
The Hypostominae are a subfamily of catfishes of the family Loricariidae. Most members are restricted to tropical and subtropical South America, but there are also several species in southern Central America. Hypostomus plecostomus, which is popular in the aquarium trade, has been introduced to several regions far from its native range.

Guyanancistrus is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes.

Guyanancistrus nassauensis is a species of catfish belonging to the family Loricariidae, the suckermouth armored catfishes. It is discovered in 2005 and formally described in 2018. G. nassauensis is a rare species, highly endemic to the Nassau Mountains in Suriname, and is threatened with extinction by proposed or ongoing mining activities.

The Nassau Mountains is a mountain range in the Sipaliwini District of Suriname. It is named after the House of Nassau.
Pseudoqolus koko is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae and the only species in the genus Pseudoqolus. It is a freshwater fish native to South America, where it occurs in the Maroni basin. It is usually found on or near stony substrates in the main river channel at a depth of around 2 m. The species has been collected alongside multiple other loricariid species, including Hemiancistrus medians, Peckoltia otali, Pseudancistrus barbatus, Harttia guianensis, Loricaria cataphracta, and Rineloricaria stewarti. It is noted that the gut contents of one specimen of this species contained primarily spicules and sponge fragments, indicating that it may feed on freshwater sponges. The species reaches 9 cm SL.
Peckoltia simulata is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Oyapock River in French Guiana. The species is typically found in small forested creeks with a substrate of gravel or sand, as well as rocks, leaves, and wood. It has been collected alongside a variety of other species, including other loricariids belonging to the genera Ancistrus, Farlowella, Guyanancistrus, Otocinclus, and Rineloricaria.
Pseudancistrus asurini is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Xingu River basin in the state of Pará in Brazil. The species reaches 19.6 cm SL. Its specific epithet, asurini, refers to the Asurini people, native speakers of the Xingu Asurini language, who inhabit the Xingu basin near Altamira. It was described in 2015 by Gabriel S. C. Silva, Fábio F. Roxo, and Claudio Oliveira alongside the related species Pseudancistrus kayabi from the Tapajós basin.
Pseudancistrus kayabi is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Teles Pires River, which is part of the Tapajós basin in the state of Mato Grosso in Brazil. The species reaches 8.8 cm SL. Its specific epithet, kayabi, refers to the Kayabí people who historically inhabited the region surrounding the Teles Pires, Arinos, and Dos Peixes river basins in Mato Grosso. It was described in 2015 by Gabriel S. C. Silva, Fábio F. Roxo, and Claudio Oliveira alongside the related species Pseudancistrus asurini from the Xingu River basin.
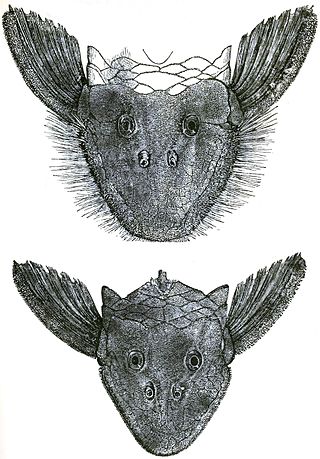
Pseudancistrus barbatus, commonly known as the bearded catfish, is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the basins of the Oyapock, the Mana River, the Maroni, the Suriname River, the Courantyne River, and the Essequibo River. Within its range, the bearded catfish is typically found in rocky, fast-flowing rapids.

Pseudancistrus corantijniensis is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Courantyne River in Suriname. The species reaches 17.9 cm SL, and it is named for the Courantyne, which is its only known habitat.

Pseudancistrus depressus is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is a freshwater fish native to South America, where it is known only from Suriname, reportedly occurring in the Coppename River. The species reaches 13 cm in total length.
Pseudancistrus genisetiger is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Jaguaribe River basin in Brazil. The species reaches 10.3 cm SL.
Pseudancistrus kwinti is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Coppename River in Suriname. The species reaches 9.4 cm (3.7 in) SL. P. kwinti was described in 2010 by Phil Willink of the Field Museum of Natural History, Jan Mol of Anton de Kom University of Suriname, and Barry Chernoff of Wesleyan University on the basis of distinctive morphology and coloration.

Pseudancistrus zawadzkii is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Tapajós basin, including the Tracuá River, in Brazil. It is typically found in areas with clear water, rocky outcrops, small waterfalls, and a substrate of rocks and sand. The species reaches 12.9 cm SL.

Pseudancistrus nigrescens is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the upper Potaro River basin in Guyana. The species reaches 18.2 cm in total length.
Pseudancistrus yekuana is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae.
'Pseudancistrus' megacephalus is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is of uncertain and disputed classification.
Hypostomus papariae is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it is believed to occur in the Potenji River basin in the state of Rio Grande do Norte in Brazil. The species reaches 11.4 cm in total length and is believed to be a facultative air-breather. The specific epithet papariae likely refers to Lake Papari, which the species is known from, an etymology shared with another loricariid species, Pseudancistrus papariae.

Guyanancistrus brevispinis is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is a freshwater fish native to South America, where it occurs in the Atlantic coastal drainages of the Guianas, ranging from the Nickerie River basin to the Oyapock basin in French Guiana and Suriname. It has also been reported from Guyana, but this is believed to be a misidentification. The species is considered the most common and abundant member of the genus Guyanancistrus, occurring in rocky streams with flowing water, especially in the vicinity of plunging waters. It is known to coexist with members of the genus Lithoxus in small forested creeks as well as rapids. The species reaches 14.2 cm in standard length.

Guyanancistrus brownsbergensis is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the upper Kumbu Creek, which is part of the Saramacca River basin, in Brownsberg Nature Park in the Brownsberg Mountains in Suriname. The type locality of the species is a small mountain stream with a width of 2.5 to 3.7 m, a depth of 28 to 50 cm, a temperature of 23.1 to 23.2 °C, an oxygen concentration of 7.08 to 7.72 g/mL, an oxygen saturation of 93% to 96%, a pH of 7 to 7.5, a conductivity of 30.8 to 31.6 μS/cm, and a current strength of 0.29 to 0.56 m/s. The stream has clear water and a substrate composed of sand, gravel, pebbles, bedrock, and boulders, and overhanging vegetation, leaf litter, and woody debris are present. The species reaches 6.4 cm in standard length. It is known that the habitat of the species is threatened by illegal gold mining.







