
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents of the Northern Hemisphere. There are two existing species: the North American beaver and the Eurasian beaver. Beavers are the second-largest living rodents, after capybaras, weighing up to 50 kg (110 lb). They have stout bodies with large heads, long chisel-like incisors, brown or gray fur, hand-like front feet, webbed back feet, and tails that are flat and scaly. The two species differ in skull and tail shape and fur color. Beavers can be found in a number of freshwater habitats, such as rivers, streams, lakes and ponds. They are herbivorous, consuming tree bark, aquatic plants, grasses and sedges.

Castoridae is a family of rodents that contains the two living species of beavers and their fossil relatives. A formerly diverse group, only a single genus is extant today, Castor. Two other genera of "giant beavers", Castoroides and Trogontherium, became extinct in the Late Pleistocene.

The Eurasian beaver or European beaver is a species of beaver widespread across Eurasia, with a rapidly increasing population of at least 1.5 million in 2020. The Eurasian beaver was hunted to near-extinction for both its fur and castoreum, with only about 1,200 beavers in eight relict populations from France to Mongolia in the early 20th century. It has since been reintroduced into much of its former range and now lives from Western, Southern, Central and Eastern Europe, Scandinavia, Russia through China and Mongolia, with about half the population in Russia. It is listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List.

The North American beaver is one of two extant beaver species, along with the Eurasian beaver. It is native to North America and has been introduced in South America (Patagonia) and Europe. The North American beaver is one of the official national wildlife of Canada symbols and is the official state mammal of Oregon and New York. North American beavers are widespread across the continental United States, Canada, southern Alaska, and some parts of northern Mexico.

The mountain beaver is a North American rodent. It is the only living member of its genus, Aplodontia, and family, Aplodontiidae. It should not be confused with true North American and Eurasian beavers, to which it is not closely related; the mountain beaver is instead more closely related to squirrels, although its less-efficient renal system was thought to indicate greater relative antiquity for the species. There are seven subspecies of mountain beavers, six of which are found in California and three of which are endemic to the state.

Castoroides, or the giant beaver, is an extinct genus of enormous, bear-sized beavers that lived in North America during the Pleistocene. Two species are currently recognized, C. dilophidus in the Southeastern United States and C. ohioensis in most of North America. C. leiseyorum was previously described from the Irvingtonian age but is now regarded as an invalid name. All specimens previously described as C. leiseyorum are considered to belong to C. dilophidus.

Aquatic mammals and semiaquatic mammals are a diverse group of mammals that dwell partly or entirely in bodies of water. They include the various marine mammals who dwell in oceans, as well as various freshwater species, such as the European otter. They are not a taxon and are not unified by any distinct biological grouping, but rather their dependence on and integral relation to aquatic ecosystems. The level of dependence on aquatic life varies greatly among species. Among freshwater taxa, the Amazonian manatee and river dolphins are completely aquatic and fully dependent on aquatic ecosystems. Semiaquatic freshwater taxa include the Baikal seal, which feeds underwater but rests, molts, and breeds on land; and the capybara and hippopotamus which are able to venture in and out of water in search of food.

Adinotherium is an extinct genus of toxodontid, large bodied hoofed ungulates which inhabited South America during the Middle to Late Miocene, from 17.5 to 6.8 Ma and existed for approximately 10.7 million years, Santacrucian to Huayquerian in the South American land mammal ages (SALMA). Fossils of Adinotherium have been found in the Santa Cruz and Ituzaingó Formations of Argentina and the Chucal and Río Frías Formations of Chile.

Heliscomyidae is a family of extinct rodents from the mid-Tertiary of North America related to pocket gophers and kangaroo rats and their relatives. The family contains four genera, Apletotomeus, Heliscomys, Passaliscomys, and Tylionomys. McKenna and Bell (1997) placed the first two genera in synonymy, with Heliscomys as the senior synonym.

The Rattlesnake Formation is a Miocene to late Pliocene geologic formation found along the John Day River Valley of Oregon, in the Western United States.

Castor californicus is an extinct species of beaver that lived in western North America from the end of the Miocene to the early Pleistocene. Castor californicus was first discovered in Kettleman Hills in California, United States. The species was similar to but larger than the extant North American beaver, C. canadensis.

Hegetotheriidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals known from the Oligocene through the Pliocene of South America.
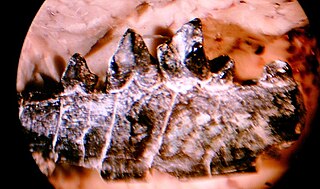
Ictidopappus is an extinct genus of mammals from extinct subfamily Ictidopappinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during the early Paleocene.
Carpocyon is an extinct genus of the Borophaginae subfamily of canids native to North America. It lived from the Middle to the Late Miocene, 13.6 to 5.3 Ma Mya, existing for approximately 16.5 million years. The four species in the genus varied in size, with the largest being about the size of a wolf; all had relatively small teeth, suggesting a diet that was more omnivorous than that of other contemporary borophagines.

Raphictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during late Paleocene.

The North American beaver had a historic range that overlapped the Sierra Nevada in California. Before the European colonization of the Americas, beaver were distributed from the arctic tundra to the deserts of northern Mexico. The California Golden beaver subspecies was prevalent in the Sacramento and San Joaquin River watersheds, including their tributaries in the Sierra Nevada. Recent evidence indicates that beaver were native to the High Sierra until their extirpation in the nineteenth century.

The beaver beetle is an ectoparasitic beetle that is only found on its host species, beavers, and the sole member of the genus Platypsyllus. It is flattened and eyeless, resembling a flea or tick. It used to be placed in a separate family called Leptinidae, but is now placed in the family Leiodidae, in the subfamily Platypsyllinae.
Monosaulax is an extinct genus of beaver-grouped rodents. It is sometimes treated as a synonym of Eucastor.

















