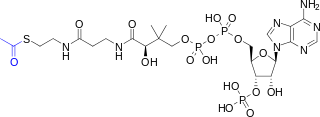
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production.

Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals, plants, and some bacteria. In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids from the cytosol into mitochondria to be oxidized for free energy production, and also participates in removing products of metabolism from cells. Given its key metabolic roles, carnitine is concentrated in tissues like skeletal and cardiac muscle that metabolize fatty acids as an energy source. Generally individuals, including strict vegetarians, synthesize enough L-carnitine in vivo.

Ketogenesis is the biochemical process through which organisms produce ketone bodies by breaking down fatty acids and ketogenic amino acids. The process supplies energy to certain organs, particularly the brain, heart and skeletal muscle, under specific scenarios including fasting, caloric restriction, sleep, or others.

Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency is a disorder of fatty acid oxidation that impairs the body's ability to break down medium-chain fatty acids into acetyl-CoA. The disorder is characterized by hypoglycemia and sudden death without timely intervention, most often brought on by periods of fasting or vomiting.
Fatty acid metabolism consists of various metabolic processes involving or closely related to fatty acids, a family of molecules classified within the lipid macronutrient category. These processes can mainly be divided into (1) catabolic processes that generate energy and (2) anabolic processes where they serve as building blocks for other compounds.

Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive fatty acid oxidation disorder that prevents the body from converting certain fats into energy. This can become life-threatening, particularly during periods of fasting.
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta oxidation (also β-oxidation) is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, generating NADH and FADH2, which are electron carriers used in the electron transport chain. It is named as such because the beta carbon of the fatty acid chain undergoes oxidation and is converted to a carbonyl group to start the cycle all over again. Beta-oxidation is primarily facilitated by the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, an enzyme complex associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane, although very long chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes.
Numerous genetic disorders are caused by errors in fatty acid metabolism. These disorders may be described as fatty oxidation disorders or as a lipid storage disorders, and are any one of several inborn errors of metabolism that result from enzyme defects affecting the ability of the body to oxidize fatty acids in order to produce energy within muscles, liver, and other cell types.

Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency is a rare metabolic disorder that prevents the body from converting certain fats called long-chain fatty acids(LCFA) into energy, particularly during periods without food. It is caused by a mutation in CPT1A on chromosome 11.

Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency is an autosomal recessive fatty acid oxidation disorder that prevents the body from converting certain fats to energy, particularly during periods without food. People with this disorder have inadequate levels of an enzyme that breaks down a certain group of fats called long-chain fatty acids.

Very long-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency is a fatty-acid metabolism disorder which prevents the body from converting certain fats to energy, particularly during periods without food.

ACADM is a gene that provides instructions for making an enzyme called acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase that is important for breaking down (degrading) a certain group of fats called medium-chain fatty acids.
Glutaric acidemia type 2 is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that is characterised by defects in the ability of the body to use proteins and fats for energy. Incompletely processed proteins and fats can build up, leading to a dangerous chemical imbalance called acidosis. It is a metabolic myopathy, categorized under fatty acid metabolism disorder as that is the bioenergetic system that it affects the most. It also affects choline metabolism.

Short-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency (SCADD) is an autosomal recessive fatty acid oxidation disorder which affects enzymes required to break down a certain group of fats called short chain fatty acids.

Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, long chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACADL gene.
Lipid metabolism is the synthesis and degradation of lipids in cells, involving the breakdown and storage of fats for energy and the synthesis of structural and functional lipids, such as those involved in the construction of cell membranes. In animals, these fats are obtained from food and are synthesized by the liver. Lipogenesis is the process of synthesizing these fats. The majority of lipids found in the human body from ingesting food are triglycerides and cholesterol. Other types of lipids found in the body are fatty acids and membrane lipids. Lipid metabolism is often considered the digestion and absorption process of dietary fat; however, there are two sources of fats that organisms can use to obtain energy: from consumed dietary fats and from stored fat. Vertebrates use both sources of fat to produce energy for organs such as the heart to function. Since lipids are hydrophobic molecules, they need to be solubilized before their metabolism can begin. Lipid metabolism often begins with hydrolysis, which occurs with the help of various enzymes in the digestive system. Lipid metabolism also occurs in plants, though the processes differ in some ways when compared to animals. The second step after the hydrolysis is the absorption of the fatty acids into the epithelial cells of the intestinal wall. In the epithelial cells, fatty acids are packaged and transported to the rest of the body.
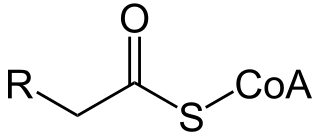
Acyl-CoA is a group of CoA-based coenzymes that metabolize carboxylic acids. Fatty acyl-CoA's are susceptible to beta oxidation, forming, ultimately, acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, eventually forming several equivalents of ATP. In this way, fats are converted to ATP, the common biochemical energy carrier.
3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency is a rare condition that prevents the body from converting certain fats to energy, particularly during fasting. Normally, through a process called fatty acid oxidation, several enzymes work in a step-wise fashion to metabolize fats and convert them to energy. People with 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency have inadequate levels of an enzyme required for a step that metabolizes groups of fats called medium chain fatty acids and short chain fatty acids; for this reason this disorder is sometimes called medium- and short-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase (M/SCHAD) deficiency.

Electron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers electrons from electron-transferring flavoprotein in the mitochondrial matrix, to the ubiquinone pool in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is part of the electron transport chain. The enzyme is found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes and contains a flavin and FE-S cluster. In humans, it is encoded by the ETFDH gene. Deficiency in ETF dehydrogenase causes the human genetic disease multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency.













