
Nathan Bedford Forrest was a Confederate Army general during the American Civil War.

Chapel Hill is a town in northeastern Marshall County, Tennessee, United States. The town was named after Chapel Hill, North Carolina by settlers from that area. The population was 1,445 as of the 2010 census.
Forest Hills or Forrest Hills may refer to:

The Army of Tennessee was the principal Confederate army operating between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River during the American Civil War. It was formed in late 1862 and fought until the end of the war in 1865, participating in most of the significant battles in the Western Theater. It should not be confused with the Union Army of the Tennessee, named after the Tennessee River.

The Battle of Nashville was a two-day battle in the Franklin-Nashville Campaign that represented the end of large-scale fighting west of the coastal states in the American Civil War. It was fought at Nashville, Tennessee, on December 10–19, 1864, between the Confederate Army of Tennessee under Lieutenant General John Bell Hood and Federal forces under Major General George H. Thomas. In one of the largest victories achieved by the Union Army during the war, Thomas attacked and routed Hood's army, largely destroying it as an effective fighting force.

Nathan Bedford Forrest State Park is a state park in Benton County, Tennessee, in the southeastern United States. The park is situated on the western shore of the Kentucky Lake impoundment of the Tennessee River, just north of the community of Eva. Established in 1929, the park consists of 2,587 acres (10.47 km2) managed by the Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation.

The Battle of Columbia was a series of military actions that took place November 24–29, 1864, in Maury County, Tennessee, as part of the Franklin-Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War. It concluded the movement of Lt. Gen. John Bell Hood's Confederate Army of Tennessee from the Tennessee River in northern Alabama to Columbia, Tennessee, and across the Duck River. A Union force under Maj. Gen. John M. Schofield skirmished with Hood's cavalry, commanded by Maj. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest, and fortified a defensive line south of Columbia, but soon withdrew north across the Duck River, abandoning the town. Hood's invasion of Tennessee continued as he attempted to intercept Schofield's retreating army at Spring Hill.

The Battle of Brentwood was a battle of the American Civil War, occurring on March 25, 1863, in Williamson County, Tennessee.
The Battle of Johnsonville was fought November 4–5, 1864, in Benton County, Tennessee and Humphreys County, Tennessee, during the American Civil War. Confederate cavalry commander Major General Nathan Bedford Forrest culminated a 23-day raid through western Tennessee by attacking the Union supply base at Johnsonville. Forrest's attack destroyed numerous boats in the Tennessee River and millions of dollars of supplies, disrupting the logistical operations of Union Major General George H. Thomas in Nashville. As a result, Thomas's army was hampered in its plan to defeat Confederate Lieutenant General John Bell Hood's invasion of Tennessee, the Franklin-Nashville Campaign.
The Third Battle of Murfreesboro, also known as Wilkinson Pike or the Cedars, was fought December 5–7, 1864, in Rutherford County, Tennessee, as part of the Franklin-Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War.
The Battle of Thompson's Station was a battle of the American Civil War, occurring on March 5, 1863 in Williamson County, Tennessee.

The Franklin–Nashville Campaign, also known as Hood's Tennessee Campaign, was a series of battles in the Western Theater, conducted from September 18 to December 27, 1864, in Alabama, Tennessee, and northwestern Georgia during the American Civil War.
Forest School or Forrest School may refer to:
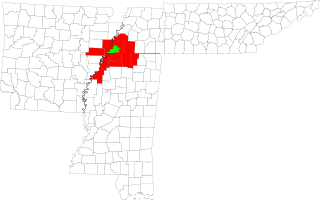
The Memphis–Forrest City Combined Statistical Area, TN–MS–AR (CSA) is the commercial and cultural hub of The Mid-South or Ark-Miss-Tenn. The census defined combined statistical area covers ten counties in three states – Tennessee, Mississippi, and Arkansas. As of census 2010 the MSA had a population of 1,324,108. The Forrest City Micropolitan area was added to the Memphis area in 2012 to form the Memphis–Forrest City Combined Statistical area and had a population of 1,369,548 according to census estimates. The greater Mid-South area as a whole has a population of 2.4 million according to 2013 census estimates. This area is covered by Memphis local news channels and includes the Missouri Bootheel, Northeast Arkansas, West Tennessee, and North Mississippi.
The Battle of Anthony's Hill was an engagement that occurred December 25, 1864, in Tennessee during the American Civil War between combined Confederate cavalry and infantry units commanded by Maj. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest and Union forces commanded by Maj. Gen. James H. Wilson. The battle was a part of the Franklin–Nashville Campaign.

Forrest School is a public school in Chapel Hill, Tennessee. It serves grades 7-12 and is part of the Marshall County School District. The school is also known as Forrest Middle School for grades 7-8 and Forrest High School for grades 9-12. It is named for Nathan Bedford Forrest, a Confederate general and first Grand Wizard of the Ku Klux Klan, who was born in Chapel Hill.

Fort Wright was constructed in 1861 and located on the second Chickasaw Bluff at Randolph, Tipton County, Tennessee. Fort Wright was a Civil War fortification and the first military training facility of the Confederate Army in Tennessee.
Tre Hargett is an American Republican Party politician who is serving as the Secretary of State of Tennessee. He is the son of Tennessee Adjutant General Gus L. Hargett Jr. He is a Southern Baptist.

Forrest's Cavalry Corps was part of the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War and commanded by Lieutenant General Nathan Bedford Forrest. Formed during the summer of 1862, it took part in the various battles in the Western Theater during the second half of the war. At first serving as part of the Army of Tennessee, both Forrest and the corps were then transferred to northern Mississippi and often launched independent raids into Union occupied western and central Tennessee.

The Nathan Bedford Forrest Boyhood Home is a historic log house in Chapel Hill, Tennessee, U.S.. It was the childhood home of Confederate General and Ku Klux Klan leader Nathan Bedford Forrest from 1830 to 1833. It is owned by the Sons of Confederate Veterans.














