
The Miocene is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about 23.03 to 5.333 million years ago (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words μείων and καινός and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene.

Charadriiformes is a diverse order of small to medium-large birds. It includes about 390 species and has members in all parts of the world. Most charadriiform birds live near water and eat invertebrates or other small animals; however, some are pelagic (seabirds), others frequent deserts, and a few are found in dense forest. Members of this group can also collectively be referred to as shorebirds.

Auks or alcids are a group of birds of the family Alcidae in the order Charadriiformes. The alcid family includes the murres, guillemots, auklets, puffins, and murrelets. The family contains 25 extant or recently extinct species that are divided into 11 genera. Auks are found throughout the Northern Hemisphere.

Falcons are birds of prey in the genus Falco, which includes about 40 species. Some small species of falcons with long, narrow wings are called hobbies, and some that hover while hunting are called kestrels. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene.

The falcons and caracaras are around 65 species of diurnal birds of prey that make up the family Falconidae. The family likely originated in South America during the Paleocene and is divided into three subfamilies: Herpetotherinae, which includes the laughing falcon and forest falcons; Polyborinae, which includes the spot-winged falconet and the caracaras; and Falconinae, the falcons and kestrels (Falco) and falconets (Microhierax).

Guillemot is the common name for several species of seabird in the Alcidae or auk family, part of the order Charadriiformes. In Europe, the term covers two genera, Uria and Cepphus. In North America the Uria species are called murres and only the Cepphus species are called "guillemots".

The Anatidae are the biological family of water birds that includes ducks, geese, and swans. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring on all the world's continents except Antarctica. These birds are adapted for swimming, floating on the water surface, and, in some cases, diving in at least shallow water. The family contains around 174 species in 43 genera.

Anas is a genus of dabbling ducks. It includes the pintails, most teals, and the mallard and its close relatives. It formerly included additional species but following the publication of a molecular phylogenetic study in 2009 the genus was split into four separate genera. The genus now contains 31 living species. The name Anas is the Latin for "duck".

Ostriches are large flightless birds. Two living species are recognised, the common ostrich, native to large areas of sub-Saharan Africa, and the Somali ostrich, native to the Horn of Africa.

Eutamias is a genus of chipmunks within the tribe Marmotini of the squirrel family. It includes a single living species, the Siberian chipmunk. The genus is often treated as a subgenus of Tamias, which is now restricted to the eastern chipmunk of North America. Neotamias, which now includes the western North American chipmunks, has also been included in Eutamias.
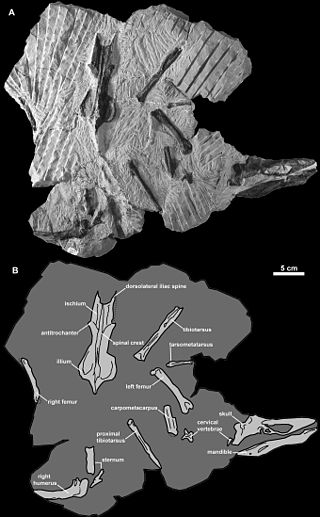
Mancallinae is an extinct subfamily of prehistoric flightless alcids that lived on the Pacific coast of today's California and Mexico from the late Miocene epoch to the early Pleistocene. They are sometimes collectively referred to as Lucas auks after the scientist who described the first species, Frederic Augustus Lucas.

Anser is a waterfowl genus that includes the grey geese and the white geese. It belongs to the true goose and swan subfamily of Anserinae under the family of Anatidae. The genus has a Holarctic distribution, with at least one species breeding in any open, wet habitats in the subarctic and cool temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere in summer. Some also breed farther south, reaching into warm temperate regions. They mostly migrate south in winter, typically to regions in the temperate zone between the January 0 °C (32 °F) and 5 °C (41 °F) isotherms.

The term kestrel is the common name given to several species of predatory birds from the falcon genus Falco. Kestrels are most easily distinguished by their typical hunting behaviour which is to hover at a height of around 10–20 metres (35–65 ft) over open country and swoop down on ground prey, usually small mammals, lizards or large insects, while other falcons are more adapted for active hunting during flight.

Gomphotherium is an extinct genus of gomphothere proboscidean from the Neogene of Eurasia, Africa and North America. It is the most diverse genus of gompothere, with over a dozen valid species. The genus is probably paraphyletic.

Mesopithecus is an extinct genus of Old World monkey belonging to the subfamily Colobinae that lived in Europe and Asia during the Late Miocene and Pliocene epochs, around 8.2-2.6 million years ago. Fossils span from Great Britain and the Iberian Peninsula in the west, eastwards to the Indian Subcontinent and China. Species of Mesopithecus had a body length of about 40 centimetres (16 in), possessing a slender body with long, muscular limbs and flexible fingers. Analysis of its anatomy suggests that members of the genus were semiterrestrial, spending a considerable amount of the time on the ground, though some authors have argued that some species were likely arboreal. Species of Mesopithecus were likely capable climbers and probably occasionally engaged in leaping. Dental microwear analysis suggests that it fed on hard seeds as well as probably leaves. The relationship of Mesopithecus to living members of Colobinae is uncertain, some have interpreted it as an early offshoot outside the split between Asian and African colobines, while others have interpreted it as a close relative of the Asian doucs (Pygathrix).

Uria is a genus of seabirds in the auk family known in Europe as guillemots, in most of North America as murres, and in Newfoundland and Labrador as turr. These are medium-sized birds with mainly brown or black plumage in the breeding season. They breed on the coasts of the northern Atlantic and Pacific oceans.

Lufengpithecus is an extinct genus of ape, known from the Late Miocene of East Asia. It is known from thousands of dental remains and a few skulls and probably weighed about 50 kg (110 lb). It contains three species: L. lufengensis, L. hudienensis and L. keiyuanensis. Lufengpithecus lufengensis is from the Late Miocene found in China, named after the Lufeng site and dated around 6.2 Ma. Lufengpithecus is either thought to be the sister group to Ponginae, or the sister to the clade containing Ponginae and Homininae.

The Gypaetinae is one of two subfamilies of Old World vultures the other being the Aegypiinae. Some taxonomic authorities place the Gypaetinae within the Perninae hawks. They are presently found throughout much of Africa, Asia, and southern Europe, hence being considered "Old World" vultures, but as recently as the Late Pleistocene, they were also present in North America.

Neogyps is an extinct monotypic genus of Old World vulture. Despite being an "Old World" vulture taxonomically, it was native to the New World, with its fossils having been found in western North America, including in the La Brea Tar Pits of southern California, dating to the Late Pleistocene. Several morphological characters suggest that Neogyps is closely related to the subfamily Gypaetinae.

The Liushu Formation is a geological formation in Gansu province, China that spans up to 100 m thick and is widely distributed within the Linxia Basin, with a paleomagnetic age between 11 and 6.4 mya.


















