
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimorpha and are the sister group to the Batoidea. Some sources extend the term "shark" as an informal category including extinct members of Chondrichthyes with a shark-like morphology, such as hybodonts. Shark-like chondrichthyans such as Cladoselache and Doliodus first appeared in the Devonian Period, though some fossilized chondrichthyan-like scales are as old as the Late Ordovician. The earliest confirmed modern sharks (selachimorphs) are known from the Early Jurassic around 200 million years ago, with the oldest known member being Agaleus, though records of true sharks may extend back as far as the Permian.
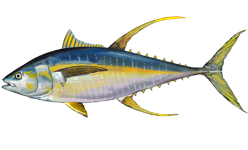
The yellowfin tuna is a species of tuna found in pelagic waters of tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide.

The brook trout is a species of freshwater fish in the char genus Salvelinus of the salmon family Salmonidae native to Eastern North America in the United States and Canada. Two ecological forms of brook trout have been recognized by the US Forest Service. One ecological form is short-lived potamodromous populations in Lake Superior known as coaster trout or coasters. The second ecological form is the long-living predaceous anadromous populations which are found in northern lakes and coastal rivers from Long Island to Hudson Bay, which are referred to as salters. In parts of its range, it is also known as the eastern brook trout, speckled trout, brook char, squaretail, brookie, or mud trout, among others. Adult coaster brook trout are capable of reaching sizes over 2 feet in length and weigh up to 6.8 kg (15 lb), whereas adult salters average between 6 and 15 inches in length and weigh between 0.5 and 2.3 kg. The brook trout is characterized by its distinctive olive-green body with yellow and blue-rimmed red spots, white and black edged orange fins, and dorsal vermiculation. The diet of the brook trout is restrictive to the season and location of the fish, but will typically consist of terrestrial and aquatic insects, fry, crustaceans, zooplankton, and worms.

The skipjack tuna is a perciform fish in the tuna family, Scombridae, and is the only member of the genus Katsuwonus. It is also known as katsuo, arctic bonito, mushmouth, oceanic bonito, striped tuna or victor fish. It grows up to 1 m (3 ft) in length. It is a cosmopolitan pelagic fish found in tropical and warm-temperate waters. It is a very important species for fisheries. It is also the namesake of the USS Skipjack.

The parore also known as luderick, black bream, black snapper or blackfish,, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea chub from the family Kyphosidae which is found in the southwestern Pacific Ocean off Australia and New Zealand. Parore or paraore is the common name in New Zealand but in Australia luderick is preferred.

The sea chubs, also known as rudderfish and pilot fish and in Hawaiian as enenue or nenue, are a family, Kyphosidae, of fishes in the order Perciformes native to the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans usually close to shore in marine waters.

Girellidae is a family of ray-finned fish in the order Centrarchiformes. They may be referred to as nibblers.

Girella cyanea, also known as the blue drummer or Australian bluefish, is a species of sea chub native to inshore waters, around 6 metres (20 ft) depth, from Australia to New Zealand and the Kermadec Islands. Sightings were first recorded in 1881 but the species made its debut in scientific publications in 1919 in Theodore Roughly's Fishes of Australia and Their Technology.

Enoplosus armatus, commonly referred to as the old wife, is a species of centrarchiform ray-finned fish endemic to the temperate coastal waters of Australia. It is the only modern species in the family Enoplosidae.

Girella fimbriata, the caramel drummer, is a species of ray-finned fish endemic to the waters around the Kermadec Islands on reefs at a depth of about 6 metres (20 ft). This species can reach a length of 36 centimetres (14 in) TL.

Toxascaris leonina is a common parasitic roundworm found in dogs, cats, foxes, and related host species. T. leonina is an ascarid nematode, a worldwide distributed helminth parasite which is in a division of eukaryotic parasites that, unlike external parasites such as lice and fleas, live inside their host. The definitive hosts of T. leonina include canids and felines (cats), while the intermediate hosts are usually rodents, such as mice or rats. Infection occurs in the definitive host when the animal eats an infected rodent. While T. leonina can occur in either dogs or cats, it is far more frequent in cats.

Until the 1960s, agriculture and fishing were the dominant industries of the economy of South Korea. The fishing industry of South Korea depends on the existing bodies of water that are shared between South Korea, China and Japan. Its coastline lies adjacent to the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea and the Sea of Japan, and enables access to marine life such as fish and crustaceans.

The southern elephant seal is one of two species of elephant seals. It is the largest member of the clade Pinnipedia and the order Carnivora, as well as the largest extant marine mammal that is not a cetacean. It gets its name from its massive size and the large proboscis of the adult male, which is used to produce very loud roars, especially during the breeding season. A bull southern elephant seal is about 40% heavier than a male northern elephant seal, which is nearly twice the weight of a male walrus, or 6–7 times heavier than the largest living mostly terrestrial carnivorans, the Kodiak bear and the polar bear.

Girella is a genus of ray-finned fish mostly native to the Pacific Ocean with a smaller presence in the Atlantic oceans.

Girella nigricans, commonly known as the opaleye or rudderfish, is a species of sea chub found in the Eastern Pacific, from California to southern Baja California. A rarely documented isolated population also exists in the Gulf of California, which might be genetically different from the rest of the species. They are commonly found in shallow waters and intertidal zones, usually over rocks and kelp beds, at depths of 1 to 32 m. They feed primarily on algae, but will occasionally consume sessile invertebrates. They are considered commercially important game fish.
Peripatopsis leonina, the Lion's Hill velvet worm, is a species of velvet worm in the Peripatopsidae family. This species has 20 to 24 pairs of legs, usually 21 or 22 leg pairs, with the last pair of legs reduced. Females of this species range from 7 mm to 41 mm in length, whereas males range from 7 mm to 34 mm.

Girella elevata, the rock blackfish, Eastern rock blackfish, black rockfish or Eastern rock blackfish drummer is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea chub from the family Kyphosidae. It is found in the southwestern Pacific Ocean around eastern Australia and northern New Zealand.

Girella zebra, also known as zebrafish or stripey bream, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea chub in the family Kyphosidae. It lives in the Indo-Pacific, where it is endemic to the coastal waters of the southern parts of Australia.

Kyphosus cinerascens is a species of marine ray-finned fish. It is a sea chub from the family Kyphosidae. Kyphosus Cinerascens has 11 dorsal fins and 12 anal fins. Kyphosus cinerascens are widely distributed in the Indo-Pacific region. The Kyphosus cinerascens has a strict diet on phaeophytes, chlorophytes, and rhodophytes, making them herbivores.
Girella nebulosa, the Rapanui nibbler, is a species of ray-finned fish within the family Girellidae. It is found in the Southeast Pacific off Easter Island, and can grow up to a length of 30 centimeters.














