
Fusarium wilt is a common vascular wilt fungal disease, exhibiting symptoms similar to Verticillium wilt. This disease has been investigated extensively since the early years of this century. The pathogen that causes Fusarium wilt is Fusarium oxysporum. The species is further divided into formae speciales based on host plant.

Panama disease is a plant disease that infects banana plants. It is a wilting disease caused by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc). The pathogen is resistant to fungicides and its control is limited to phytosanitary measures.

Coffea arabica, also known as the Arabica coffee, is a species of flowering plant in the coffee and madder family Rubiaceae. It is believed to be the first species of coffee to have been cultivated and is currently the dominant cultivar, representing about 60% of global production. Coffee produced from the less acidic, more bitter, and more highly caffeinated robusta bean makes up most of the remaining coffee production. The natural populations of Coffea arabica are restricted to the forests of South Ethiopia and Yemen.

Verticillium is a genus of fungi in the division Ascomycota, and are an anamorphic form of the family Plectosphaerellaceae. The genus used to include diverse groups comprising saprobes and parasites of higher plants, insects, nematodes, mollusc eggs, and other fungi, thus the genus used to have a wide-ranging group of taxa characterised by simple but ill-defined characters. The genus, currently thought to contain 51 species, may be broadly divided into three ecologically based groups - mycopathogens, entomopathogens, and plant pathogens and related saprotrophs. However, the genus has undergone recent revision into which most entomopathogenic and mycopathogenic isolates fall into a new group called Lecanicillium.

Hemileia vastatrix is a multicellular basidiomycete fungus of the order Pucciniales that causes coffee leaf rust (CLR), a disease affecting the coffee plant. Coffee serves as the obligate host of coffee rust, that is, the rust must have access to and come into physical contact with coffee in order to survive.

Ceratocystis fimbriata is a fungus and a plant pathogen, attacking such diverse plants as the sweet potato and the tapping panels of the Para rubber tree. It is a diverse species that attacks a wide variety of annual and perennial plants. There are several host-specialized strains, some of which, such as Ceratocystis platani that attacks plane trees, are now described as distinct species.

Mycosphaerella coffeicola is a sexually reproducing fungal plant pathogen. It is most commonly referred to as the asexual organism Cercospora coffeicola.

Colletotrichum kahawae is a fungal plant pathogen that causes coffee berry disease (CBD) on Coffea arabica crops. The pathogen is an ascomycete that reproduces asexually. The asexual spores (conidia) are stored within acervuli. This disease is considered to be one of the major factors hampering C.arabica production in the African continent, which represents the current geographic range of the fungus. Coffee berry disease causes dark necrosis in spots and causes the green berries of the coffee to drop prematurely. High humidity, relatively warm temperatures, and high altitude are ideal for disease formation. Given the severity of the disease and the lack of effective control measures, there is great concern that the fungus may spread to other coffee producing continents, such as South America, which could have catastrophic consequences.

Gibberella zeae, also known by the name of its anamorph Fusarium graminearum, is a fungal plant pathogen which causes fusarium head blight (FHB), a devastating disease on wheat and barley. The pathogen is responsible for billions of dollars in economic losses worldwide each year. Infection causes shifts in the amino acid composition of wheat, resulting in shriveled kernels and contaminating the remaining grain with mycotoxins, mainly deoxynivalenol (DON), which inhibits protein biosynthesis; and zearalenone, an estrogenic mycotoxin. These toxins cause vomiting, liver damage, and reproductive defects in livestock, and are harmful to humans through contaminated food. Despite great efforts to find resistance genes against F. graminearum, no completely resistant variety is currently available. Research on the biology of F. graminearum is directed towards gaining insight into more details about the infection process and reveal weak spots in the life cycle of this pathogen to develop fungicides that can protect wheat from scab infection.
Ceratocystis paradoxa or Black Rot of Pineapple is a plant pathogen that is a fungus, part of the phylum Ascomycota. It is characterized as the teleomorph or sexual reproduction stage of infection. This stage contains ascocarps, or sacs/fruiting bodies, which contain the sexually produced inoculating ascospores. These are the structures which are used primarily to survive long periods of time or overwinter to prepare for the next growing season of its host. Unfortunately, the sexual stage is not often seen in the natural field but instead the anamorph, or asexual stage is more commonly seen. This asexual stage name is Thielaviopsis paradoxa and is the common cause of Black rot or stem-end rot of its hosts.
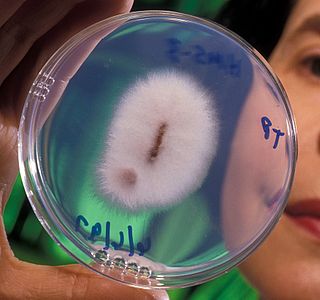
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. ciceris is a fungal plant pathogen that causes fusarium wilt of chickpea.
Fusarium sporotrichioides is a fungal plant pathogen, one of various Fusarium species responsible for damaging crops, in particular causing a condition known as Fusarium head blight in wheat, consequently being of notable agricultural and economic importance. The species is ecologically widespread, being found across tropical and temperate regions, and is a significant producer of mycotoxins, particularly trichothecenes. Although mainly infecting crops, F. sporotrichioides-derived mycotoxins can have repercussions for human health in the case of the ingestion of infected cereals. One such example includes the outbreak of alimentary toxic aleukia (ATA) in Russia, of which F. sporotrichioides-infected crop was suspected to be the cause. Although current studies on F. sporotrichioides are somewhat limited in comparison to other species in the genus, Fusarium sporotrichioides has found several applications as a model system for experimentation in molecular biology.

Coffea liberica, commonly known as the Liberian coffee, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae from which coffee is produced. It is native to western and central Africa, and has become naturalised in areas including Colombia, Venezuela, the Philippines, Borneo and Java.

A wilt disease is any number of diseases that affect the vascular system of plants. Attacks by fungi, bacteria, and nematodes can cause rapid killing of plants, large tree branches or even entire trees.

Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense is a fungal plant pathogen that causes Panama disease of banana, also known as fusarium wilt of banana. The fungi and the related disease are responsible for widespread pressure on banana growing regions, destroying the economic viability of several commercially important banana varieties.

Fusarium circinatum is a fungal plant pathogen that causes the serious disease pitch canker on pine trees and Douglas firs. The most common hosts of the pathogen include slash pine, loblolly pine, Monterey pine, Mexican weeping pine, and Douglas fir. Like other Fusarium species in the phylum Ascomycota, it is the asexual reproductive state of the fungus and has a teleomorph, Gibberella circinata.
The foamy bark canker is a disease affecting oak trees in California caused by the fungus Geosmithia sp. #41 and spread by the Western oak bark beetle. This disease is only seen through the symbiosis of the bark beetles and the fungal pathogen. The bark beetles target oak trees and bore holes through the peridermal tissues, making tunnels within the phloem. The fungal spores are brought into these tunnels by the beetles and begin to colonize the damaged cells inside the tunnels. Symptoms of the developing fungus include wet discoloration seeping from the beetle entry holes as the fungus begins to consume phloem and likely other tissues. If bark is removed, necrosis of the phloem can be observed surrounding the entry hole(s). As the disease progresses, a reddish sap and foamy liquid oozes from entry holes, thus giving the disease the name foamy bark canker. Eventually, after the disease has progressed, the tree dies. This disease is important because of its detrimental effects on oak trees and its ability to spread to several new Californian counties in just a couple of years.

Koa wilt is a relatively new disease to Hawaii, discovered in 1980. Koa wilt is caused by a forma specialis of the fungus Fusarium oxysporum, which is now abundant in Hawaiian soils and infects the native Acacia koa tree, a once-dominant species in the canopy of Hawaiian forests. Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. koae is believed to have been brought into Hawaii on an ornamental acacia plant. Fusarium fungi clog the tree xylem, causing significant wilt and mortality among these beautiful and iconic Hawaiian trees.
Phytomonas is a genus of trypanosomatids that infect plant species. Initially described using existing genera in the family Trypanosomatidae, such as Trypanosoma or Leishmania, the nomenclature of Phytomonas was proposed in 1909 in light of their distinct hosts and morphology. When the term was originally coined, no strict criterion was followed, and the term was adopted by the scientific community to describe flagellate protozoa in plants as a matter of convenience. Members of the taxon are globally distributed and have been discovered in members of over 24 plant families. Of these 24, the two main families that are infected by Phytomonas are Euphorbiaceae and Asclepiadiacae. These protists have been found in hosts between 50° latitude North and South, and thus they can be found on all continents save for Antarctica.
Coffee wilt disease (tracheomycosis) is a common wilt that results in complete death of coffee trees it infects. This vascular disease is induced by the fungal pathogen known by its teleomorph Gibberella xylarioides. In 1927, coffee wilt disease (CWD) was first observed in the Central African Republic where it developed slowly and went on to cause two epidemics between the 1930s and the 1960s. Coffee wilt disease was first seen in Coffea excelsa.













