| Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-1 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Autosomal recessive is how this condition is inherited |
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-1 (LAD1) is a rare and often fatal genetic disorder in humans.
| Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-1 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Autosomal recessive is how this condition is inherited |
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-1 (LAD1) is a rare and often fatal genetic disorder in humans.
The main sign of the disease is life-threatening, recurrent bacterial or fungal soft tissue infections. These infections are often apparent at birth and may spread throughout the body. Omphalitis (infection of the umbilical cord stump) is common shortly after birth. Other signs include delayed separation of the umbilical cord, periodontal disease, elevated neutrophils, and impaired wound healing, but not increased vulnerability to viral infections or cancer. Such patients have fever as the manifestation of infection, inflammatory responses are indolent.[ citation needed ]
LAD1 is caused by mutations in the ITGB2 gene which are inherited autorecessively. This gene encodes CD18, a protein present in several cell surface receptor complexes found on white blood cells, [1] including lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1), complement receptor 3 (CR-3), and complement receptor 4 (CR-4). The deficiency of LFA-1 causes neutrophils to be unable to adhere to and migrate out of blood vessels, so their counts can be high. It also impairs immune cell interaction, immune recognition, and cell-killing lymphocyte functions. The lack of CR3 interferes with chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and respiratory burst [ citation needed ]
Flow cytometry with monoclonal antibodies is used to screen for deficiencies of CD18.[ citation needed ]
Because the CD18 gene has been cloned and sequenced, this disorder is a potential candidate for gene therapy. [2]
As of 2010 [update] , LAD1 has been observed in several hundred children worldwide. [3]

Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also known as Swiss-type agammaglobulinemia, is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the disturbed development of functional T cells and B cells caused by numerous genetic mutations that result in differing clinical presentations. SCID involves defective antibody response due to either direct involvement with B lymphocytes or through improper B lymphocyte activation due to non-functional T-helper cells. Consequently, both "arms" of the adaptive immune system are impaired due to a defect in one of several possible genes. SCID is the most severe form of primary immunodeficiencies, and there are now at least nine different known genes in which mutations lead to a form of SCID. It is also known as the bubble boy disease and bubble baby disease because its victims are extremely vulnerable to infectious diseases and some of them, such as David Vetter, have become famous for living in a sterile environment. SCID is the result of an immune system so highly compromised that it is considered almost absent.
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID.

Adenosine deaminase deficiency is a metabolic disorder that causes immunodeficiency. It is caused by mutations in the ADA gene. It accounts for about 10–20% of all cases of autosomal recessive forms of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) after excluding disorders related to inbreeding.
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by immunodeficiency resulting in recurrent infections. LAD is currently divided into three subtypes: LAD1, LAD2, and the recently described LAD3, also known as LAD-1/variant. In LAD3, the immune defects are supplemented by a Glanzmann thrombasthenia-like bleeding tendency.

The common gamma chain (γc), also known as interleukin-2 receptor subunit gamma or IL-2RG, is a cytokine receptor sub-unit that is common to the receptor complexes for at least six different interleukin receptors: IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 and interleukin-21 receptor. The γc glycoprotein is a member of the type I cytokine receptor family expressed on most lymphocyte populations, and its gene is found on the X-chromosome of mammals.

ICAM-1 also known as CD54 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ICAM1 gene. This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein which is typically expressed on endothelial cells and cells of the immune system. It binds to integrins of type CD11a / CD18, or CD11b / CD18 and is also exploited by rhinovirus as a receptor for entry into respiratory epithelium.

X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID) is an immunodeficiency disorder in which the body produces very few T cells and NK cells.

CD11c, also known as Integrin, alpha X (ITGAX), is a gene that encodes for CD11c.
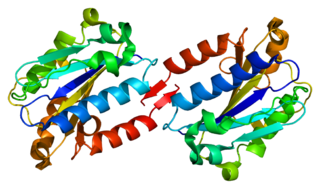
Integrin, alpha L , also known as ITGAL, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITGAL gene. CD11a functions in the immune system. It is involved in cellular adhesion and costimulatory signaling. It is the target of the drug efalizumab.
Primary immunodeficiencies are disorders in which part of the body's immune system is missing or does not function normally. To be considered a primary immunodeficiency (PID), the immune deficiency must be inborn, not caused by secondary factors such as other disease, drug treatment, or environmental exposure to toxins. Most primary immunodeficiencies are genetic disorders; the majority are diagnosed in children under the age of one, although milder forms may not be recognized until adulthood. While there are over 430 recognized inborn errors of immunity (IEIs) as of 2019, the vast majority of which are PIDs, most are very rare. About 1 in 500 people in the United States are born with a primary immunodeficiency. Immune deficiencies can result in persistent or recurring infections, auto-inflammatory disorders, tumors, and disorders of various organs. There are currently limited treatments available for these conditions; most are specific to a particular type of PID. Research is currently evaluating the use of stem cell transplants (HSCT) and experimental gene therapies as avenues for treatment in limited subsets of PIDs.
Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) is an integrin found on lymphocytes and other leukocytes. LFA-1 plays a key role in emigration, which is the process by which leukocytes leave the bloodstream to enter the tissues. LFA-1 also mediates firm arrest of leukocytes. Additionally, LFA-1 is involved in the process of cytotoxic T cell mediated killing as well as antibody mediated killing by granulocytes and monocytes. As of 2007, LFA-1 has 6 known ligands: ICAM-1, ICAM-2, ICAM-3, ICAM-4, ICAM-5, and JAM-A. LFA-1/ICAM-1 interactions have recently been shown to stimulate signaling pathways that influence T cell differentiation. LFA-1 belongs to the integrin superfamily of adhesion molecules.

The interferon-gamma receptor (IFNGR) protein complex is the heterodimer of two chains: IFNGR1 and IFNGR2. It binds interferon-γ, the sole member of interferon type II.

In molecular biology, CD18 is an integrin beta chain protein that is encoded by the ITGB2 gene in humans. Upon binding with one of a number of alpha chains, CD18 is capable of forming multiple heterodimers, which play significant roles in cellular adhesion and cell surface signaling, as well as important roles in immune responses. CD18 also exists in soluble, ligand binding forms. Deficiencies in CD18 expression can lead to adhesion defects in circulating white blood cells in humans, reducing the immune system's ability to fight off foreign invaders.

In immunology, leukocyte extravasation is the movement of leukocytes out of the circulatory system (extravasation) and towards the site of tissue damage or infection. This process forms part of the innate immune response, involving the recruitment of non-specific leukocytes. Monocytes also use this process in the absence of infection or tissue damage during their development into macrophages.

CD226, PTA1 or DNAM-1 is a ~65 kDa immunoglobulin-like transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on the surface of natural killer cells, NK T cell, B cells, dendritic cells, hematopoietic precursor cells, platelets, monocytes and T cells.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to immunology:

White blood cells, also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. White blood cells include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes.

Congenital disorder of glycosylation type IIc or Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-2 (LAD2) is a type of leukocyte adhesion deficiency attributable to the absence of neutrophil sialyl-LewisX, a ligand of P- and E-selectin on vascular endothelium. It is associated with SLC35C1.

Fermitin family homolog 3) (FERMT3), also known as kindlin-3 (KIND3), MIG2-like protein (MIG2B), or unc-112-related protein 2 (URP2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FERMT3 gene. The kindlin family of proteins, member of the B4.1 superfamily, comprises three conserved protein homologues, kindlin 1, 2, and 3. They each contain a bipartite FERM domain comprising four subdomains F0, F1, F2, and F3 that show homology with the FERM head (H) domain of the cytoskeletal Talin protein. Kindlins have been linked to Kindler syndrome, leukocyte adhesion deficiency, cancer and other acquired human diseases. They are essential in the organisation of focal adhesions that mediate cell-extracellular matrix junctions and are involved in other cellular compartments that control cell-cell contacts and nucleus functioning. Therefore, they are responsible for cell to cell crosstalk via cell-cell contacts and integrin mediated cell adhesion through focal adhesion proteins and as specialised adhesion structures of hematopoietic cells they are also present in podosome's F actin surrounding ring structure. Isoform 2 may act as a repressor of NF-kappa-B and apoptosis