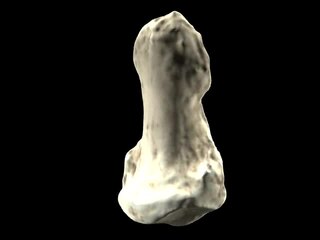
Orrorin is an extinct genus of primate within Homininae from the Miocene Lukeino Formation and Pliocene Mabaget Formation, both of Kenya.

Stag beetles are a family of about 1,200 species of beetles in the family Lucanidae, currently classified in four subfamilies. Some species grow to over 12 centimetres, but most to about 5 cm (2 in).
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for pecking, grasping, and holding, preening, courtship, and feeding young. The terms beak and rostrum are also used to refer to a similar mouth part in some ornithischians, pterosaurs, cetaceans, dicynodonts, rhynchosaurs, anuran tadpoles, monotremes, sirens, pufferfish, billfishes and cephalopods.

The Blossom-headed parakeet, Psittacula roseata or Himalayapsitta roseata, is a parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It has a lime green body and a pink or bluish grey-head and is found in Southeast Asia. This species is sometimes also referred to as Rosy-headed parakeet. Biswamoy Biswas, an Indian ornithologist, is credited as the authority on this species due to his contributions researching the birds of Nepal and Bhutan.

Andrewsarchus, meaning "Andrews' ruler", is an extinct genus of artiodactyl that lived during the Middle Eocene in what is now China. The genus was first described by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1924 with the type species A. mongoliensis based on a largely complete cranium. A second species, A. crassum, was described in 1977 based on teeth. A mandible, formerly described as Paratriisodon, does probably belong to Andrewsarchus as well. The genus has been historically placed in the families Mesonychidae or Arctocyonidae, or was considered to be a close relative of whales. It is now regarded as the sole member of its own family, Andrewsarchidae, and may have been related to entelodonts. Fossils of Andrewsarchus have been recovered from the Middle Eocene Irdin Manha, Lushi, and Dongjun Formations of Inner Mongolia, each dated to the Irdinmanhan Asian land mammal age.

Erica tetralix, the cross-leaved heath, is a species of flowering plant in the family Ericaceae, native to western Europe.

The yellow-throated toucan is a Near Threatened species of bird in the family Ramphastidae, the toucans, toucanets, and aracaris. It is found from Honduras south into northern South America and beyond to Peru.

The ericoid mycorrhiza is a mutualistic relationship formed between members of the plant family Ericaceae and several lineages of mycorrhizal fungi. This symbiosis represents an important adaptation to acidic and nutrient poor soils that species in the Ericaceae typically inhabit, including boreal forests, bogs, and heathlands. Molecular clock estimates suggest that the symbiosis originated approximately 140 million years ago.

The groove-billed toucanet is a near-passerine bird in the toucan family Ramphastidae. It is found in Colombia and Venezuela.

The ivory-billed aracari or ivory-billed araçari is a near-passerine bird in the toucan family Ramphastidae. It is found in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela.

The pale-mandibled aracari or pale-billed araçari is a near-passerine bird in the toucan family Ramphastidae. It is found in Ecuador and Peru.

The brown-mandibled aracari is a near-passerine bird in the toucan family Ramphastidae. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil, and Peru.
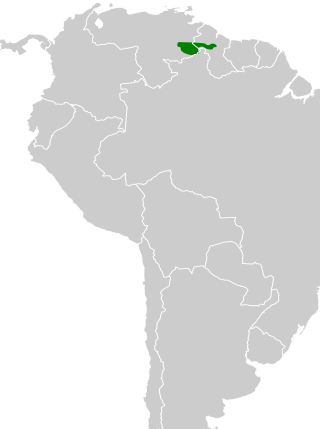
The Roraiman antbird is a species of passerine bird in subfamily Thamnophilinae of family Thamnophilidae, the "typical antbirds". It is found in Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela.
Testudovolva ericae is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Ovulidae, the ovulids, cowry allies or false cowries.

Gnamptogenys is a genus of ants in the subfamily Ectatomminae. The genus has a wide distribution. It is known to occur in the Nearctic, Neotropic, Indomalayan and Australasian realms. Camacho et al, 2022 revised this genus, significantly reducing its size to only 32 valid extant species and 5 valid fossil species by splitting off most species into four formerly synonymized genera Alfaria, Holcoponera, Poneracantha, and Stictoponera.

Poneracantha triangularis is a Neotropical species of ant in the subfamily Ectatomminae. Native to the forests of South and Central America, P. triangularis is a predatory ant that feeds on millipedes. In its native range, this species is known from Buenos Aires, Argentina in the south to Costa Rica in the north, with records from eight countries in South America, and two countries of Central America. The first records of P. triangularis outside its native range came from Florida beginning in 1985 and Alabama in 1996.

Pseudectatomma is an extinct genus of ants in the formicid subfamily Ectatomminae described by from fossils found in Europe. The genus contains two species dating from the Eocene, Pseudectatomma eocenica and Pseudectatomma striatula.

Gnamptogenys hartmani is a species of ectaheteromorph ant native to South America, Central America, Mexico, Texas, and Louisiana.
Hypostomus ericae is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the upper Tocantins River drainage in Brazil. The species reaches 24 cm in total length. Its specific epithet, ericae, honors Erica Pellegrini Caramaschi, who collected the first specimens of the species. The fish was formally described as a species new to science in 2005 by Pedro Hollanda Carvalho and Claude Weber in 2005. Characteristics that distinguish it from other catfish in genus Hypostomus include the number of odontodes in the opercle; its colour pattern, which features widely spaced spots on its body; the presence of a buccal papilla; and the depth of its caudal peduncle.
Panaspis ericae is a species of lidless skinks in the family Scincidae, native to Africa. It was first discovered in 2022 in Angola. It is named for Erica Tavares, an Angolan conservationist and biologist. P. ericae has a coppery-brown appearance and robust body.















