
The Russian Far East is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast.

The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.

The Western Ghats, also known as the Sahyadri, is a mountain range that stretches 1,600 km (990 mi) along the western coast of the Indian peninsula. Covering an area of 160,000 km2 (62,000 sq mi), it traverses the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. The range forms an almost continuous chain of mountains along the western edge of the Deccan Plateau, from the Tapti River to Swamithoppe in Kanyakumari district at the southern tip of the Indian peninsula. The Western Ghats meet with the Eastern Ghats at Nilgiris before continuing south.
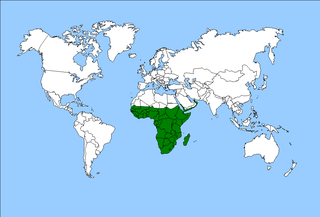
The Afrotropical realm is one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Sub-Saharan Africa, the southern Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, and the islands of the western Indian Ocean. It was formerly known as the Ethiopian Zone or Ethiopian Region.

The African Great Lakes are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. The series includes Lake Victoria, the second-largest freshwater lake in the world by area; Lake Tanganyika, the world's second-largest freshwater lake by volume and depth; Lake Malawi, the world's eighth-largest freshwater lake by area; and Lake Turkana, the world's largest permanent desert lake and the world's largest alkaline lake. Collectively, they contain 31,000 km3 (7,400 cu mi) of water, which is more than either Lake Baikal or the North American Great Lakes. This total constitutes about 25% of the planet's unfrozen surface fresh water. The large rift lakes of Africa are the ancient home of great biodiversity, and 10% of the world's fish species live in this region.

Northeast India, officially the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura, and the "brother" state of Sikkim.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, and Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the island of New Guinea, formerly Dutch and granted to Indonesia in 1962. Given the island is alternatively named Papua, the region is also called West Papua.

Potter wasps, the Eumeninae, are a cosmopolitan wasp group presently treated as a subfamily of Vespidae, but sometimes recognized in the past as a separate family, Eumenidae.

The Prawle Point and Start Point Site of Special Scientific Interest is a 341.2 hectare biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest in southern Devon, notified in 1976.
Pachodynerus is a fairly large neotropical and nearctic genus of potter wasps with higher diversity in central South America. At least one species has been introduced in other biogeographical regions, including several oceanic islands, while Pachodynerus erynnis occurs on Ascension Island as well as in North America. This genus is most closely related to the genus Euodynerus.

Odynerus is a primarily Holarctic genus of potter wasps.

Monobia quadridens, also known as the four-toothed mason wasp, is a species of solitary potter wasp found in North America. It grows to a wingspan of 18 mm (0.71 in), and feeds on small caterpillars and pollen. Two generations occur per year, with one generation overwintering as pupae.

Waterton Biosphere Region is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve encompassing Waterton Lakes National Park in the extreme southwest of the Province of Alberta, Canada. The region includes a section of the east slopes of the Rocky Mountains extending from the Continental Divide to the edge of the Canadian Great Plains to the east, including the Municipality of Pincher Creek and Cardston County. The Glacier Biosphere Reserve and National Park in Montana, USA is located to the south of the area.

Euodynerus hidalgo is a species of potter wasp in the family Vespidae. It is distributed in North America.

Euodynerus annulatus is a species of stinging wasp in the family Vespidae.

Euodynerus auranus is a species of stinging wasp in the family Vespidae.

Euodynerus crypticus is a species of stinging wasp in the family Vespidae.

Euodynerus schwarzi is a nearctic species of potter wasp in the family Vespidae.

















