In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.

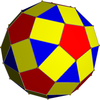
In geometry, the rhombicosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed of two or more types of regular polygon faces.

In geometry, the snub dodecahedron, or snub icosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.

In geometry, the 5-cell is the convex 4-polytope with Schläfli symbol {3,3,3}. It is a 5-vertex four-dimensional object bounded by five tetrahedral cells. It is also known as a C5, pentachoron, pentatope, pentahedroid, or tetrahedral pyramid. It is the 4-simplex (Coxeter's polytope), the simplest possible convex 4-polytope, and is analogous to the tetrahedron in three dimensions and the triangle in two dimensions. The 5-cell is a 4-dimensional pyramid with a tetrahedral base and four tetrahedral sides.

In mathematics, a Catalan solid, or Archimedean dual, is a polyhedron that is dual to an Archimedean solid. There are 13 Catalan solids. They are named after the Belgian mathematician Eugène Catalan, who first described them in 1865.
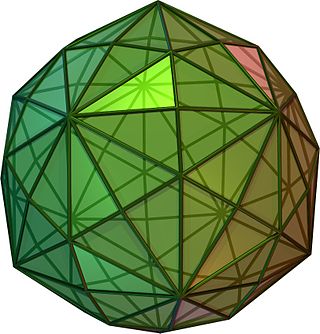
In geometry, a disdyakis triacontahedron, hexakis icosahedron, decakis dodecahedron or kisrhombic triacontahedron is a Catalan solid with 120 faces and the dual to the Archimedean truncated icosidodecahedron. As such it is face-uniform but with irregular face polygons. It slightly resembles an inflated rhombic triacontahedron: if one replaces each face of the rhombic triacontahedron with a single vertex and four triangles in a regular fashion, one ends up with a disdyakis triacontahedron. That is, the disdyakis triacontahedron is the Kleetope of the rhombic triacontahedron. It is also the barycentric subdivision of the regular dodecahedron and icosahedron. It has the most faces among the Archimedean and Catalan solids, with the snub dodecahedron, with 92 faces, in second place.

In geometry, a pentagonal hexecontahedron is a Catalan solid, dual of the snub dodecahedron. It has two distinct forms, which are mirror images of each other. It has 92 vertices that span 60 pentagonal faces. It is the Catalan solid with the most vertices. Among the Catalan and Archimedean solids, it has the second largest number of vertices, after the truncated icosidodecahedron, which has 120 vertices.

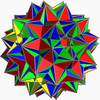
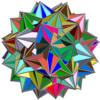
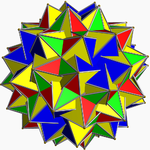
In geometry, the great dirhombicosidodecahedron (or great snub disicosidisdodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed last as U75. It has 124 faces (40 triangles, 60 squares, and 24 pentagrams), 240 edges, and 60 vertices.

In geometry, the great stellated dodecahedron is a Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron, with Schläfli symbol {5⁄2,3}. It is one of four nonconvex regular polyhedra.

In geometry, the great icosahedron is one of four Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra, with Schläfli symbol {3,5⁄2} and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram of . It is composed of 20 intersecting triangular faces, having five triangles meeting at each vertex in a pentagrammic sequence.

In geometry, the great snub icosidodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U57. It has 92 faces (80 triangles and 12 pentagrams), 150 edges, and 60 vertices. It can be represented by a Schläfli symbol sr{5⁄2,3}, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram .

In geometry, the small snub icosicosidodecahedron or snub disicosidodecahedron is a uniform star polyhedron, indexed as U32. It has 112 faces (100 triangles and 12 pentagrams), 180 edges, and 60 vertices. Its stellation core is a truncated pentakis dodecahedron. It also called a holosnub icosahedron, ß{3,5}.

In geometry, the snub dodecadodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U40. It has 84 faces (60 triangles, 12 pentagons, and 12 pentagrams), 150 edges, and 60 vertices. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5⁄2,5}, as a snub great dodecahedron.

In geometry, the nonconvex great rhombicosidodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U67. It has 62 faces (20 triangles, 30 squares and 12 pentagrams), 120 edges, and 60 vertices. It is also called the quasirhombicosidodecahedron. It is given a Schläfli symbol rr{5⁄3,3}. Its vertex figure is a crossed quadrilateral.
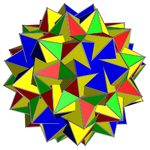
In geometry, the inverted snub dodecadodecahedron (or vertisnub dodecadodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U60. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5/3,5}.

In geometry, the great inverted snub icosidodecahedron (or great vertisnub icosidodecahedron) is a uniform star polyhedron, indexed as U69. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{5⁄3,3}, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram . In the book Polyhedron Models by Magnus Wenninger, the polyhedron is misnamed great snub icosidodecahedron, and vice versa.
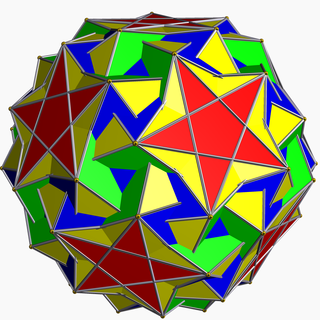
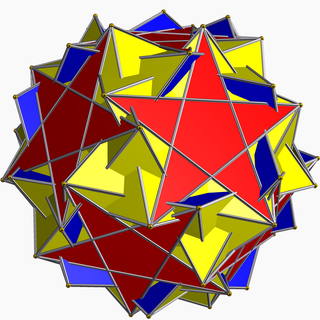
In geometry, the snub icosidodecadodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U46. It has 104 faces (80 triangles, 12 pentagons, and 12 pentagrams), 180 edges, and 60 vertices. As the name indicates, it belongs to the family of snub polyhedra.
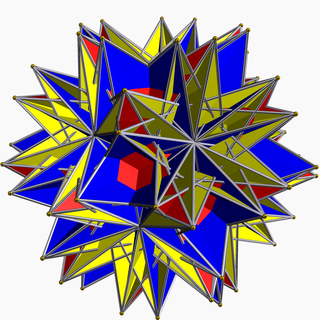
In geometry, the small retrosnub icosicosidodecahedron (also known as a retrosnub disicosidodecahedron, small inverted retrosnub icosicosidodecahedron, or retroholosnub icosahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U72. It has 112 faces (100 triangles and 12 pentagrams), 180 edges, and 60 vertices. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{⁵/₃,³/₂}.
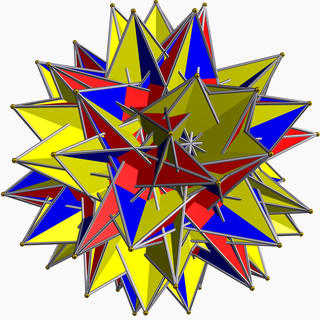
In geometry, the great retrosnub icosidodecahedron or great inverted retrosnub icosidodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U74. It has 92 faces (80 triangles and 12 pentagrams), 150 edges, and 60 vertices. It is given a Schläfli symbol sr{3⁄2,5⁄3}.
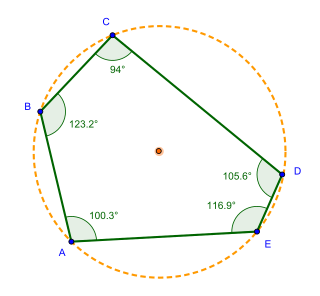
In geometry, a pentagon is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540°.
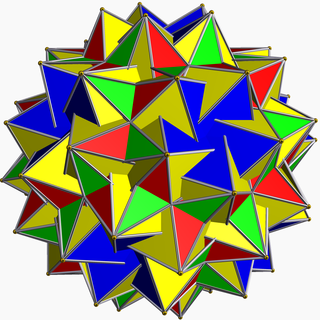


![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . It has the unusual feature that its 24 pentagram faces occur in 12 coplanar pairs.
. It has the unusual feature that its 24 pentagram faces occur in 12 coplanar pairs.