
Vicia hirsuta or Ervilia hirsuta is a species of flowering plant from the large genus Vicia.
Pseuduvaria galeata is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is a tree endemic to Peninsular Malaysia. James Sinclair, the Scottish botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the dome formed by inner petals shaped like a helmet.
Hackelia bella is a species of flowering plant in the borage family known by the common name greater showy stickseed.
Euphorbia hooveri is a species of euphorb known by the common names Hoover's sandmat and Hoover's spurge. It is endemic to California, where it grows in the rare vernal pools of the Central Valley. Due to the elimination of most of its habitat, it became a federally listed threatened species in 1997.

Euphorbia melanadenia is a species of Euphorbia known by the common name red-gland spurge. It is native to the deserts and mountains of Baja California and southern California and Arizona, where it grows in dry, rocky habitat. It is a perennial herb forming a small clump or mat of very slender, tangling red stems. The stems are lined with pairs of slightly woolly oval-shaped leaves 2 to 9 millimeters wide. The tiny inflorescence is a cyathium less than 2 millimeters wide. The cyathium is a bell-shaped array of white, scalloped petal-like appendages surrounding the actual flowers. Each appendage has at its base a shiny red nectar gland. At the center of the appendages is a ring of male staminate flowers around a single female flower. The female flower develops into an oval-shaped fruit which bears wrinkled white seeds.

Euphorbia micromera is a species of flowering plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is known by the common name Sonoran sandmat. It is native to the southwestern United States from California to Texas, and northern Mexico, where it grows in sandy soils in desert and other dry habitat. It is an annual herb forming a small mat of slender stems. The hairy to hairless leaves are oblong in shape and just a few millimeters long. The tiny inflorescence is a cyathium less than a millimeter wide. It lacks the appendages that many similar species have in their cyathia. It has only a central female flower and 2 to 5 male flowers surrounded by round red nectar glands. The fruit is a minute round capsule.

Euphorbia serpyllifolia is a species of euphorb known by the common names thymeleaf sandmat or thyme-leafed spurge. It is native to a large part of North America from Canada to Mexico, where it is a common member of the flora in many types of habitat. This is an annual herb growing as a prostrate mat or taking a somewhat erect form. The oblong leaves are up to about 1.5 centimeters long, sometimes hairy and finely toothed along the edges. The tiny inflorescence is a cyathium about a millimeter wide. It bears scalloped white petal-like appendages arranged around the actual flowers. At the center are several male flowers and one female flower, which develops into a lobed, oval fruit up to 2 millimeters wide. This plant had a number of traditional medicinal uses for many Native American groups.
Nemophila breviflora is a species of flowering plant in the borage family known by the common names basin nemophila, Great Basin nemophila, and Great Basin baby-blue-eyes. It is native to southwestern Canada and the northwestern United States, where it generally grows in wooded and forested areas in thickets and moist streambanks.

Nemophila heterophylla is a species of flowering plant in the borage family known by the common name small baby blue eyes.
Salix cheilophila is a shrub or small tree from the genus of willow (Salix) with initially tomentose hairy and later balding branches. The leaf blades have lengths of 2.5 to sometimes 6 centimeters. The natural range of the species is in China.
Pseuduvaria fragrans is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Thailand. Yvonne Su, Tanawat Chaowasku and Richard Saunders the botanists who first formally described the species, named it after its strongly fragrant flowers.
Pseuduvaria luzonensis is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to The Philippines. Elmer Drew Merrill, the American botanist who first formally described the species using the synonym Orophea luzoniensis, named it after Luzon in the Province of Battan, Philippines where the specimen he examined was collected along the Lamao River.
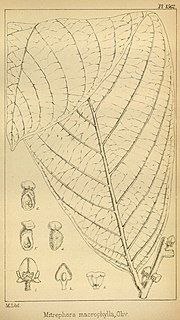
Pseuduvaria macrophylla is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra and Thailand. Daniel Oliver, the English botanists who first formally described the species using the synonym Mitrephora macrophylla, named it after its large leaves.

Pseuduvaria megalopus is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to New Guinea. Karl Schumann, the German botanist who first formally described the species using the synonym Petalolophus megalopus, named it after the large wings that extend downwards from the underside of the inner petals to form a foot of dark red tissue that resembles carrion and is thought to attract fly pollinators.
Pseuduvaria mindorensis is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to the Philippines. Yvonne Su and Richard Saunders, the botanists who first formally described the species, named it after the island of Mindoro where the specimen they examined was collected in the municipality of Puerto Galera.
Pseuduvaria multiovulata is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Myanmar. Cecil Fischer, the Indian botanist who first formally described the species using the basionym Mitrephora multiovulata, named it after its many ovuled ovaries.
Pseuduvaria obliqua is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Borneo. Yvonne Su and Richard Saunders, the botanists who first formally described the species, named it after its slightly uneven leaf bases.
Pseuduvaria pamattonis is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Borneo and the Philippines. Friedrich Miquel, the Dutch botanist who first formally described the species using the basionym Orophea pamattonis, named it after a mountain in Borneo called Gunung Pamaton.
Pseuduvaria parvipetala is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Borneo and Sumatra. Yvonne Su and Richard Saunders, the botanists who first formally described the species, named it after its small petals.

Pseuduvaria reticulata is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Bangladesh, Borneo, Java, the Lesser Sunda Islands, Myanmar and Sumatra. Carl Ludwig Blume, the botanist who first formally described the species under the basionym Uvaria reticulata, named it after the net-like pattern of veins on the underside of its leaves.








