Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and discipline of money, currency, assets and liabilities. As a subject of study, it is related to but distinct from economics, which is the study of the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Based on the scope of financial activities in financial systems, the discipline can be divided into personal, corporate, and public finance.

Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 18th century. In addition to sociology, it now encompasses a wide array of academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, geography, linguistics, management, communication studies, psychology, culturology and political science.

Economic history is the study of history using methodological tools from economics or with a special attention to economic phenomena. Research is conducted using a combination of historical methods, statistical methods and the application of economic theory to historical situations and institutions. The field can encompass a wide variety of topics, including equality, finance, technology, labour, and business. It emphasizes historicizing the economy itself, analyzing it as a dynamic entity and attempting to provide insights into the way it is structured and conceived.
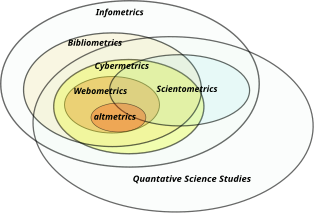
Informetrics is the study of quantitative aspects of information, it is an extension and evolution of traditional bibliometrics and scientometrics. Informetrics uses bibliometrics and scientometrics methods to study mainly the problems of literature information management and evaluation of science and technology. Informetrics is an independent discipline that uses quantitative methods from mathematics and statistics to study the process, phenomena, and law of informetrics. Informetrics has gained more attention as it is a common scientific method for academic evaluation, research hotspots in discipline, and trend analysis.

Articles in economics journals are usually classified according to JEL classification codes, which derive from the Journal of Economic Literature. The JEL is published quarterly by the American Economic Association (AEA) and contains survey articles and information on recently published books and dissertations. The AEA maintains EconLit, a searchable data base of citations for articles, books, reviews, dissertations, and working papers classified by JEL codes for the years from 1969. A recent addition to EconLit is indexing of economics journal articles from 1886 to 1968 parallel to the print series Index of Economic Articles.

Jean Tirole is a French economist who is currently a professor of economics at Toulouse 1 Capitole University. He focuses on industrial organization, game theory, banking and finance, and psychology. In particular, he focuses on the regulation of economic activity in a way that does not hinder innovation while maintaining fair rules.

Gokhale Institute of Politics and Economics (GIPE), commonly known as Gokhale Institute, is one of the oldest research and training institutes in economics in India.

Harold James is an economic historian specialising in the history of Germany and European economic history. He is a Professor of History at Princeton University as well as the university's Princeton School of Public and International Affairs. He currently writes monthly columns for Project Syndicate covering economic history. He is also a senior fellow at the Centre for International Governance Innovation.
Business history is a historiographical field which examines the history of firms, business methods, government regulation and the effects of business on society. It also includes biographies of individual firms, executives, and entrepreneurs. It is related to economic history. It is distinct from "company history" which refers to official histories, usually funded by the company itself.

Kozminski University is a private, nonprofit business school in Warsaw, Poland; according to the Financial Times, it is considered to be "Poland’s highest rated private university". It was established in 1993 and named after Leon Koźmiński, a Polish professor of economics and entrepreneurship, and also the father of Andrzej Koźmiński, the founder and the first rector of the school. It is one of the top business schools in the world, contains the Central Eastern campus of ESCP as of 2015, and the only institution of higher education in Poland, holding the "triple accreditation ". Less than 1% of business education providers worldwide hold these three major international quality accreditations. The Financial Times named the university as the best business school in Poland and Central Europe.
Economic Geography is a peer-reviewed academic journal published quarterly by Taylor & Francis on behalf of Clark University. The journal was established in 1925 and is currently edited by James T. Murphy, Jane Pollard, Andrés Rodríguez-Pose, and Henry Wai-chung Yeung.

Shandong University of Finance and Economics is a public research university in Jinan, Shandong province, China. It is a full-time comprehensive institution of higher education which was founded upon approval by Shandong Provincial Government in 1952 and originally known as Shandong Institute of Finance and Economics. The current university resulted from a merger of two second-tier universities - the Shandong University of Finance (山东财政学院) and the Shandong Economic University (山东经济学院) in 2011.
Sérgio T. Rebelo is a Portuguese economist who is the current MUFG Bank Distinguished Professor of International Finance at the Kellogg School of Management in Illinois, United States. He is also a co-director of the Center for International Macroeconomics at Northwestern University.
Brigitte Evelyne Granville is an economist with dual French and British nationality. She is Professor of International Economics and Economic Policy in the School of Business and Management at Queen Mary University of London. She founded the Centre for Globalisation Research (CGR).
Reint E. Gropp is a German economist, the president of the Halle Institute for Economic Research (IWH) as well as professor of economics at Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg. His fields of research cover financial economics, macroeconomics, corporate finance as well as money and banking.

The European Association for Banking and Financial History (eabh) is an independent, non-profit association based in Frankfurt am Main. Founded in 1990, eabh aims to promote research on banking history; support the preservation historically valuable archive material of public and private banking institutions; and facilitate dialogue on key challenges and opportunities to the historical study of finance, insurance, and globalization. It maintains a global network of financial professionals and academics who meet to discuss and encourage projects in the field of financial and banking history. The eabh currently has 80 member organisations.

The Center for Operations Research and Econometrics (CORE) is an interdisciplinary research institute of the University of Louvain (UCLouvain) located in Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium. Since 2010, it is part of the Louvain Institute of Data Analysis and Modeling in economics and statistics (LIDAM), along with the Institute for Economic and Social Research (IRES), Louvain Finance (LFIN) and the Institute of Statistics, Biostatistics and Actuarial Sciences (ISBA).
The Society for Financial Studies (SFS) is a nonprofit, academic society in the field of finance. It owns and runs three academic journals: (1) the Review of Financial Studies, (2) the Review of Asset Pricing Studies, and (3) the Review of Corporate Finance Studies. It organizes the SFS Cavalcade North America and the SFS Cavalcade Asia-Pacific, which are annual academic conferences. It financially supports and co-sponsors many independent finance academic conferences. Its governing board is the SFS Council.

Asli Demirgüç-Kunt is a Turkish economist. She is a non-resident Fellow at the Center for Global Development and a former chief economist of the Europe and Central Asia Region of The World Bank. During her 33-year career at The World Bank, she also served as the Director of Research, Director of Development Policy, and the Chief Economist of the Finance and Private Sector Development Network, conducting research and advising on financial and private sector development issues. She has authored more than 100 research papers, as well as books, is widely published in academic journals, and is among the most-cited researchers in the world. Demirguc-Kunt has been named one of the top 10 women in economics as of June 2015 and one of the top 10 percent of Female Economists for her contributions to the field of economics.











