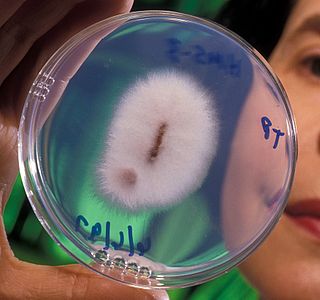
Fusarium oxysporum, an ascomycete fungus, comprises all the species, varieties and forms recognized by Wollenweber and Reinking within an infrageneric grouping called section Elegans. It is part of the family Nectriaceae.

Fusarium wilt is a common vascular wilt fungal disease, exhibiting symptoms similar to Verticillium wilt. This disease has been investigated extensively since the early years of this century. The pathogen that causes Fusarium wilt is Fusarium oxysporum. The species is further divided into formae speciales based on host plant.

Fusarium is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health if they enter the food chain. The main toxins produced by these Fusarium species are fumonisins and trichothecenes. Despite most species apparently being harmless, some Fusarium species and subspecific groups are among the most important fungal pathogens of plants and animals.

Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. albedinis is a fungal plant pathogen that causes a disease known as Bayoud disease or fusarium wilt primarily on date palm.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. asparagi is a fungal plant pathogen infecting asparagus.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. batatas is a fungal plant pathogen infecting sweet potatoes.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. betae is a destructive fungal plant pathogen. It causes Fusarium yellows or fusarium wilt, characterized by yellowing and dwarfing.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. carthami is a fungal plant pathogen.

Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. ciceris is a fungal plant pathogen that causes fusarium wilt of chickpea.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cyclaminis is a fungal plant pathogen infecting cyclamens.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lentis is a fungal plant pathogen infecting lentils.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lini is a fungal plant pathogen. Among the diseases it causes is flax wilt.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. pisi is a fungal plant pathogen infecting peas, endemic to Moldova.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. vasinfectum is a fungal plant pathogen.

Fusarium subglutinans is a fungal plant pathogen.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. medicaginis is a fungal plant pathogen infecting alfalfa.

Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici is a fungal plant pathogen. It is a big pathogen to the tomato plant. It has a violet to white color on most media but does not produce a pigment on King's B medium.
Polygalacturonase inhibitor proteins (PGIPs), also known as polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins, are plant proteins capable of inhibiting the action of polygalacturonase (PG) enzymes produced by bacterial and fungal pathogens. PGs can be produced by pathogens to degrade the polygalacturonan component of plant cell walls. PGIPs are leucine-rich repeat glycoproteins of approximately 360 amino acids in length, and PGIPs may reduce the activity of PGs by one or two orders of magnitude. Both competitive and non-competitive inhibition has been observed for various PGIPs. However, no inhibition of endogenous plant PGs that participate in fruit ripening by PGIPs have been reported.

Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense is a fungal plant pathogen that causes Panama disease of banana, also known as fusarium wilt of banana. The fungi and the related disease are responsible for widespread pressure on banana growing regions, destroying the economic viability of several commercially important banana varieties.



























