Related Research Articles

In biochemistry, fermentation theory refers to the historical study of models of natural fermentation processes, especially alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation. Notable contributors to the theory include Justus Von Liebig and Louis Pasteur, the latter of whom developed a purely microbial basis for the fermentation process based on his experiments. Pasteur's work on fermentation later led to his development of the germ theory of disease, which put the concept of spontaneous generation to rest. Although the fermentation process had been used extensively throughout history prior to the origin of Pasteur's prevailing theories, the underlying biological and chemical processes were not fully understood. In the contemporary, fermentation is used in the production of various alcoholic beverages, foodstuffs, and medications.
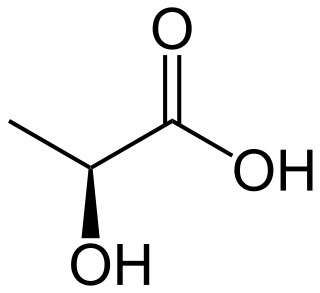
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has the molecular formula C3H6O3. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate (or the lactate anion). The name of the derived acyl group is lactoyl.

Sourdough or sourdough bread is a bread made by allowing the dough to ferment using naturally occurring lactobacillaceae and yeast before baking. The fermentation process produces lactic acid, which gives the bread a sour taste and improves its keeping-qualities.

Lactobacillus is a genus of gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus Lactobacillus comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera.

Lactic acid fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose or other six-carbon sugars are converted into cellular energy and the metabolite lactate, which is lactic acid in solution. It is an anaerobic fermentation reaction that occurs in some bacteria and animal cells, such as muscle cells.

Lactobacillus bulgaricus is the main bacterium used for the production of yogurt. It also plays a crucial role in the ripening of some cheeses, as well as in other processes involving naturally fermented products. It is defined as homofermentive lactic acid bacteria due to lactic acid being the single end product of its carbohydrate digestion. It is also considered a probiotic.

Malolactic conversion is a process in winemaking in which tart-tasting malic acid, naturally present in grape must, is converted to softer-tasting lactic acid. Malolactic fermentation is most often performed as a secondary fermentation shortly after the end of the primary fermentation, but can sometimes run concurrently with it. The process is standard for most red wine production and common for some white grape varieties such as Chardonnay, where it can impart a "buttery" flavor from diacetyl, a byproduct of the reaction.
Leuconostoc is a genus of gram-positive bacteria, placed within the family of Lactobacillaceae. They are generally ovoid cocci often forming chains. Leuconostoc spp. are intrinsically resistant to vancomycin and are catalase-negative. All species within this genus are heterofermentative and are able to produce dextran from sucrose. They are generally slime-forming. The name Leuconostoc comes from Greek adjective leukos meaning clear; and the word nostoc gelatinous colonies, Leuconostoc - colorless nostoc.

Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped (bacilli) or spherical (cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bacteria, usually found in decomposing plants and milk products, produce lactic acid as the major metabolic end product of carbohydrate fermentation, giving them the common name lactic acid bacteria (LAB).

Fermentation is a type of redox metabolism carried out in the absence of oxygen. During fermentation, organic molecules are catabolized and donate electrons to other organic molecules. In the process, ATP and organic end products are formed.

In food processing, fermentation is the conversion of carbohydrates to alcohol or organic acids using microorganisms—yeasts or bacteria—without an oxidizing agent being used in the reaction. Fermentation usually implies that the action of microorganisms is desired. The science of fermentation is known as zymology or zymurgy.

Dadiah (Minangkabau) or dadih a traditional fermented milk popular among people of West Sumatra, Indonesia, is made by pouring fresh, raw, unheated, buffalo milk into a bamboo tube capped with a banana leaf and allowing it to ferment spontaneously at room temperature for two days.
Leuconostoc mesenteroides is a species of lactic acid bacteria associated with fermentation, under conditions of salinity and low temperatures. In some cases of vegetable and food storage, it was associated with pathogenicity. L. mesenteroides is approximately 0.5-0.7 μm in diameter and has a length of 0.7-1.2 μm, producing small grayish colonies that are typically less than 1.0 mm in diameter. It is facultatively anaerobic, Gram-positive, non-motile, non-sporogenous, and spherical. It often forms lenticular coccoid cells in pairs and chains, however, it can occasionally form short rods with rounded ends in long chains, as its shape can differ depending on what media the species is grown on. L. mesenteroides grows best at 30 °C, but can survive in temperatures ranging from 10 °C to 30 °C. Its optimum pH is 5.5, but can still show growth in pH of 4.5-7.0.
Levilactobacillus brevis is a gram-positive, rod shaped species of lactic acid bacteria which is heterofermentative, creating CO2, lactic acid and acetic acid or ethanol during fermentation. L. brevis is the type species of the genus Levilactobacillus (previously L. brevis group), which comprises 24 species. It can be found in many different environments, such as fermented foods, and as normal microbiota. L. brevis is found in food such as sauerkraut and pickles. It is also one of the most common causes of beer spoilage. Ingestion has been shown to improve human immune function, and it has been patented several times. Normal gut microbiota L. brevis is found in human intestines, vagina, and feces.
Lentilactobacillus buchneri is a gram-positive, non-spore forming, anaerobic, rod prokaryote. L. buchneri is a heterofermentative bacteria that produces lactic acid and acetic acid during fermentation. It is used as a bacterial inoculant to improve the aerobic stability of silage. These bacteria are inoculated and used for preventing heating and spoilage after exposure to air.

Kefir is a fermented milk drink similar to a thin yogurt or ayran that is made from kefir grains, a specific type of mesophilic symbiotic culture. It is prepared by inoculating the milk of cows, goats, or sheep with kefir grains.
Microbial food cultures are live bacteria, yeasts or moulds used in food production. Microbial food cultures carry out the fermentation process in foodstuffs. Used by humans since the Neolithic period fermentation helps to preserve perishable foods and to improve their nutritional and organoleptic qualities. As of 1995, fermented food represented between one quarter and one third of food consumed in Central Europe. More than 260 different species of microbial food culture are identified and described for their beneficial use in fermented food products globally, showing the importance of their use.

Fermented sausage, or dry sausage, is a type of sausage that is created by salting chopped or ground meat to remove moisture, while allowing beneficial bacteria to break down sugars into flavorful molecules. Bacteria, including Lactobacillus species and Leuconostoc species, break down these sugars to produce lactic acid, which not only affects the flavor of the sausage, but also lowers the pH from 6.0 to 4.5–5.0, preventing the growth of bacteria that could spoil the sausage. These effects are magnified during the drying process, as the salt and acidity are concentrated as moisture is extracted.
Limosilactobacillus pontis is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive facultatively anaerobic bacterium. Along with other Lactobacillus species, it is capable of converting sugars, such as lactose, into lactic acid. Limosilactobacillus pontis is classified under the phylum Bacillota, class Bacilli, and is a member of the family Lactobacillaceae and is found to be responsible for the fermentation of sourdough, along with many other Lactobacillus species. This microorganism produces lactic acid during the process of fermentation, which gives sourdough bread its characteristic sour taste.
Lactiplantibacillus fabifermentans is a member of the genus Lactiplantibacillus and a type of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), a group of Gram-positive bacteria that produce lactic acid as their major fermented end product and that are often involved in food fermentation. L. fabifermentans was proposed in 2009 as a new species, after the type strain LMG 24284T has been isolated from Ghanaian cocoa fermentation. Analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence demonstrated that this species is a member of the Lactobacillus plantarum species group but further analysis demonstrated that it is possible to differentiate it from the nearest neighbors by means of DNA-DNA hybridization experiments, pheS sequence analysis, whole-cell protein electrophoresis, fluorescent amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis and biochemical characterization.
References
Dicks, L. M. T., and A. Endo. 2009. "Taxonomic Status of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Wine and Key Characteristics to Differentiate Species." S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. Vol. 30. No. 1
Nam, S.-H., S.-H. Choi, A. Kang, K. S. Lee, D.-W. Kim, R. N. Kim, D.-S. Kim, and H.-S. Park. "Genome Sequence of Lactobacillus Fructivorans KCTC 3543." Journal of Bacteriology 194.8 (2012): 2111-112. Web.