
The Thomisidae are a family of spiders, including about 170 genera and over 2,100 species. The common name crab spider is often linked to species in this family, but is also applied loosely to many other families of spiders. Many members of this family are also known as flower spiders or flower crab spiders.

Orb-weaver spiders are members of the spider family Araneidae. They are the most common group of builders of spiral wheel-shaped webs often found in gardens, fields, and forests. The English word "orb" can mean "circular", hence the English name of the group. Araneids have eight similar eyes, hairy or spiny legs, and no stridulating organs.

Theridiosoma is a genus of ray spiders that was first described by Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1879. They use their web as a high speed slingshot to actively hunt for prey.

Agobardus is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Eugen von Keyserling in 1885.
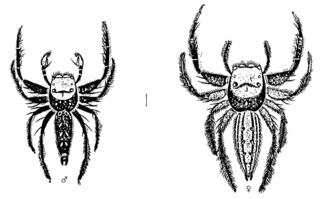
Bavia is a genus of jumping spiders.

Hasarius is a spider genus of the family Salticidae.

Saitis is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1876. The Australian species may belong to other genera, such as Maratus.

Trite is a genus of jumping spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1885. Most of the 18 described species occur in Australia and New Zealand, with several spread over islands of Oceania, one species even reaching Rapa in French Polynesia.

Bertrana is a genus of Central and South American orb-weaver spiders first described by Eugen von Keyserling in 1884. It includes some of the smallest known araneid orb-weavers. Bertrana striolata females are 4.5 mm long or less. The eight eyes are in two rows. The abdomen is white on top and on the sides, with multiple hieroglyphic-like lines and bars of many different shapes and length. In females, these are red, in males, black.

Mimetus is a genus of pirate spiders in the family Mimetidae. They are found worldwide.
Lipocrea epeiroides is an orb-weaving spider species found in Greece, Cyprus, Turkey, Israel, Yemen and India.

Euryopis is a genus of comb-footed spiders that was first described by Anton Menge in 1868.

Linyphia is a genus of dwarf spiders that was first described by Pierre André Latreille in 1804. The name is Greek, and means "thread-weaver" or "linen maker".

Sidymella is a genus of spider in the family Thomisidae, found in South America, Australia and New Zealand. It was originally named Sidyma, but this was later found to have been used already for a genus of moths.

Dipoena is a genus of tangle-web spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1869.

Mimetus epeiroides is a species of pirate spider in the family Mimetidae. It is found in the United States.

Xenoctenidae is a family of araneomorph spiders separated from Miturgidae in 2017.
Isometroides angusticaudus, also known as the slender spider-hunting scorpion, is a species of scorpion in the Buthidae family. It is native to Australia, and was first described by German arachnologist Eugen von Keyserling in 1885.















