a subspecies of the whitespotted char Salvelinus leucomaenis but was listed as a separate species in the IUCN Red List (1996).

Afrocyclops pauliani is an extinct species of copepod in the family Cyclopidae. A single specimen was discovered in 1951 in a small freshwater pool near Antananarivo, Madagascar, but the species has not been seen in collections since.
Aglaodiaptomus is a genus of copepods in the family Diaptomidae. They are often bright red or blue due to carotenoid pigments.
Boeckella is a genus of copepods in the family Centropagidae.
Calamoecia is a genus of copepods in the family Centropagidae confined to Australasia. It is thought to have evolved since the separation of the Australian continent from Antarctica. Three of the Australian endemic species are listed as vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List. The genus contains the following species:
Dussartius baeticus is a species of crustacean in the family Diaptomidae. It is endemic to the Iberian Peninsula, having been found in south-eastern Spain, and in the waters of the Tagus estuary, the Caniçada reservoir, and four reservoirs in the Mondego system in Portugal.
Eodiaptomus is a genus of copepods in the family Diaptomidae, containing the following species:
Eodiaptomus shihi is a species of crustacean in the family Diaptomidae. It is endemic to India, where it is found in the Gandhi Sagar reservoir, in the Narmada River and in a hill pool in Madhya Pradesh, and is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.
Fibulacamptus is an Australian endemic genus of crustacean in the family Canthocamptidae. Two of the four species are listed as vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List :
Hemiboeckella powellensis, is a zooplankton copepod of which only four of its kind have ever been observed. "Hemiboeckella" refers to this genus being a subvariant of Boeckella, whilst “powellensis” refers to Lake Powell in Western Australia, the region it is endemic to. Its existence was initially recorded in May and June of 1977, and has not been observed since.
Hesperodiaptomus is a genus of copepods in the family Diaptomidae, containing 18 species. Two species – Hesperodiaptomus augustaensis and Hesperodiaptomus californiensis – are endemic to the United States and listed as vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List.
Mexistenasellus is a genus of isopod crustaceans in the family Stenasellidae. It contains 6 species, of which 4 are listed as endangered or vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.
Muscocyclops is a genus of copepod crustaceans in the family Cyclopidae, comprising three species found only in South America. Two of the species – Muscocyclops bidentatus Reid, 1987 and Muscocyclops therasiae Reid, 1987 – are endemic to the Distrito Federal in Brazil, and are listed as conservation dependent on the IUCN Red List. The third species is Muscocyclops operculatus.
Neodiaptomus intermedius is a species of freshwater copepod, in the family Diaptomidae. It lives in South India's inland freshwater areas of the Nilgiri Hills, Tirmala Hills, Kaza, and at Shornur. It inhabits any bodies of water in plains or elevated hills.
Neodiaptomus is a genus of freshwater copepods in the family Diaptomidae. It contains the following species, four of which are listed as vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List :
Notodiaptomus is a genus of copepods in the family Diaptomidae. It is the most widely distributed, most abundant and most species-rich genus of freshwater calanoid copepods in the Neotropics. The genus was erected in 1936 by Friedrich Kiefer for eleven species formerly placed in a wider Diaptomus. Notodiaptomus deitersi was chosen to be the type species by Raúl Adolfo Ringuelet in 1958.
Skistodiaptomus is a genus of freshwater copepods in the family Diaptomidae, found across North America. The genus contains eight species, three of which are endemic to the United States and are listed on the IUCN Red List as vulnerable species (VU) or Data Deficient (DD).

Vanacampus phillipi, also known as the Port Phillip pipefish is a species of marine fish belonging to the family Syngnathidae. They can be found inhabiting seaweed and seagrass beds along the southern coast of Australia from Perth to Jervis Bay, New South Wales including the coast of Tasmania. Their diet consists of small crustaceans such as copepods, amphipods, and mysid shrimps. Reproduction occurs through ovoviviparity in which the males brood eggs before giving live birth to 50 or less offspring.





