In artificial intelligence, genetic programming (GP) is a technique of evolving programs, starting from a population of unfit programs, fit for a particular task by applying operations analogous to natural genetic processes to the population of programs.

In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to generate high-quality solutions to optimization and search problems via biologically inspired operators such as selection, crossover, and mutation. Some examples of GA applications include optimizing decision trees for better performance, solving sudoku puzzles, hyperparameter optimization, and causal inference.

Digital art refers to any artistic work or practice that uses digital technology as part of the creative or presentation process. It can also refer to computational art that uses and engages with digital media. Since the 1960s, various names have been used to describe digital art, including computer art, electronic art, multimedia art, and new media art.
In computational intelligence (CI), an evolutionary algorithm (EA) is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses mechanisms inspired by biological evolution, such as reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection. Candidate solutions to the optimization problem play the role of individuals in a population, and the fitness function determines the quality of the solutions. Evolution of the population then takes place after the repeated application of the above operators.

Generative art is post-conceptual art that has been created with the use of an autonomous system. An autonomous system in this context is generally one that is non-human and can independently determine features of an artwork that would otherwise require decisions made directly by the artist. In some cases the human creator may claim that the generative system represents their own artistic idea, and in others that the system takes on the role of the creator.

In computer science, evolutionary computation is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the subfield of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms. In technical terms, they are a family of population-based trial and error problem solvers with a metaheuristic or stochastic optimization character.
NeuroEvolution of Augmenting Topologies (NEAT) is a genetic algorithm (GA) for the generation of evolving artificial neural networks developed by Kenneth Stanley and Risto Miikkulainen in 2002 while at The University of Texas at Austin. It alters both the weighting parameters and structures of networks, attempting to find a balance between the fitness of evolved solutions and their diversity. It is based on applying three key techniques: tracking genes with history markers to allow crossover among topologies, applying speciation to preserve innovations, and developing topologies incrementally from simple initial structures ("complexifying").
Evolutionary programming is one of the four major evolutionary algorithm paradigms. It is similar to genetic programming, but the structure of the program to be optimized is fixed, while its numerical parameters are allowed to evolve.

Karl Sims is a computer graphics artist and researcher, who is best known for using particle systems and artificial life in computer animation.
Interactive evolutionary computation (IEC) or aesthetic selection is a general term for methods of evolutionary computation that use human evaluation. Usually human evaluation is necessary when the form of fitness function is not known or the result of optimization should fit a particular user preference.
Human-based computation (HBC), human-assisted computation, ubiquitous human computing or distributed thinking is a computer science technique in which a machine performs its function by outsourcing certain steps to humans, usually as microwork. This approach uses differences in abilities and alternative costs between humans and computer agents to achieve symbiotic human–computer interaction. For computationally difficult tasks such as image recognition, human-based computation plays a central role in training Deep Learning-based Artificial Intelligence systems. In this case, human-based computation has been referred to as human-aided artificial intelligence.

Algorithmic art or algorithm art is art, mostly visual art, in which the design is generated by an algorithm. Algorithmic artists are sometimes called algorists.
Evolutionary music is the audio counterpart to evolutionary art, whereby algorithmic music is created using an evolutionary algorithm. The process begins with a population of individuals which by some means or other produce audio, which is either initialized randomly or based on human-generated music. Then through the repeated application of computational steps analogous to biological selection, recombination and mutation the aim is for the produced audio to become more musical. Evolutionary sound synthesis is a related technique for generating sounds or synthesizer instruments. Evolutionary music is typically generated using an interactive evolutionary algorithm where the fitness function is the user or audience, as it is difficult to capture the aesthetic qualities of music computationally. However, research into automated measures of musical quality is also active. Evolutionary computation techniques have also been applied to harmonization and accompaniment tasks. The most commonly used evolutionary computation techniques are genetic algorithms and genetic programming.
Compositional pattern-producing networks (CPPNs) are a variation of artificial neural networks (ANNs) that have an architecture whose evolution is guided by genetic algorithms.
Artificial development, also known as artificial embryogeny or machine intelligence or computational development, is an area of computer science and engineering concerned with computational models motivated by genotype–phenotype mappings in biological systems. Artificial development is often considered a sub-field of evolutionary computation, although the principles of artificial development have also been used within stand-alone computational models.
Universal Darwinism, also known as generalized Darwinism, universal selection theory, or Darwinian metaphysics, is a variety of approaches that extend the theory of Darwinism beyond its original domain of biological evolution on Earth. Universal Darwinism aims to formulate a generalized version of the mechanisms of variation, selection and heredity proposed by Charles Darwin, so that they can apply to explain evolution in a wide variety of other domains, including psychology, linguistics, economics, culture, medicine, computer science, and physics.
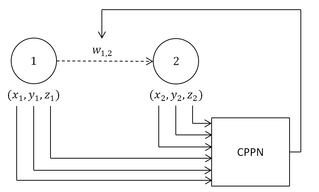
Hypercube-based NEAT, or HyperNEAT, is a generative encoding that evolves artificial neural networks (ANNs) with the principles of the widely used NeuroEvolution of Augmented Topologies (NEAT) algorithm developed by Kenneth Stanley. It is a novel technique for evolving large-scale neural networks using the geometric regularities of the task domain. It uses Compositional Pattern Producing Networks (CPPNs), which are used to generate the images for Picbreeder.orgArchived 2011-07-25 at the Wayback Machine and shapes for EndlessForms.comArchived 2018-11-14 at the Wayback Machine. HyperNEAT has recently been extended to also evolve plastic ANNs and to evolve the location of every neuron in the network.

Generative design is an iterative design process that uses software to generate outputs that fulfill a set of constraints iteratively adjusted by a designer. Whether a human, test program, or artificial intelligence, the designer algorithmically or manually refines the feasible region of the program's inputs and outputs with each iteration to fulfill evolving design requirements. By employing computing power to evaluate more design permutations than a human alone is capable of, the process is capable of producing an optimal design that mimics nature's evolutionary approach to design through genetic variation and selection. The output can be images, sounds, architectural models, animation, and much more. It is, therefore, a fast method of exploring design possibilities that is used in various design fields such as art, architecture, communication design, and product design.
Design Automation usually refers to electronic design automation, or Design Automation which is a Product Configurator. Extending Computer-Aided Design (CAD), automated design and Computer-Automated Design (CAutoD) are more concerned with a broader range of applications, such as automotive engineering, civil engineering, composite material design, control engineering, dynamic system identification and optimization, financial systems, industrial equipment, mechatronic systems, steel construction, structural optimisation, and the invention of novel systems.
The Fly Algorithm is a computational method within the field of evolutionary algorithms, designed for direct exploration of 3D spaces in applications such as computer stereo vision, robotics, and medical imaging. Unlike traditional image-based stereovision, which relies on matching features to construct 3D information, the Fly Algorithm operates by generating a 3D representation directly from random points, termed "flies." Each fly is a coordinate in 3D space, evaluated for its accuracy by comparing its projections in a scene. By iteratively refining the positions of flies based on fitness criteria, the algorithm can construct an optimized spatial representation. The Fly Algorithm has expanded into various fields, including applications in digital art, where it is used to generate complex visual patterns.








