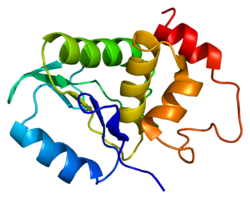
A mitogen-activated protein kinase is a type of protein kinase that is specific to the amino acids serine and threonine. MAPKs are involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflammatory cytokines. They regulate cell functions including proliferation, gene expression, differentiation, mitosis, cell survival, and apoptosis.
The MAPK/ERK pathway is a chain of proteins in the cell that communicates a signal from a receptor on the surface of the cell to the DNA in the nucleus of the cell.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1, (MAPK 1), also known as ERK2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK1 gene.
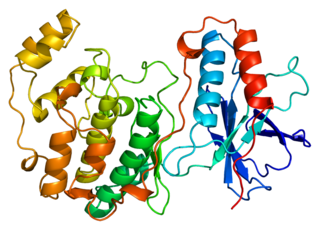
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14, also called p38-α, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK14 gene.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3, also known as p44MAPK and ERK1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK3 gene.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 is a ubiquitous enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK8 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP1 gene.

Dual specificity phosphatase 6 (DUSP6) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP6 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP3 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP4 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 10 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP10 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP7 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 16 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP16 gene.
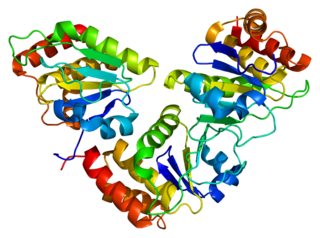
Dual specificity protein phosphatase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP5 gene.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK4 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 12 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP12 gene.
Dual-specificity phosphatase is a form of phosphatase that can act upon tyrosine or serine/threonine residues.

MAPK phosphatases (MKPs) are the largest class of phosphatases involved in down-regulating Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling. MAPK signalling pathways regulate multiple features of development and homeostasis. This can involve gene regulation, cell proliferation, programmed cell death and stress responses. MAPK phosphatases are therefore important regulator components of these pathways.
Candidalysin is a cytolytic 31-amino acid α-helical amphipathic peptide toxin secreted by the opportunistic pathogen Candida albicans. This toxin is a fungal example of a classical virulence factor. Hyphal morphogenesis in C. albicans is associated with damage to host epithelial cells; during this process Candidalysin is released and intercalates in host membranes. Candidalysin promotes damage of oral epithelial cells and induces lactate dehydrogenase release and calcium ion influx. It is unique in the fact that it is the first peptide toxin to be identified in any human fungal pathogen.

Dual specificity phosphatase 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DUSP8 gene.