
Merope, designated 23 Tauri, is a star in the constellation of Taurus and a member of the Pleiades star cluster. It is approximately 440 light-years (135 pc) away.

HD 32188 is suspected variable star in the northern constellation of Auriga, and is positioned roughly in between Eta and Zeta Aurigae. It has a white hue and is just barely visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 6.08. The distance to this star is approximately 3,000 light years, based on parallax. It has an absolute magnitude of −2.87.

HD 24479, also designated as HR 1204, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. The star is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.04. Based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, it is located 385 light years from the Sun. However, it is receding with a somewhat constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 4.6 km/s. At its current distance, HD 24479's brightness is diminished by 0.29 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

Omega1 Cygni, Latinized from ω1 Cygni, is the Bayer designation for a solitary star in the northern constellation of Cygnus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.94. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 2.59 mas, it is estimated to lie roughly 1,260 light years from the Sun. Relative to its neighbors, this star has a peculiar velocity of 25.7±2.2 km/s.

V1073 Scorpii is a variable star in the constellation Scorpius. It has a non-Greek Bayer designation of k Scorpii. The star has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around +4.87. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of approximately 2,920 ly (896 pc) from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +7 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −6.8

R Octantis, also known as HD 40857, is a solitary, red hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude that varies in-between 6.4 and 13.2 within 405 days. At is maximum, it is barely visible to the naked eye. The object is located relatively far at a distance of about 1,900 light years based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 46 km/s.
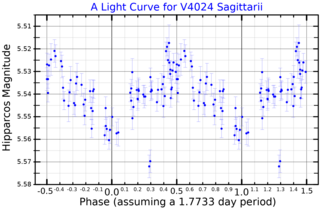
V4024 Sagittarii is a single variable star in the southern constellation of Sagittarius. It has a blue-white hue and is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates from about 5.3 to 5.6. The star is located at a distance of approximately 1,700 light years based on stellar parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −20 km/s. The position of this star near the ecliptic means it is subject to lunar occultations.

Eta Octantis, Latinized from η Octantis, is a solitary star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.19, making it faintly visible to the naked eye. The object is situated at a distance of 358 light years but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −1.7 km/s.

Phi Octantis, Latinized from φ Octantis, is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.46, making it faintly visible to the naked eye if viewed under ideal conditions. The star is relatively close at a distance of 194 light years but is receding from the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of 5 km/s.

Pi2 Octantis, Latinized from π2 Octantis, is a solitary star situated in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.64, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Located 1,570 light years away, the star is approaching the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of −13.8 km/s.

Chi Octantis, Latinized from χ Octantis, is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.28, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. Located 261 light years away, it is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity 33.6 km/s.

Tau Octantis, Latinized from τ Octantis, is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.50, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. The object is located at a distance of 480 light years but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 31 km/s.
γ2 Octantis, Latinized to Gamma2 Octantis, is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.72, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. Parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 320 light years and is currently receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 27 km/s.

Omega Octantis,, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.87, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. Based on the object's parallax measurements, it is estimated to be 328 light years distant. However, it is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity −7.6 km/s.

WZ Columbae, also known as HD 38170, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the southern constellation Columba, the dove. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.28, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is about 365 light years distant. It appears to be receding from the Solar System, having a heliocentric radial velocity of 36.3 km/s.

CW Octantis, also known as HD 148542, is a solitary, white hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.03, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements from Gaia DR3 place the object at a distance of 629 light years. It appears to be receding from the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of 7.1 km/s.
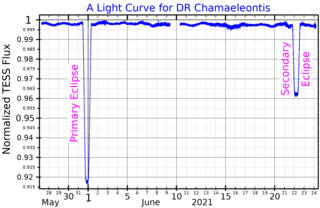
DR Chamaeleontis, also known as HD 93237, is a star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon. The system has an average apparent magnitude of 5.97, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. DR Cha is located relatively far at a distance of 1,060 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, but is receding with a poorly constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 18 km/s.

23 Leonis Minoris is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the northern constellation Leo Minor. It is positioned 7° south and 11" west from β Leonis Minoris. It is rarely called 7 H. Leonis Minoris, which is its Hevelius designation.

40 Leonis Minoris is a white hued star located in the northern constellation Leo Minor. It is rarely called 14 H. Leonis Minoris, which is the designation given by Polis astronomer Johann Hevelius.

HD 197630, also known as HR 7933 or rarely 23 G. Microscopii, is a probable astrometric binary located in the southern constellation Microscopium. The visible component is a bluish-white hued star that is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 5.47. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia satellite, the system is estimated to be 328 light years away. However, it is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −30 km/s. At its current distance, HD 197630's brightness is diminished by 0.11 magnitudes due to interstellar dust. A 2012 multiplicity survey failed to confirm the velocity variations.















