
Banksia serrata, commonly known as the saw banksia, the old man banksia, the saw-tooth banksia or the red honeysuckle and as wiriyagan by the Cadigal people, is a species of woody shrub or tree of the genus Banksia, in the family Proteaceae. Native to the east coast of Australia, it is found from Queensland to Victoria with outlying populations on Tasmania and Flinders Island. Commonly growing as a gnarled tree up to 16 m (50 ft) in height, it can be much smaller in more exposed areas. This Banksia species has wrinkled grey bark, shiny dark green serrated leaves and large yellow or greyish-yellow flower spikes appearing over summer. The flower spikes, or inflorescences, turn grey as they age and pollinated flowers develop into large, grey, woody seed pods called follicles.

Banksia dentata, commonly known as the tropical banksia, is a species of tree in the genus Banksia. It occurs across northern Australia, southern New Guinea and the Aru Islands. Growing as a gnarled tree to 7 m (23 ft) high, it has large green leaves up to 22 cm (8.7 in) long with dentate margins. The cylindrical yellow inflorescences, up to 13 cm (5.1 in) high, appear between November and May, attracting various species of honeyeaters, sunbirds, the sugar glider and a variety of insects. Flowers fall off the ageing spikes, which swell and develop follicles containing up to two viable seeds each.

Callitris columellaris is a species of coniferous tree in the family Cupressaceae, native to most of Australia. Common names include white cypress, white cypress-pine, Murray River cypress-pine, Bribie Island pine and northern cypress-pine. Callitris columellaris has become naturalised in Hawaii and in southern Florida.

Toona ciliata is a forest tree in the mahogany family which grows throughout South Asia from Afghanistan to Papua New Guinea and Australia.

Grewia asiatica, commonly known as phalsa or falsa, is a species of flowering plant in the mallow family Malvaceae. It was first found in Varanasi, India, and was taken by Buddhist scholars to other Asian countries including Pakistan and the rest of the world. Grewia celtidifolia was initially considered a mere variety of phalsa, but is now recognized as a distinct species.

Geniostoma is a genus of around 49 species of flowering plants in the family Loganiaceae. They are shrubs or small trees, with inflorescences borne in the axils of the simple, petiolate, oppositely-arranged leaves. The flowers are arranged in cymes, and each is pentamerous.

Buchanania arborescens, commonly known as the little gooseberry tree or sparrow's mango, is a small and slender tree native to seasonal tropical forests of northern Australia, Southeast Asia, and the Solomon Islands.

Olea paniculata, commonly known as the native olive, is a plant of the genus Olea and a relative of the olive. It grows natively in Pakistan and southwestern China (Yunnan) through tropical Asia to Australia and the Pacific islands of New Caledonia, Vanuatu and Lord Howe Island.

Ailanthus triphysa is a medium to tall evergreen rainforest tree that is native to Asia and Australia. The wood is used for matchwood and plywood. The tree is known as halmaddi in India, where its resin, also called halmaddi, may be used in incense. Inappropriate extraction methods were resulting in trees dying, thus by the 1990s the Indian forestry department had banned extraction.

Hicksbeachia pinnatifolia is a small tree in the family Proteaceae. This rare species is native to subtropical rainforest in New South Wales and Queensland in Australia. Common names include red bopple nut, monkey nut, red nut, beef nut, rose nut and ivory silky oak. The tree produces fleshy, red fruits during spring and summer. These contain edible seeds.

Hakea decurrens, commonly known as bushy needlewood, is a species of shrub or small tree in the family Proteaceae.
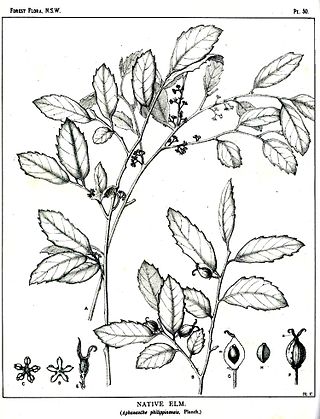
Aphananthe philippinensis is a common rainforest tree in the family Cannabaceae. In Australia it occurs from the Manning River in New South Wales to near Herberton in tropical Queensland. It was first described from the island of Luzon in the Philippines, hence the species name. The generic name of Aphananthe refers to insignificant flowers. This plant also occurs on the Solomon Islands and in Papua New Guinea

Drypetes deplanchei is a tree of eastern and northern Australia. It also occurs in New Caledonia and Lord Howe Island. The genus is derived from the Greek, dryppa meaning "olive fruit". The species named after Dr. Emile Deplanche, who collected this plant at New Caledonia. Common names include yellow tulip, grey boxwood, white myrtle, grey bark and yellow tulipwood.

Homalanthus nutans, known locally as the mamala tree, is a species of plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. In Australia it is known as the bleeding heart and the Queensland poplar.

Cenarrhenes is a monytypic genus in the family Proteaceae containing the single species Cenarrhenes nitida, known as the Port Arthur plum or native plum. Cenarrhenes nitida is an evergreen shrub to small tree endemic to the rainforests and scrublands of western Tasmania. It bears white flowers in late spring followed by the development of fleshy fruit.

Corokia carpodetoides, simply known locally as corokia, is a flowering plant in the Argophyllaceae family. The specific epithet derives from a resemblance to the genus Carpodetus, with the addition of the Latin suffix -oides (“resembling”).

Cryptocarya gregsonii, commonly known as native blackbutt, black plum or laurel, is a flowering plant in the laurel family. The specific epithet honours Jesse Gregson of Newcastle, New South Wales, a botanical friend of Maiden.
Geniostoma huttonii is a flowering plant in the Loganiaceae family. The specific epithet honours Ian Hutton who discovered the species in the course of his explorations of the Island.

Myrsine platystigma is a flowering plant in the family Primulaceae. It is a shrub or tree endemic to Lord Howe Island. The specific epithet comes from the Greek platys (“broad”) and stigma, with reference to the relatively broad stigma.

Goniocheton arborescens, commonly known in Australia as Mossman mahogany, is a small tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is native to rainforests of Malesia, Papuasia, Queensland and nearby islands.


















