Related Research Articles

A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood.
Agranulocytosis, also known as agranulosis or granulopenia, is an acute condition involving a severe and dangerous lowered white blood cell count and thus causing neutropenia in the circulating blood. It is a severe lack of one major class of infection-fighting white blood cells. People with this condition are at very high risk of serious infections due to their suppressed immune system.

Neutrophilia is leukocytosis of neutrophils, that is, a high number of neutrophils in the blood. Because neutrophils are the main type of granulocytes, mentions of granulocytosis often overlap in meaning with neutrophilia.
Monocytosis is an increase in the number of monocytes circulating in the blood. Monocytes are white blood cells that give rise to macrophages and dendritic cells in the immune system.
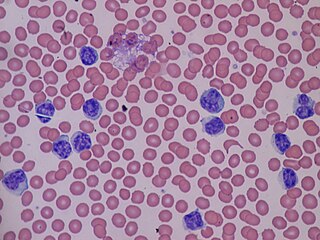
Lymphocytosis is an increase in the number or proportion of lymphocytes in the blood. Absolute lymphocytosis is the condition where there is an increase in the lymphocyte count beyond the normal range while relative lymphocytosis refers to the condition where the proportion of lymphocytes relative to white blood cell count is above the normal range. In adults, absolute lymphocytosis is present when the lymphocyte count is greater than 5000 per microliter (5.0 x 109/L), in older children greater than 7000 per microliter and in infants greater than 9000 per microliter. Lymphocytes normally represent 20% to 40% of circulating white blood cells. When the percentage of lymphocytes exceeds 40%, it is recognized as relative lymphocytosis.
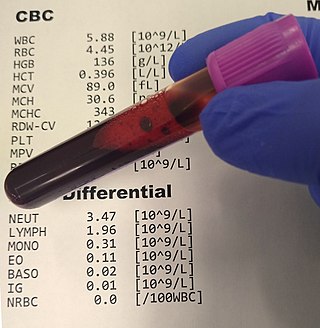
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, the concentration of hemoglobin, and the hematocrit. The red blood cell indices, which indicate the average size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells, are also reported, and a white blood cell differential, which counts the different types of white blood cells, may be included.
Leukocytosis is a condition in which the white cell is above the normal range in the blood. It is frequently a sign of an inflammatory response, most commonly the result of infection, but may also occur following certain parasitic infections or bone tumors as well as leukemia. It may also occur after strenuous exercise, convulsions such as epilepsy, emotional stress, pregnancy and labor, anesthesia, as a side effect of medication, and epinephrine administration. There are five principal types of leukocytosis:
- Neutrophilia
- Lymphocytosis
- Monocytosis
- Eosinophilia
- Basophilia

Leukopenia is a decrease in the number of leukocytes (WBC). Found in the blood, they are the white blood cells, and are the body's primary defense against an infection. Thus the condition of leukopenia places individuals at increased risk of infection.
Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is a measure of the number of neutrophil granulocytes present in the blood. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that fights against infection.
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a rare bone marrow blood cancer. It is classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, a group of cancers in which there is activation and growth of mutated cells in the bone marrow. This is most often associated with a somatic mutation in the JAK2, CALR, or MPL genes. In PMF, the bony aspects of bone marrow are remodeled in a process called osteosclerosis; in addition, fibroblast secrete collagen and reticulin proteins that are collectively referred to as (fibrosis). These two pathological processes compomise the normal function of bone marrow resulting in decreased production of blood cells such as erythrocytes granulocytes and megakaryocytes, the latter cells responsible for the production of platelets.

Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are a group of rare blood cancers in which excess red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets are produced in the bone marrow. Myelo refers to the bone marrow, proliferative describes the rapid growth of blood cells and neoplasm describes that growth as abnormal and uncontrolled.
The term leukemoid reaction describes an increased white blood cell count, which is a physiological response to stress or infection. It often describes the presence of immature cells such as myeloblasts or red blood cells with nuclei in the peripheral blood.

Left shift or blood shift is an increase in the number of immature cell types among the blood cells in a sample of blood. Many clinical mentions of left shift refer to the white blood cell lineage, particularly neutrophil-precursor band cells, thus signifying bandemia. Less commonly, left shift may also refer to a similar phenomenon in the red blood cell lineage in severe anemia, when increased reticulocytes and immature erythrocyte-precursor cells appear in the peripheral circulation.

Sweet syndrome (SS), or acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, is a skin disease characterized by the sudden onset of fever, an elevated white blood cell count, and tender, red, well-demarcated papules and plaques that show dense infiltrates by neutrophil granulocytes on histologic examination.

Basophilia is the condition of having greater than 200 basophils/μL in the venous blood.
Leukostasis is a medical emergency most commonly seen in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. It is characterized by an extremely elevated blast cell count and symptoms of decreased tissue perfusion. The pathophysiology of leukostasis is not well understood, but inadequate delivery of oxygen to the body's cells is the result. Leukostasis is diagnosed when white cell plugs are seen in the microvasculature. The most common symptoms are dyspnea and hypoxia, usually accompanied by visual changes, headaches, dizziness, confusion, somnolence, and coma. Prompt treatment is required since, if left untreated, it has a very high mortality rate. Treatments aim to rapidly reduce white blood cell counts while also treating the underlying disorder.

White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. White blood cells include three main subtypes; granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes.

Toxic vacuolation, also known as toxic vacuolization, is the formation of vacuoles in the cytoplasm of neutrophils in response to severe infections or inflammatory conditions.

A white blood cell differential is a medical laboratory test that provides information about the types and amounts of white blood cells in a person's blood. The test, which is usually ordered as part of a complete blood count (CBC), measures the amounts of the five normal white blood cell types – neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and basophils – as well as abnormal cell types if they are present. These results are reported as percentages and absolute values, and compared against reference ranges to determine whether the values are normal, low, or high. Changes in the amounts of white blood cells can aid in the diagnosis of many health conditions, including viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections and blood disorders such as leukemia.
A granulocyte transfusion is a medical procedure in which granulocytes are infused into a person's blood. Granulocyte transfusions were historically used to prevent and treat infections in people with neutropenia, but the practice declined in popularity in the 1980s. Interest in the procedure increased in the 1990s due to the development of more effective methods for harvesting granulocytes and a growing population of people with severe neutropenia from chemotherapy. However, the treatment's efficacy remains poorly understood and its use is controversial.
References
- ↑ George, Tracy I. (8 December 2012). "Malignant or benign leukocytosis". Hematology. American Society of Hematology. Education Program. 2012: 475–484. doi: 10.1182/asheducation.V2012.1.475.3798515 . PMID 23233622 . Retrieved 13 March 2019.