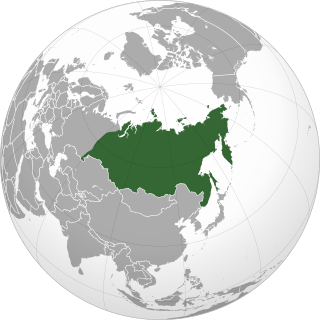
Siberia is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the centuries-long conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in the late 16th century and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over 13.1 million square kilometres (5,100,000 sq mi), but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area.

The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over 9,289 kilometers, it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the east.

Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siberia and the third-most populous city in Russia after Moscow and Saint Petersburg. It is also the most populous city in the Asian part of Russia. Novosibirsk is located in southwestern Siberia, on the banks of the Ob River.

Krasnoyarsk Krai is a federal subject of Russia located in Siberia. Its administrative center is the city of Krasnoyarsk, the second-largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk. Comprising half of the Siberian Federal District, Krasnoyarsk Krai is the largest krai in Russia, the second-largest federal subject in the country after neighboring Sakha, and the third-largest country subdivision by area in the world. The krai covers an area of 2,366,797 square kilometers (913,825 sq mi), constituting roughly 13% of Russia's total area. Krasnoyarsk Krai has a population of 2,856,971 as of the 2021 Census.

The Russian Far East is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast.
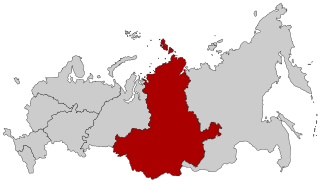
Siberian Federal District is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. Its population was 17,178,298 according to the 2010 Census, living in an area of 4,361,800 square kilometers (1,684,100 sq mi). The entire federal district lies within the continent of Asia.

The Siberian tiger or Amur tiger is a population of the tiger subspecies Panthera tigris tigris native to the Russian Far East, Northeast China and possibly North Korea. It once ranged throughout the Korean Peninsula, but currently inhabits mainly the Sikhote-Alin mountain region in southwest Primorye Province in the Russian Far East. In 2005, there were 331–393 adult and subadult Siberian tigers in this region, with a breeding adult population of about 250 individuals. The population had been stable for more than a decade because of intensive conservation efforts, but partial surveys conducted after 2005 indicate that the Russian tiger population was declining. An initial census held in 2015 indicated that the Siberian tiger population had increased to 480–540 individuals in the Russian Far East, including 100 cubs. This was followed up by a more detailed census which revealed there was a total population of 562 wild Siberian tigers in Russia. As of 2014, about 35 individuals were estimated to range in the international border area between Russia and China.

The West Siberian Plain is a large plain that occupies the western portion of Siberia, between the Ural Mountains in the west and the Yenisei River in the east, and the Altai Mountains on the southeast. Much of the plain is poorly drained and consists of some of the world's largest swamps and floodplains. Important cities include Chelyabinsk, Novosibirsk, Omsk, and Tomsk, as well as Surgut and Nizhnevartovsk.

The East Siberian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east. This sea borders on the Laptev Sea to the west and the Chukchi Sea to the east.

The Siberian is a centuries-old landrace of domestic cat in Russia, and recently developed as a formal breed with standards promulgated the world over since the late-1980s. Since 2006, the breed is recognised for registry and championship status with all major cat registries.

Siberian Tatars are the indigenous Turkic-speaking population of the forests and steppes of Western Siberia, originating in areas stretching from somewhat east of the Ural Mountains to the Yenisey River in Russia. The Siberian Tatars call themselves Yerle Qalıq, to distinguish themselves from more recent Volga Tatar immigrants to the region.

The Siberian roe deer, eastern roe deer, or Asian roe deer, is a species of roe deer found in northeastern Asia. In addition to Siberia and Mongolia, it is found in Kazakhstan, the Tian Shan Mountains of Kyrgyzstan, eastern Tibet, the Korean Peninsula and forested regions of northern China.

The Siberian musk deer is a musk deer found in the mountain forests of Northeast Asia. It is most common in the taiga of southern Siberia, but is also found in parts of Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Manchuria and the Korean peninsula.

The Siberian intervention or Siberian expedition of 1918–1922 was the dispatch of troops of the Entente powers to the Russian Maritime Provinces as part of a larger effort by the western powers, Japan, and China to support White Russian forces and the Czechoslovak Legion against Soviet Russia and its allies during the Russian Civil War. The Imperial Japanese Army continued to occupy Siberia even after other Allied forces withdrew in 1920.

Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early periods, practically the whole Russian population in Siberia, especially the serving-men, were called Cossacks, but only in the loose sense of being neither land-owners nor peasants. Most of these people came from northwest Russia and had little connection to the Don Cossacks or Zaporozhian Cossacks.

Siberia is a vast region spanning the northern part of the Asian continent and forming the Asiatic portion of Russia. As a result of the Russian conquest of Siberia and of the subsequent population movements during the Soviet era (1917–1991), the modern-day demographics of Siberia is dominated by ethnic Russians (Siberiaks) and other Slavs. However, there remains a slowly increasing number of Indigenous groups, accounting for about 5% of the total Siberian population, some of which are closely genetically related to Indigenous peoples of the Americas.

Siberian regionalism was a political movement that advocated for the formation of an autonomous Siberian state. The idea originated in the mid-19th century and reached a high tide with the White movement military activities of Aleksandr Kolchak (1874–1920) and Viktor Pepelyayev (1885–1920) during the Russian Civil War of 1917–1922.
Siberian Tatar (Себертатарца) is a Turkic language spoken in Western Siberia, Russia, primarily in the oblasts of Tyumen, Novosibirsk, Omsk but also in Tomsk and Kemerovo. According to Marcel Erdal, due to its particular characteristics, Siberian Tatar can be considered as a bridge to Siberian Turkic languages.

The Russian State was a White Army anti-Bolshevik state proclaimed by the Act of the Ufa State Conference of September 23, 1918, “On the formation of the all-Russian supreme power” in the name of “restoring state unity and independence of Russia” affected by the revolutionary events of 1917, the October Revolution and the signing of the treaty of Brest-Litovsk with Germany.

The Great Russian Regions are eight geomorphological regions of the Russian Federation displaying characteristic forms of relief. Seven of them are parts of Siberia, located east of the Ural Mountains.


















