
Euphorbia is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants, commonly called spurge, in the family Euphorbiaceae.

Benue–Congo is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa.

The Biu–Mandara or Central Chadic languages of the Afro-Asiatic family are spoken in Nigeria, Chad and Cameroon.
The Adamawa languages are a putative family of 80–90 languages scattered across the Adamawa Plateau in Central Africa, in northern Cameroon, north-western Central African Republic, southern Chad, and eastern Nigeria, spoken altogether by only one and a half million people. Joseph Greenberg classified them as one branch of the Adamawa–Ubangi family of Niger–Congo languages. They are among the least studied languages in Africa, and include many endangered languages; by far the largest is Mumuye, with 400,000 speakers. A couple of unclassified languages—notably Laal and Jalaa—are found along the fringes of the Adamawa area.
Tiv is a Tivoid language spoken in some states in North Central Nigeria, with some speakers in Cameroon. It had over 5.2 million speakers in 2024. The largest population of Tiv speakers are found in Benue state in Nigeria. The language is also widely spoken in some Nigerian states namely, Plateau, Taraba, Nasarawa, Cross River, Adamawa, Kaduna, and Abuja. It is by far the largest of the Tivoid languages, a group of languages belonging to the Southern Bantoid languages.

The Kirdi are the many cultures and ethnic groups who inhabit northwestern Cameroon and northeastern Nigeria.

Roger Marsh Blench is a British linguist, ethnomusicologist and development anthropologist. He has an M.A. and a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge and is based in Cambridge, England. He researches, publishes, and works as a consultant.
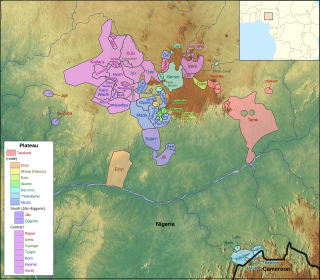
The forty or so Plateau languages are a tentative group of Benue–Congo languages spoken by 15 million people on the Jos Plateau, Southern Kaduna, Nasarawa State and in adjacent areas in central Nigeria.

There are over 520 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. The English-based creole Nigerian Pidgin – first used by the British and African slavers to facilitate the Atlantic slave trade in the late 17th century – is the most widely spoken lingua franca and spoken by over 60 million people.
The Berom is one of the largest autochthonous ethnic group in Plateau State, central Nigeria. Covering about four local government areas, which include Riyom, Jos North, Jos South and Barkin Ladi (Gwol). Berom people are also found in some southern Kaduna State local government areas like Fadan Karshe with Berom settlers tracing their origins to Za'ang a Berom district on the Jos Plateau. They emigrated during the British Colonial Government of Nigeria. A large number of this tribe, if not all, are Christians. Statistics also have it that a large number of the population of Plateau State is made up of Berom people.

Middle Belt or Central Nigeria is a term used in human geography to designate a belt region stretching across central Nigeria longitudinally and forming a transition zone between Northern and Southern Nigeria. It is composed of the southern half of the defunct Northern Region of Nigeria, now comprising mostly the North Central and parts of the North East and North West geopolitical zones, and is characterised by its lack of a clear majority ethnic group. It is also the location of Nigeria's Federal Capital Territory.

Euphorbia candelabrum is a succulent species of plant in the family Euphorbiaceae, one of several plants commonly known as candelabra tree. It is endemic to the Horn of Africa and eastern Africa along the East African Rift system. It is known in Ethiopia by its Amharic name, qwolqwal, or its Oromo name, adaamii. It is closely related to three other species of Euphorbia: Euphorbia ingens in the dry regions of southern Africa, Euphorbia conspicua from western Angola, and Euphorbia abyssinica, which is native to countries including Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, Ethiopia and Somalia.
The Savannas languages, also known as Gur–Adamawa or Adamawa–Gur, is a branch of the Niger–Congo languages that includes Greenberg's Gur and Adamawa–Ubangui families.

Euphorbia poissonii, also known as Euphorbia poissoni and, incorrectly, as Euphorbia poisoni, is a highly irritant and toxic succulent member of the large and varied spurge family of plants. It is native to northern Nigeria, where local farmers extract its latex for use as a pesticide. Its powerfully irritant and pain-producing nature mandates use as a fencing plant. It is known to the Berom people of the Jos area as pyùlúp who transplant it to their compounds where it is regarded as protection against witchcraft.

The Jukunoid languages are a branch of the Benue-Congo languages spoken by the Jukun and related peoples of Nigeria and Cameroon. They are distributed mostly throughout Taraba State, Nigeria and surrounding regions.
Fali comprises two languages spoken in northern Cameroon. Included in Greenberg's Adamawa languages, it was excluded from that family by Boyd (1989). Roger Blench suspects it may represent one of the earlier lineages to have branched off the Atlantic–Congo stock.

The Fali people are any of several small ethnic groups of Africa. The Fali are concentrated in mountainous areas of northern Cameroon, but some also live in northeastern Nigeria. The Fali are composed of four major groups, each corresponding to a geographic region: The Bossoum Fali, the Kangou Fali, the Peske–Bori Fali, and the Tingelin Fali. The Fali in Cameroon have been described as being centered on Garoua as well as the rocky plateaus and peaks of the Adamawa mountains in the country's north. The Fali are sometimes referred to as the Kirdi, meaning "pagan," a term given by the neighboring Muslim Fulani; after they fought against the jihadists and rejected Islam. Today the Fali in Mubi North Adamawa state are predominantly Christians.
Berom or Birom is the most widely spoken Plateau language in Nigeria. The language is locally numerically important and is consistently spoken by Berom of all ages in rural areas. However, the Berom are shifting to Hausa in cities. The small Cen and Nincut dialects may be separate languages. Approximately 1 million (2010) people speak in this language.
Herder–farmer conflicts in Nigeria are a series of disputes over arable land resources across Nigeria between the mostly-Muslim Fulani herders and the mostly-Christian non-Fulani farmers. The conflicts have been especially prominent in the Middle Belt since the return of democracy in 1999. More recently, they have deteriorated into attacks on farmers by Fulani herdsmen.












