Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN, is the chemical compound with the formula CH3CN and structure H3C−C≡N. This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile. It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene. The N≡C−C skeleton is linear with a short C≡N distance of 1.16 Å.
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a −C≡N functional group. The prefix cyano- is used interchangeably with the term nitrile in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons.

Gordonia is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid from the Late Permian of Scotland. Fossils have been found from the Elgin sandstone of Cutties Hillock Sandstone in Elgin, Moray. These are among the many amniote fossils referred to as the Elgin Reptiles. Gordonia was named in 1893 with four species: G. traquairi, G. duffiana, G. huxleyana, and G. juddiana. Currently, the only recognized species is the type G. traquairi. All other species are considered synonyms of the type.
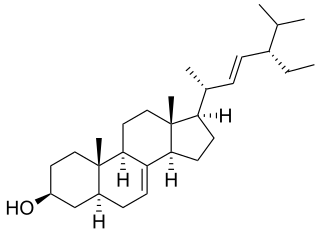
α-Spinasterol is a stigmastane-type phytosterol found in a variety of plant sources such as spinach, from which it gets its name.
Gordonia is a genus of gram-positive, aerobic, catalase-positive bacterium in the Actinomycetota, closely related to the Rhodococcus, Mycobacterium, Skermania, and Nocardia genera. Gordonia bacteria are aerobic, motile, and non-sporulating. Gordonia is from the same lineage that includes Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The genus was discovered by Tsukamura in 1971 and named after American bacteriologist Ruth Gordon.. Many species are often found in the soil, while other species have been isolated from aquatic environments. Gordonia species are rarely known to cause infections in humans.
Gordonia ceylanica is a species of plant in the family Theaceae. It is endemic to Sri Lanka.
Gordonia alkanivorans is a bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolated from soil which was contaminated with tar and phenol in Rositz in Germany. Gordonia alkanivorans has the ability to metabolize hexadecane. The strain RIPI90A of Gordonia alkanivorans can desulfurize dibenzothiophene.
Gordonia cholesterolivorans is a bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from sewage sludge from a sewage treatment plant in Ciudad Real in Spain. Gordonia cholesterolivorans has the ability to degrade cholesterol.
Gordonia defluvii is a Gram-positive and non-motile bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from activated sludge foams in Australia.
Gordonia hankookensis is a Gram-positive, aerobic and non-motile bacterium from the genus Gordonia.
Gordonia hirsuta is a bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from a biofilter of an animal rendering plant in Germany.
Gordonia humi is a Gram-positive and non-spore-forming bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from soil near the mushroom Agaricus brasiliensis in Taiwan.
Gordonia iterans is a bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from a patient with pneumonia.
Gordonia lacunae is a bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from soil from the Plettenberg Bay in South Africa.
Gordonia neofelifaecis is a bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from faeces from the leopard in the Sichuan Province in China.
Gordonia otitidis is a bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from a patient with external otitis in Japan.
Gordonia paraffinivorans is a bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from the Daqing Oil Field in China. Gordonia paraffinivorans has the ability to degrade hydrocarbon.
Gordonia rhizosphera is a bacterium from the genus Gordonia which has been isolated from rhizosphere soil from a mangrove plant in Japan.
Gordonia sihwensis is a Gram-positive and nitrate-reducing bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolated from an autotrophic denitrification reactor in Sihwa in Korea.
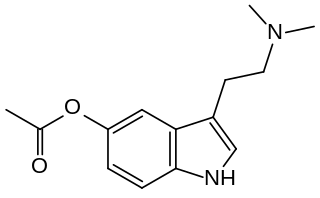
O-Acetylbufotenine is a tryptamine derivative which produces psychedelic-appropriate responding in animal studies. It is an acylated derivative of bufotenine with higher lipophilicity that allows it to cross the blood–brain barrier; once inside the brain, it is metabolised to bufotenine. It also acts directly as an agonist at 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptors.


