Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain cereal grains. Although "gluten" often only refers to wheat proteins, in medical literature it refers to the combination of prolamin and glutelin proteins naturally occurring in all grains that have been proved capable of triggering an immune reaction for people with celiac disease. These include any species of wheat, barley, rye and some oat cultivars, as well as any cross hybrids of these grains. Gluten makes up 75–85% of the total protein in bread wheat.

Bread is a staple food prepared from a dough of flour and water, usually by baking. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cultures' diet. It is one of the oldest human-made foods, having been of significance since the dawn of agriculture, and plays an essential role in both religious rituals and secular culture.

Shortcrust pastry is a type of pastry often used for the base of a tart, quiche, pie, or flan. Shortcrust pastry can be used to make both sweet and savory pies such as apple pie, quiche, lemon meringue or chicken pie.

Flour is a powder made by grinding raw grains, roots, beans, nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredient of bread, which is a staple food for many cultures. Corn flour has been important in Mesoamerican cuisine since ancient times and remains a staple in the Americas. Rye flour is a constituent of bread in central and northern Europe.

Pastry is baked food made with a dough of flour, water and shortening that may be savoury or sweetened. Sweetened pastries are often described as bakers' confectionery. The word "pastries" suggests many kinds of baked products made from ingredients such as flour, sugar, milk, butter, shortening, baking powder, and eggs. Small tarts and other sweet baked products are called pastries as a synecdoche. Common pastry dishes include pies, tarts, quiches, croissants, and pasties.

A croissant is a buttery, flaky, viennoiserie pastry inspired by the shape of the Austrian kipferl but using the French yeast-leavened laminated dough. Croissants are named for their historical crescent shape, the dough is layered with butter, rolled and folded several times in succession, then rolled into a thin sheet, in a technique called laminating. The process results in a layered, flaky texture, similar to a puff pastry.

Sourdough or sourdough bread is a bread made by the fermentation of dough using wild lactobacillaceae and yeast. Lactic acid from fermentation imparts a sour taste and improves keeping qualities.

Dough is a thick, malleable, sometimes elastic paste made from grains or from leguminous or chestnut crops. Dough is typically made by mixing flour with a small amount of water or other liquid and sometimes includes yeast or other leavening agents, as well as ingredients such as fats or flavorings.

A bread making machine or breadmaker is a home appliance for baking bread. It consists of a bread pan, at the bottom of which are one or more built-in paddles, mounted in the center of a small special-purpose oven. The machine is usually controlled by a built-in computer using settings input via a control panel. Most bread machines have different cycles for different kinds of dough—including white bread, whole grain, European-style, and dough-only. Many also have a timer to allow the bread machine to function without operator input, and some high-end models allow the user to program a custom cycle.

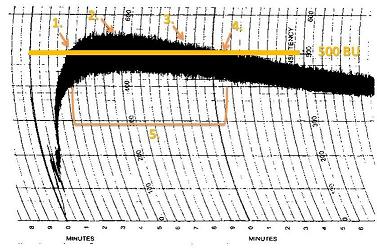
In cooking, kneading is a process in the making of bread or dough, used to mix the ingredients and add strength to the final product. Its importance lies in the mixing of flour with water; when these two ingredients are combined and kneaded, the gliadin and glutenin proteins in the flour expand and form strands of gluten, which gives bread its texture. The kneading process warms and stretches these gluten strands, eventually creating a springy and elastic dough. If bread dough is not kneaded enough, it will not be able to hold the tiny pockets of gas created by the leavening agent, and will collapse, leaving a heavy and dense loaf.

A ferment is a fermentation starter used in indirect methods of bread making. It may also be called mother dough.
The Chorleywood bread process (CBP) is a method of efficient dough production to make yeasted bread quickly, producing a soft, fluffy loaf. Compared to traditional bread-making processes, CBP uses more yeast, added fats, chemicals, and high-speed mixing to allow the dough to be made with lower-protein wheat, and produces bread in a shorter time. It was developed by Bill Collins, George Elton and Norman Chamberlain of the British Baking Industries Research Association at Chorleywood in 1961. As of 2009, 80% of bread made in the United Kingdom used the process.

In cooking, proofing is a step in the preparation of yeast bread and other baked goods in which the dough is allowed to rest and rise a final time before baking. During this rest period, yeast ferments the dough and produces gases, thereby leavening the dough.

Vienna bread is a type of bread that is produced from a process developed in Vienna, Austria, in the 19th century. The Vienna process used high milling of Hungarian grain, and cereal press-yeast for leavening.
The sponge and dough method is a two-step bread making process: in the first step a sponge is made and allowed to ferment for a period of time, and in the second step the sponge is added to the final dough's ingredients, creating the total formula. In this usage, synonyms for sponge are yeast starter or yeast pre-ferment. In French baking the sponge and dough method is known as levain-levure. The method is reminiscent of the sourdough or levain methods; however, the sponge is made from all fresh ingredients prior to being used in the final dough.

A dough conditioner, flour treatment agent, improving agent or bread improver is any ingredient or chemical added to bread dough to strengthen its texture or otherwise improve it in some way. Dough conditioners may include enzymes, yeast nutrients, mineral salts, oxidants and reductants, bleaching agents and emulsifiers. They are food additives combined with flour to improve baking functionality. Flour treatment agents are used to increase the speed of dough rising and to improve the strength and workability of the dough. While they are an important component of modern factory baking, some small-scale bakers reject them in favour of longer fermentation periods that produce greater depth of flavour.

Instant noodles, or instant ramen, is a type of food consisting of noodles sold in a precooked and dried block with flavoring powder and/or seasoning oil. The dried noodle block was originally created by flash-frying cooked noodles, and this is still the main method used in Asian countries; air-dried noodle blocks are favored in Western countries. Dried noodle blocks are designed to be cooked or soaked in boiling water before eating. Ramen, a Japanese adaptation of Chinese noodle soup, is sometimes used as a descriptor for instant noodle flavors by some Japanese manufacturers. It has become synonymous in the United States with all instant noodle products.

No-knead bread is a method of bread baking that uses a very long fermentation (rising) time instead of kneading to form the gluten strands that give the bread its texture. It is characterized by a low yeast content and a very wet dough. Some recipes improve the quality of the crust by baking the bread in a Dutch oven or other covered vessel.

Straight dough is a single-mix process of making bread. The dough is made from all fresh ingredients, and they are all placed together and combined in one kneading or mixing session. After mixing, a bulk fermentation rest of about 1 hour or longer occurs before division. It is also called the direct dough method.

Batter is a flour mixture with liquid and other ingredients such as sugar, salt and leavening used for cooking. It usually contains more liquid than doughs, which are also mixtures of flour and liquid. Batters are usually a pourable consistency that can't be kneaded. Batter is most often used for pancakes, light cakes, and as a coating for fried foods. It is also used for a variety of batter breads.