
Allamanda is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. They are native to the Americas, where they are distributed from Mexico to Argentina. Some species are familiar as ornamental plants cultivated for their large, colorful flowers. Most species produce yellow flowers; A. blanchetii bears pink flowers. The genus name Allamanda honors the Swiss botanist and physician Frédéric-Louis Allamand (1736–1809). It is the official flower of Kuching North City Hall.

Crotonogyne is a shrub of the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae) first described as a genus in 1864. It is native to western and central Africa. It is dioecious.
Manniophyton is a genus of lianas of the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae) described as a genus in 1864. It contains only one known species, Manniophyton fulvum, native to tropical western and central Africa from Guinea to Angola. It is dioecious.

Neoboutonia is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1864. It is the only genus in subtribe Neoboutoniinae, and native to tropical Africa. It is dioecious.
- Neoboutonia macrocalyx Pax - Burundi, Cameroon, Rwanda, Zaire, Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Malawi, Zambia, Zimbabwe
- Neoboutonia manniiBenth. & Hook.f. - tropical Africa from Liberia to Mozambique
- Neoboutonia melleri(Müll.Arg.) Prain - tropical Africa from Nigeria to Mozambique

Johann Müller was a Swiss botanist who was a specialist in lichens. He published under the name Johannes Müller Argoviensis to distinguish himself from other naturalists with similar names.

Helicia australasica, also known as Austral oak or creek silky oak, is a species of rainforest tree in the macadamia family Proteaceae, native to New Guinea and northern and northeastern Australia.

Phyllanthus microcladus, commonly known as the brush sauropus or small-leaved Phyllanthus, is a plant in the family Phyllanthaceae found in tropical and sub tropical areas of eastern Queensland and northeastern New South Wales in Australia. It is listed as endangered in New South Wales, but in Queensland it is assessed as least concern. It occurs by streams in rainforest, from near Grafton northwards to around Cairns.

Dicrastylis is a genus of plants in the Lamiaceae, first described in 1855. The entire genus is endemic to Australia. The type species is Dicrastylis fulva.
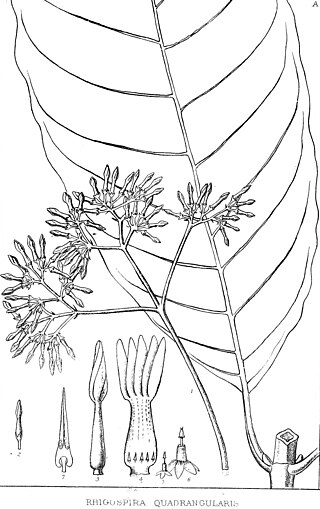
Rhigospira is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1878 by John Miers. The species, Rhigospira quadrangularis was first described as Ambelania quadrangularis by Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1860 but was transferred to the genus, Rhigospira, in 1878 by John Miers. The genus contains only one known species, Rhigospira quadrangularis, native to northwestern South America.

Syzygium forte, commonly known as flaky-barked satinash, white apple or brown satinash, is a tree in the family Myrtaceae native to New Guinea and northern Australia.
Excoecaria cuspidata is a species of flowering plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It was originally described as Excoecaria hialayensis var. cuspidataMüll.Arg. It is native to China and Meghalaya, India.
Excoecaria goudotiana is a species of flowering plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It was originally described as Stillingia goudotianaBaill. in 1861. It is native to Madagascar.
Excoecaria guineensis is a species of flowering plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It was originally described as Stillingia guineensisBenth. in 1849. It is native to western and central tropical Africa.

Scaevola parvifolia is an erect, many stemmed perennial in the family Goodeniaceae, which is native to Western Australia, the Northern Territory, Queensland and South Australia. It grows to a height of 0.6 m, and its blue-purple flowers may be seen from March to October.
Mallotus floribundus is a tree in the family Euphorbiaceae, in the Stylanthus section, native to Southeast Asia, Wallaceae, New Guinea and the Solomon Islands.
Muellerargia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Cucurbitaceae.

Phyllobotryon is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Salicaceae native to the region spanning from Nigeria to Tanzania and Angola.

Phyllobotryon spathulatum is a species of tree in the family Salicaceae native to Cameroon, Gabon, and Nigeria.

Pseudanthus orbicularis is a species of flowering plant in the family Picrodendraceae and is endemic to south-eastern continental Australia. It is a compact, monoecious shrub with simple, broadly elliptic to round leaves and creamy white, red or pale red flowers arranged singly in upper leaf axils.

Ipomoea muelleri is a vine in the Convolvulaceae family. It is native to the Northern Territory, Queensland, South Australia, and Western Australia.













