The government agencies in Sweden are state-controlled organizations that act independently to carry out the policies of the Government of Sweden. The ministries are relatively small and merely policy-making organizations, allowed to monitor the agencies and preparing decision and policy papers for the government as a collective body to decide upon.
The following list outlines the structure of the federal government of Canada, the collective set of federal institutions which can be grouped into the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. In turn, these are further divided into departments, agencies, and other organizations which support the day-to-day function of the Canadian state.
A comptroller is a management-level position responsible for supervising the quality of accounting and financial reporting of an organization. A financial comptroller is a senior-level executive who acts as the head of accounting, and oversees the preparation of financial reports, such as balance sheets and income statements.
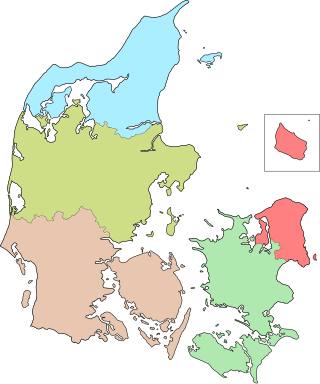
The five Regions of Denmark were created as administrative entities at a level above the municipalities and below the central government in the public sector as part of the 2007 Danish Municipal Reform, when the 13 counties (amter) were abolished. At the same time, the number of municipalities (kommuner) was cut from 270 to 98. The reform was approved and made into a law by the lawmakers in the Folketing 26 June 2005 with elections to the 98 municipalities and 5 regions being held Tuesday 15 November 2005.
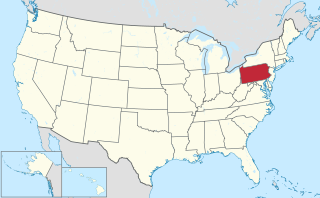
A township, under the laws of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is the lowest level of municipal incorporation of government. All of Pennsylvania's communities outside of incorporated cities, boroughs, and one town have been incorporated into individual townships that serve as the legal entities providing local self-government functions.
A regional health authority is a state-owned enterprise responsible for specialist healthcare in one of four regions of Norway. Responsibilities of the RHFs include patient treatment, education of medical staff, research and training of patients and relatives. Areas covered by the authorities are hospitals, psychiatry, ambulance service, operation of pharmacies at the hospitals, emergency telephone number and laboratories. The actual performance is done by subsidiary health trusts (HF) that usually consist of one or more hospitals, with associate responsibilities. The authorities are subordinate to the Norwegian Ministry of Health and Care Services.
The Government agencies of Norway are state controlled organizations that act independently to carry out the policies of the Government of Norway. The Government Ministries are relatively small and merely policy-making organizations, allowed to control agencies by policy decisions but not by direct orders. A Minister is explicitly prohibited from interfering with the day-to-day operation in an agency or the outcome in individual cases. While no minister is allowed to give orders to agencies personally, they are subject to decisions made by the Government. Also, the Minister is normally the instance of appeals of agencies decisions.
The county governor is a Norwegian government agency that represents the central government administration in every county in Norway. Responsible for a number of supervision and management duties, the governor is the representative of the king and the government of Norway in each county, functioning as the connection between the state and the municipalities. The county governor is subordinate to the Ministry of Local Government and Modernisation but also to the other ministries in their respective duties.

The District of Columbia has a mayor–council government that operates under Article One of the United States Constitution and the District of Columbia Home Rule Act. The Home Rule Act devolves certain powers of the United States Congress to the local government, which consists of a mayor and a 13-member council. However, Congress retains the right to review and overturn laws created by the council and intervene in local affairs.

Joakim Theodor Haagaas Lystad is a Norwegian civil servant. He served as the first Director-General of the Norwegian Food Safety Authority from 2003 to 2010, building the organization. From 2010 to 2015, he was the Labour and Welfare Director of Norway, i.e. the head of the Labour and Welfare Service and the Labour and Welfare Administration and responsible for a third of the state budget of Norway. He is now a special adviser in the Ministry of Health and Care Services.
The Norwegian Parliamentary Ombudsman for the Armed Forces is an etat subordinate to the Norwegian Parliament. The Parliamentary Ombudsman for the Armed Forces was established in 1952, as the world's first parliamentary military ombudsman. Its purpose is to "safeguard the rights of all members of the Armed Forces", allowing individuals to bring their cases forward should they need to.
Norway's elongated shape, its numerous internal geographical barriers and the often widely dispersed and separated settlements are all factors that have strongly influenced the structure of the country's administrative subdivisions. This structure has varied over time and is subject to continuous review. In 2017, the government decided to abolish some of the counties and to merge them with other counties to form larger ones, reducing the number of counties from 19 to 11, which was implemented on 1 January 2020. Following protests, the new government decided to abolish three of the new counties in 2022, and re-establish seven of the old ones. Taking effect on 1 January 2024 there are fifteen counties in Norway.

Anne Alvik is a Norwegian physician and civil servant.

Aetat was a Norwegian government agency responsible for battling unemployment.

The National Insurance Service was a Norwegian government agency responsible for social security.
Civilian oversight, sometimes referred to as civilian review or citizen oversight, is a form of civilian participation in reviewing government activities, most commonly accusations of police misconduct. Members of civilian oversight boards are generally not employed by the government entity which they are reviewing. These groups are tasked with direct involvement in the citizen complaints process and develop solutions to improve government accountability. Responsibilities of civilian oversight groups can vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction and their ability to become influential. Oversight should not simply criticize but should improve government through citizen support for government responsiveness, accountability, transparency, and overall efficiency.