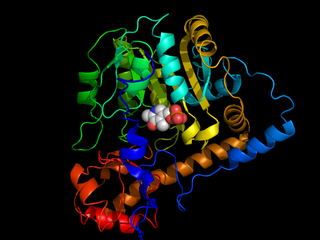
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α-keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins.

Amino acid biosynthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids.
The enzyme 2,2-dialkylglycine decarboxylase (pyruvate) (EC 4.1.1.64) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1D-1-guanidino-3-amino-1,3-dideoxy-scyllo-inositol transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-aminoethylphosphonate—pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, 4-aminobutyrate transaminase, also called GABA transaminase or 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase, or GABA-T, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
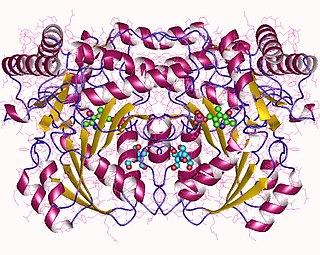
In enzymology, an alanine-glyoxylate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alanine-oxo-acid transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alanine-oxomalonate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aminolevulinate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arginine-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
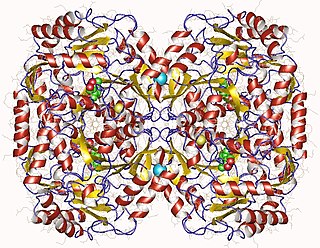
In enzymology, a beta-alanine-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-amino-acid transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a diaminobutyrate-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-methionine—pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (R)-3-amino-2-methylpropionate—pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a serine-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a valine-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Glutaminolysis (glutamine + -lysis) is a series of biochemical reactions by which the amino acid glutamine is lysed to glutamate, aspartate, CO2, pyruvate, lactate, alanine and citrate.
4-aminobutyrate---pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme with systematic name 4-aminobutanoate:pyruvate aminotransferase. This enzyme is a type of GABA transaminase, which degrades the neurotransmitter GABA. The enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction





