In biochemistry, a kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. As a result, kinase produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group. These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis.
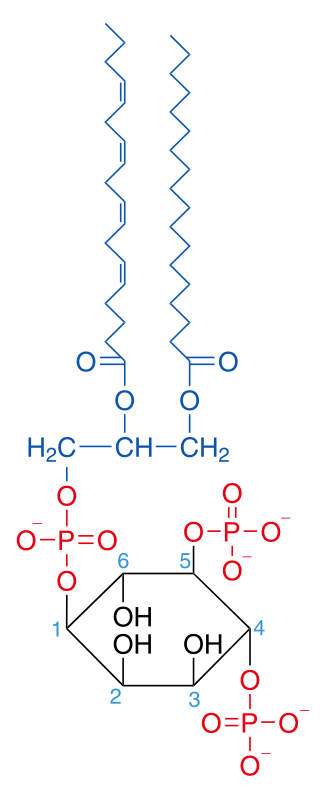
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)P2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)P2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms lipid clusters that sort proteins.

Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P) is a phospholipid found in cell membranes that helps to recruit a range of proteins, many of which are involved in protein trafficking, to the membranes. It is the product of both the class II and III phosphoinositide 3-kinases activity on phosphatidylinositol.

Phosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes, yet an important second messenger. The generation of PtdIns(3,4)P2 at the plasma membrane activates a number of important cell signaling pathways.

Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate is one of the seven phosphoinositides found in eukaryotic cell membranes. In quiescent cells, the PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels, typically quantified by HPLC, are the lowest amongst the constitutively present phosphoinositides. They are approximately 3 to 5-fold lower as compared to PtdIns3P and PtdIns5P levels, and more than 100-fold lower than the abundant PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2. PtdIns(3,5)P2 was first reported to occur in mouse fibroblasts and budding yeast S. cerevisiae in 1997. In S. cerevisiae PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels increase dramatically during hyperosmotic shock. The response to hyperosmotic challenge is not conserved in most tested mammalian cells except for differentiated 3T3L1 adipocytes.

Myelin protein zero is a single membrane glycoprotein which in humans is encoded by the MPZ gene. P0 is a major structural component of the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Myelin protein zero is expressed by Schwann cells and accounts for over 50% of all proteins in the peripheral nervous system, making it the most common protein expressed in the PNS. Mutations in myelin protein zero can cause myelin deficiency and are associated with neuropathies like Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease and Dejerine–Sottas disease.
The GRAM domain is found in glucosyltransferases, myotubularins and other membrane-associated proteins. The structure of the GRAM domain is similar to that found in PH domains.

Myotubularin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTM1 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF1B gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR3 gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR6 gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 2 also known as phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate 3-phosphatase or phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate phosphatase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR2 gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR9 gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SBF2 gene.
Myotubularin-related protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SBF1 gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR1 gene.
Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate (PtdIns5P) is a phosphoinositide, one of the phosphorylated derivatives of phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns), that are well-established membrane-anchored regulatory molecules. Phosphoinositides participate in signaling events that control cytoskeletal dynamics, intracellular membrane trafficking, cell proliferation and many other cellular functions. Generally, phosphoinositides transduce signals by recruiting specific phosphoinositide-binding proteins to intracellular membranes.

Polyphosphoinositide phosphatase also known as phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate 5-phosphatase or SAC domain-containing protein 3 (Sac3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FIG4 gene. Fig4 is an abbreviation for Factor-Induced Gene.

Protein VAC14 homolog, also known as ArPIKfyve, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAC14 gene.

Myotubularin related protein 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR12 gene.