
Cranham is a residential area of east London, and part of the London Borough of Havering. It is located 17.5 miles (28 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross and comprises an extensive built-up area to the north and a low density conservation area to the south surrounded by open land. It was historically a rural village in the county of Essex and formed an ancient parish. It is peripheral to London, forming the eastern edge of the urban sprawl. The economic history of Cranham is characterised by a shift from agriculture to housing development. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Cranham significantly increased in population, becoming part of Hornchurch Urban District in 1934 and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. The 2011 Census population of Cranham was included in Upminster.

Harold Wood is a suburban neighbourhood in East London in the London Borough of Havering. It is situated 16.5 miles (26.6 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross. Harold Wood was part of the ancient parish of Hornchurch, which became the Liberty of Havering. Most of the current area of Harold Wood became part of Hornchurch Urban District in 1926. It is near to the Greater London boundary with Essex.

Hornchurch is a suburban town in East London in the London Borough of Havering. It is located 15.2 miles (24.5 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross. It comprises a number of shopping streets and a large residential area. It historically formed a large ancient parish in the county of Essex that became the manor and liberty of Havering. The economic history of Hornchurch is underpinned by a shift away from agriculture to other industries with the growing significance of nearby Romford as a market town and centre of administration. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Hornchurch significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming an urban district in 1926 and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. It is the location of Queen's Theatre, Havering Sixth Form College and Havering College of Further and Higher Education.

Upminster is a suburban town in East London, England, within the London Borough of Havering. Located 16.5 miles (26.6 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross, it is one of the locally important district centres identified in the London Plan.
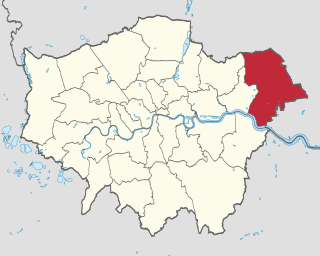
The London Borough of Havering in East London, England, forms part of Outer London. It has a population of 259,552 inhabitants; the principal town is Romford, while other communities include Hornchurch, Upminster, Collier Row and Rainham. The borough is mainly suburban, with large areas of protected open space. Romford is a major retail and night time entertainment centre, and to the south the borough extends into the London Riverside redevelopment area of the Thames Gateway. The name Havering is a reference to the Royal Liberty of Havering which occupied the area for several centuries. The local authority is Havering London Borough Council. It is the easternmost London borough.

Harold Hill is a suburban area in the London Borough of Havering, East London. 16.6 miles (26.7 km) northeast of Charing Cross. It is a district centre in the London Plan. The name refers to King Harold II, who held the manor of Havering-atte-Bower, and who was killed at the Battle of Hastings in 1066. The suburb is peripheral to London, forming an eastern edge of the urban sprawl.

Epping Forest District is a local government district in Essex, England. It is named after the ancient woodland of Epping Forest, a large part of which lies within the district. The district covers northeastern parts of the urban area of London, including the suburban towns of Epping, Loughton, Waltham Abbey, Chigwell, and Buckhurst Hill, as well as rural areas beyond it. The district is situated in the west of the county, bordering north-eastern Greater London.

The Borough of Brentwood is a local government district with borough status in Essex, England. The borough is named after its main town of Brentwood, where the council is based; it includes several villages and the surrounding rural area.

North Ockendon is the easternmost settlement of Greater London, England, and part of the London Borough of Havering. It is 18 miles (29 km) east-northeast of Central London and consists of a dispersed settlement within the Metropolitan Green Belt. It was historically an ancient parish in the county of Essex, which was abolished for civil purposes in 1936. North Ockendon is the only inhabited area in Greater London outside the M25 London Orbital Motorway. North Ockendon is north of South Ockendon, in Thurrock, Essex.

Romford is a constituency in Greater London represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2001 by Andrew Rosindell, a Conservative.

Shenfield is a suburb of Brentwood in the Borough of Brentwood, Essex, England. In 2020, it was estimated to have a population of 5,396.

Hornchurch was a local government district in southwest Essex from 1926 to 1965, formed as an urban district for the civil parish of Hornchurch. It was greatly expanded in 1934 with the addition of Cranham, Great Warley, Rainham, Upminster and Wennington; and in 1936 by gaining North Ockendon. Hornchurch Urban District Council was based at Langtons House in Hornchurch from 1929. The district formed a suburb of London and with a population peaking at 131,014 in 1961, it was one of the largest districts of its type in England. It now forms the greater part of the London Borough of Havering in Greater London.

Romford was a local government district in southwest Essex from 1851 to 1965 around the town of Romford. It was significantly expanded in 1934 and gained the status of municipal borough in 1937. The population density of the district consistently increased during its existence and its former area now corresponds to the northern part of the London Borough of Havering in Greater London.

Navestock is a civil parish in the Borough of Brentwood in south Essex, in the East of England region of the United Kingdom. It is located approximately 5 km (3.1 mi) northwest of the town of Brentwood and the M25 motorway cuts through the western edge of the parish. It covers an area of in excess of 1800 hectares and had a population of 510 in 2001, increasing to 585 in 2011. The name means ‘the stump on the headland’, which reflects its topography and landscape.

West Horndon is a village and civil parish in the south of the Borough of Brentwood in Essex, England. It is located 20 miles (32 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross in Central London. West Horndon civil parish was abolished in 1934 and created again in 2003 with new boundaries following a petition by residents in 2002. With a population of 1,650 in 2021, it is a predominantly rural parish with some residential and light industrial development. The civil parish includes the village of East Horndon. Dunton Hills, also within the civil parish, is planned to be the location of a new 3,700 home garden village. The local council of the parish is West Horndon Parish Council.
Romford Rural District was a local government district in southwest Essex, England from 1894 to 1934. It surrounded, but did not include, Romford which formed a separate urban district. During the life of the district the area changed in use from rural farm land to sprawling London suburb and in 1926 much of it was removed to form new urban districts.

Chafford was an ancient hundred in the south west of the county of Essex, England. Its area has been partly absorbed by the growth of London; with its name reused for the modern housing development of Chafford Hundred. Its former area now corresponds to part of the London Borough of Havering in Greater London and parts of the districts of Brentwood and Thurrock in Essex.

Brentwood is a town in Essex, England, in the London commuter belt 20 miles north-east of Charing Cross and close to the M25 motorway. The population of the built-up area was 55,340 in 2021.
Chelmsford Rural District was a local government district in Essex, England from 1894 to 1974. It surrounded, but did not include, the town of Chelmsford; which formed a municipal borough.
The 1994 Havering Council election took place on 5 May 1994 to elect members of Havering London Borough Council in London, England. The whole council was up for election and the council stayed in no overall control.


















