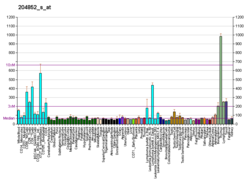
| PTPN7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PTPN7 , BPTP-4, HEPTP, LC-PTP, LPTP, PTPNI, protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 7, protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 176889; MGI: 2156893; HomoloGene: 15411; GeneCards: PTPN7; OMA:PTPN7 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN7 gene. [5] [6]