
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) is a complex of three enzymes that converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA by a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. Acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration, and this complex links the glycolysis metabolic pathway to the citric acid cycle. Pyruvate decarboxylation is also known as the "pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction" because it also involves the oxidation of pyruvate.
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion, is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structure at the cell plasma membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell.
An S-layer is a part of the cell envelope found in almost all archaea, as well as in many types of bacteria. It consists of a monomolecular layer composed of identical proteins or glycoproteins. This structure is built via self-assembly and encloses the whole cell surface. Thus, the S-layer protein can represent up to 15% of the whole protein content of a cell. S-layer proteins are poorly conserved or not conserved at all, and can differ markedly even between related species. Depending on species, the S-layers have a thickness between 5 and 25 nm and possess identical pores with 2–8 nm in diameter.

Pleckstrin homology domain or (PHIP) is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton.
Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate is one of the seven phosphoinositides found in eukaryotic cell membranes. In quiescent cells, the PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels, typically quantified by HPLC, are the lowest amongst the constitutively present phosphoinositides. They are approximately 3 to 5-fold lower as compared to PtdIns3P and PtdIns5P levels, and more than 100-fold lower than the abundant PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2. PtdIns(3,5)P2 was first reported to occur in mouse fibroblasts and budding yeast S. cerevisiae in 1997. In S. cerevisiae PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels increase dramatically during hyperosmotic shock. The response to hyperosmotic challenge is not conserved in most tested mammalian cells except for differentiated 3T3L1 adipocytes.

An alpha solenoid is a protein fold composed of repeating alpha helix subunits, commonly helix-turn-helix motifs, arranged in antiparallel fashion to form a superhelix. Alpha solenoids are known for their flexibility and plasticity. Like beta propellers, alpha solenoids are a form of solenoid protein domain commonly found in the proteins comprising the nuclear pore complex. They are also common in membrane coat proteins known as coatomers, such as clathrin, and in regulatory proteins that form extensive protein-protein interactions with their binding partners. Examples of alpha solenoid structures binding RNA and lipids have also been described.

In molecular biology the FYVE zinc finger domain is named after the four cysteine-rich proteins: Fab 1, YOTB, Vac 1, and EEA1, in which it has been found. FYVE domains bind phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, in a way dependent on its metal ion coordination and basic amino acids. The FYVE domain inserts into cell membranes in a pH-dependent manner. The FYVE domain has been connected to vacuolar protein sorting and endosome function.
The Membrane Attack Complex/Perforin (MACPF) superfamily, sometimes referred to as the MACPF/CDC superfamily, is named after a domain that is common to the membrane attack complex (MAC) proteins of the complement system and perforin (PF). Members of this protein family are pore-forming toxins (PFTs). In eukaryotes, MACPF proteins play a role in immunity and development.
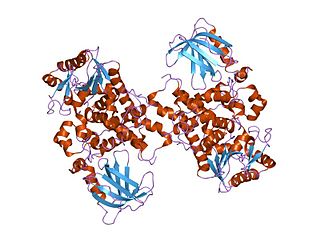
Myotubularin domain represents a region within eukaryotic myotubularin-related proteins that is sometimes found with the GRAM domain InterPro: IPR004182. Myotubularin is a dual-specific lipid phosphatase that dephosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol (3,5)-bi-phosphate. Mutations in gene encoding myotubularin-related proteins have been associated with disease.

Myotubularin-related protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR6 gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 2 also known as phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate 3-phosphatase or phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate phosphatase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR2 gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR9 gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SBF2 gene.
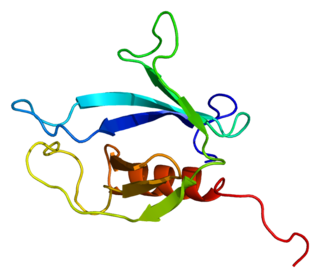
Myotubularin-related protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SBF1 gene.
Archaea constitute a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria, but this term has fallen out of use.

Myotubularin related protein 14 also known as MTMR14 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the MTMR14 gene.
The TBC (Tre-2/Bub2/Cdc16) is identified as a domain of some proteins or as a protein motif and widely recognized as a conserved one that includes approximately 200 amino acids in all eukaryotes.

GRAM domain containing 1A also known as Aster-A is a protein that is encoded by the GRAMD1A gene. It contains a transmembrane region, a GRAM domain and a VASt domain that can bind cholesterol. GRAMD1A has four paralogs: GRAMD1B and GRAMD1C and two without VASt domains, GRAMD2A and GRAMD2B. These proteins are mammalian representatives of the yeast lipid transfer proteins anchored at a membrane contact site (LAM) family.
BamA is a β-barrel, outer membrane protein found in Gram-negative bacteria and it is the main and vital component of the β-barrel assembly machinery (BAM) complex in those bacteria. BAM Complex consists of five components; BamB, BamC, BamD, BamE and BamA. This complex is responsible in catalyzing folding and insertion of β-barrel proteins into the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.
VAD1 analog of StAR-related lipid transfer (VASt) is a steroidogenic acute regulatory protein‐related lipid transfer (StART)-like lipid-binding domain first identified in the vad1 protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proteins containing these domains are found in eukaryotes and usually contain another lipid-binding domain, typically the GRAM domain and sometimes the C2 domain in plants and the integral peroxisomal membrane peroxin Pex24p domain in oomycetes.













