
Amnirana is a genus of frogs in the family Ranidae, "true frogs". The genus is primarily found in Sub-Saharan Africa, but one species occurs in parts of southern and southeastern Asia. Some of the African species are widespread but contain undescribed cryptic diversity. Most species have a white upper lip, and the genus is sometimes known as the white-lipped frogs.

Meristogenys is a genus of true frogs from Borneo. Its tadpoles are adapted to fast-flowing mountain streams and easily recognizable by their divided upper lip with ribs on the outside.

Cryptobatrachus is a genus of frogs in the family Hemiphractidae. They are found in Colombia and Venezuela. They are also known as backpack frogs, as the females have the habit of carrying their egg clutch on their backs until the young hatch; this behavior also occurs in the related hemiphractid genera Hemiphractus and Stefania.

Hemiphractus is a genus of frogs, the horned treefrogs, in the family Hemiphractidae. These overall brownish frogs have a pointed snout and a casque on the head. They are nocturnal, relatively rare and native to humid lowland and highland forests in northern South America and Panama, where typically found on the ground or at relatively low levels in vegetation.

Ctenophryne is a genus of microhylid frogs. They occur in southern Central America and South America. Their common names are egg frogs and Nelson frogs, the latter applying to species in the formerly recognized Nelsonophryne.

Necturus is a genus of aquatic salamanders in the family Proteidae. Species of the genus are native to the eastern United States and Canada. They are commonly known as waterdogs and mudpuppies. The common mudpuppy (N. maculosus) is probably the best-known species – as an amphibian with gill slits, it is often dissected in comparative anatomy classes. The common mudpuppy has the largest distribution of any fully aquatic salamander in North America.

Frostius – known as Frost's toads – is a small genus of true toads consisting of only two species endemic to Brazil. The genus was proposed by David C. Cannatella in 1986 based on an analysis of a species previously classified as Atelopus. Various morphological and life-history information first suggested that it is sister taxon to Atelopus or Atelopus + Osornophryne, but later molecular evidence suggests that it is sister taxon to Oreophrynella. It was named for Darrel Frost in recognition of his work on anuran systematics.

The marsupial frogs are a disputed family (Amphignathodontidae) in the order Anura. When treated as a separate family, it consists of two genera, Gastrotheca and Flectonotus. The frogs are native to Neotropical America. Under the dominant view, they are treated as part of the family of Hemiphractidae.

Fritziana fissilis is a species of frogs in the family Hemiphractidae. It is endemic to southeastern Brazil and known from the mountains of Espírito Santo, Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo, and Rio Grande do Sul states.

The Mount Tucuche tree frog is a species of tree frog in the family Hemiphractidae. It is found in Trinidad and Tobago and Paria Peninsula, Venezuela. It is an arboreal species occurring in various microhabitats of humid montane forest: leaf bases of bromeliads and aroids, bushes. It is threatened by habitat loss. Furthermore, they are also listed as Endangered in the IUCN Red List.

Flectonotus pygmaeus is a species of frog in the family Hemiphractidae. It is found on the Mérida Andes and Venezuelan Coastal Range in Venezuela and on adjacent eastern slopes of the northern Cordillera Oriental in Colombia. Its natural habitat is humid pre-montane forest. It is strongly associated with bromeliads, and can survive in degraded forest if bromeliads are present. It is threatened by deforestation, and locally, collection of bromeliads.

Merlin's dwarf gray frog, or Merlin's clawed frog, is a species of frog in the family Pipidae. It is monotypic within the genus Pseudhymenochirus. It is found in southern Guinea-Bissau, western Guinea, and southern Sierra Leone.

Chiropterotriton, also known as splayfoot salamanders or flat-footed salamanders, is a genus of salamanders in the family Plethodontidae. The genus is endemic to Mexico.
Rhinatrema is a genus of caecilians in the family Rhinatrematidae. Their common name is two-lined caecilians. The genus is known from the Guyanas and adjacent Brazil. Most Rhinatrema are known to inhabit and live in areas of tropical forests where there is an abundance of dense, dead vegetation matter.

The Korean brown frog is a species of frog in the genus Rana. It is native to the Korean Peninsula and Shandong, China.

Craugastoridae, commonly known as fleshbelly frogs, is a family of New World direct-developing frogs. As delineated here, following the Amphibian Species of the World, it contains 129 species. They are found from the southern United States southwards to Central and South America.

The Hemiphractidae are a family of frogs from South and Central America. Previously, this group had been classified as a subfamily (Hemiphractinae) under family Hylidae. More recent research classifies these genera into their own family, or sometimes into three separate families: Amphignathodontidae, Cryptobatrachidae, and Hemiphractidae. An active question still exists as to which of these groupings is more accurate.

Peltophryne is a genus of true toads in the family Bufonidae, from the Greater Antilles. With ten endemic species, Cuba hosts the highest diversity. Hispaniola has three endemics and Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands combined have one.
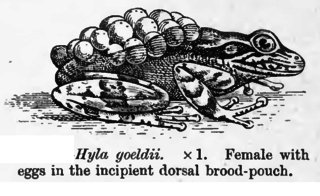
Fritziana is a genus of frogs in the family Hemiphractidae. They are endemic to southeastern Brazil and found on the mountains and adjacent coastal lowlands from Espírito Santo to São Paulo state.
Fritziana tonimi is a species of frog in the family Hemiphractidae. It is endemic to the Atlantic Forest in the State of Espírito Santo, southeastern Brazil.

















