
Ground spiders comprise Gnaphosidae, the seventh largest spider family with nearly 2,000 described species in over 100 genera distributed worldwide. There are 105 species known to central Europe, and common genera include Gnaphosa, Drassodes, Micaria, Cesonia, Zelotes and many others. They are closely related to Clubionidae. At present, no ground spiders are known to be seriously venomous to humans.

Oonopidae, also known as goblin spiders, is a family of spiders consisting of over 1,600 described species in about 113 genera worldwide, with total species diversity estimated at 2000 to 2500 species. The type genus of the family is OonopsKeyserling, 1835.
Bathippus is a genus of jumping spiders.
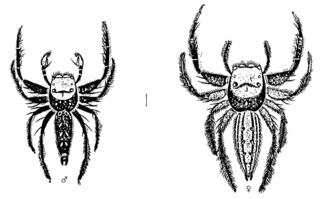
Bavia is a genus of jumping spiders.

Ballus is a spider genus of the family Salticidae.

Brettus is a genus of jumping spiders. Its six described species are found in southern Asia from India to China and Sulawesi, with a single species endemic to Madagascar.

Canama is a genus of spiders in the jumping spider family, Salticidae. Its five described species occur from Borneo to Queensland.
Charippus is a genus of spiders in the jumping spider family, Salticidae. Its only described species, Charippus errans, is endemic to Burma.

Epeus is a genus of the spider family Salticidae. They are often found on broad-leaved plants or shrubs of rain forest, or in gardens of Southeast Asia.
Langona is a spider genus of the family Salticidae (jumping spiders).
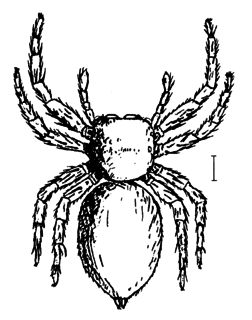
Mantius is a spider genus of the jumping spider family, Salticidae.
Microhasarius is a spider genus of the jumping spider family, Salticidae.
Padilla is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by George and Elizabeth Peckham in 1894. Most males have a characteristic long, forward projecting process on each chelicera that looks like a lance that is bent near the tip. The exception is P. javana, that doesn't have this feature.

Pseudicius is a genus of the jumping spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1885. The name is combined of Greek pseudo "false" and the salticid genus name Icius. The small genus Wesolowskana should possibly be included in this genus. There is some dispute whether Afraflacilla is a distinct genus or should be included in Pseudicius. Festucula and Marchena are other close relatives, these genera form a monophyletic group.
Rogmocrypta is a spider genus of the jumping spider family, Salticidae.

Viciria is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1877. The genus includes thirty-one accepted species.
Pseudamycus is a spider enus of the jumping spider family, Salticidae. The monotypic genus Taivala is thought to be closely related.
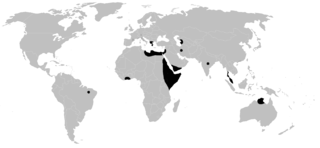
Cithaeronidae is a small family of araneomorph spiders first described by Simon in 1893 Female Cithaeron are about 5 to 7 millimetres long, males about 4 millimetres (0.16 in).
Uroballus peckhami is a spider species of the jumping spider family, Salticidae that is known only from northern Vietnam.
Platythomisus is a genus of flattened crab spiders from Africa and Southern Asia.










