Related Research Articles

NO Apodis is a solitary, red hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Apus. It has an average apparent magnitude of 5.86, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. The object is relatively far at a distance of 790 light years but is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity −18.3 km/s.
HD 164712, also known as HR 6731 is an orange hued star located in the southern constellation of Apus. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.86, making it faintly visible to the naked eye if viewed under ideal conditons. Parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 229 light-years (70 pc), and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 14.8 km/s.
HD 161988, also known as HR 6635, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Apus. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.07, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements place it at a distance of 621 light years, and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 36.8 km/s.
HD 173791 is a solitary yellow hued star located in the southern constellation Telescopium. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.80, allowing it to be viewed with the naked eye under suitable viewing conditions. Parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 364 light years, and it is currently receding from the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of 9.7 km/s.
HD 85951, formally named Felis, is a solitary orange hued star in the constellation Hydra. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.94, making faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Based on parallax measurements, the object is about 570 light-years away from the Sun and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 50 km/s.
HD 83332 is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern constellation Antlia. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.68, making it faintly visible to the naked eye if viewed under ideal conditions. The star is located 285 light years away based on its annual parallax shift, but is drifting away with a radial velocity of 30 km/s.
HD 83380 is an orange-hued star in the southern constellation of Antlia. It shines faintly with a apparent magnitude of 5.62 when viewed in ideal conditions. Parallax measurements place the object at distance of 312 light-years. It has a heliocentric radial velocity of −2.6 km/s, indicating that it is drifting towards the Solar System.

HD 197027 is a star in the constellation Capricornus. It has an apparent magnitude of 9.15, making it readily visible through a telescope but not to the naked eye. The object is located at a distance of 255 light years but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −44 km/s.
HD 50002 is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Volans. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 6.09 and is located at a distance of 708 light years. However, it is drifting further with a heliocentric radial velocity of 5.1 km/s.
HD 53501, is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Volans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.18, allowing it to be seen with the naked eye under ideal conditions. The object is located at a distance of 308 light years but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 39 km/s.
HD 75116, also known as HR 3491, is a solitary, orange hued star in the southern circumpolar constellation Volans, the flying fish. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.31, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. Parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft place the star relatively far at a distance of 930 light years. It appears to be approaching the Solar System, having a heliocentric radial velocity of −17.5 km/s.
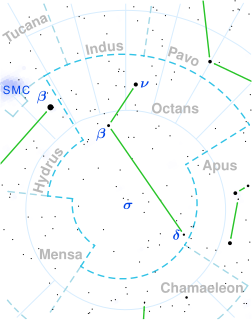
Tau Octantis, Latinized from τ Octantis, is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.50, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. The object is located at a distance of 480 light years but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 31 km/s.
Kappa Octantis, Latinized from κ Octantis, is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.55, making it visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. The object is located at a distance of 285 light years but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −9 km/s.

HD 199223 is a double star in the equatorial constellation Delphinus. However, the system was originally in Equuleus prior to the creation of official IAU constellation borders. The components have a separation of 2″ at a position angle of 282° as of 2016. They have apparent magnitudes of 6.34 and 7.49 and distances of 354 and 359 light years respectively. The system is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −33 km/s.
HD 120213 is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 5.94 and is estimated to be 910 light years away from the Solar System. However, the object is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −35 km/s.
HD 222806 is a suspected astrometric binary in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.74, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. Parallax measurements place the system at a distance of 565 light years and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 21 km/s.
HD 193721 is an astrometric binary in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.77, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. Parallax measurements place the system 760 light years away from the Solar System and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity 8.6 km/s.
HD 193373 is a solitary red hued star located in the equatorial constellation Delphinus. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.21, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. Parallax measurements place it 846 light years distant and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 22.7 km/s.
HD 182509, also designated as HR 7370, is an orange hued star located in the southern constellation Telescopium. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.69, making it faintly visible to the naked eye if viewed under ideal conditions. Parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 635 light years. It has a poorly constrained heliocentric radial velocity of −5 km/s, indicating that it is drifting towards the Solar System.
HD 208741, also known as HR 8380, is a yellowish-white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.91, making it faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements place it at a distance of 211 light years, and it is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 8 km/s.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 649: A1. arXiv: 2012.01533 . Bibcode:2021A&A...649A...1G. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202039657 . S2CID 227254300. (Erratum: doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657e). Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (March 2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27–L30. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H. ISSN 0004-6361.
- 1 2 3 Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia Collaboration) (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . arXiv: 2208.00211 . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 . Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 Houk, N.; Cowley, A. P. (1975). University of Michigan Catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars. Volume I. Declinations −90° to −53°. Bibcode:1975mcts.book.....H.
- 1 2 Johnson, H. L.; Mitchell, R. I.; Iriarte, B.; Wisniewski, W. Z. (1966). "UBVRIJKL Photometry of the Bright Stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory. 4: 99–110. Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- 1 2 Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv: 1606.08053 . Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. eISSN 1562-6873. ISSN 1063-7737. S2CID 119231169.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (May 2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331–346. arXiv: 1108.4971 . Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. eISSN 1562-6873. ISSN 1063-7737. S2CID 119257644.
- 1 2 Kervella, Pierre; Arenou, Frédéric; Thévenin, Frédéric (2022). "Stellar and substellar companions from Gaia EDR3". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 657: A7. arXiv: 2109.10912 . Bibcode:2022A&A...657A...7K. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202142146 . eISSN 1432-0746. ISSN 0004-6361.
- 1 2 3 4 Stassun, Keivan G.; et al. (9 September 2019). "The Revised TESS Input Catalog and Candidate Target List". The Astronomical Journal. 158 (4): 138. arXiv: 1905.10694 . Bibcode:2019AJ....158..138S. doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/ab3467 . ISSN 0004-6256.
- 1 2 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365 . Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 . Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 De Medeiros, J. R.; Alves, S.; Udry, S.; Andersen, J.; Nordström, B.; Mayor, M. (January 2014). "A catalog of rotational and radial velocities for evolved stars: V. Southern stars⋆⋆⋆". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 561: A126. arXiv: 1312.3474 . Bibcode:2014A&A...561A.126D. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201220762 . ISSN 0004-6361.
- ↑ Gould, B. A., Uranometria Argentina, Reprinted and updated by Pilcher, F, archived from the original on 2012-02-27, retrieved 2012-01-06
- ↑ "HR 7812". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved July 28, 2022.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (11 September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 389 (2): 869–879. arXiv: 0806.2878 . Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x . eISSN 1365-2966. ISSN 0035-8711.