RV Caeli, also known as HD 28552, is a solitary, red hued variable star located in the southern constellation Caelum, the chisel. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.4, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. The object is located relatively far at a distance of 1,340 light years based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, but is rapidly receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 98 km/s.

NO Apodis is a solitary, red hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Apus. It has an average apparent magnitude of 5.86, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. The object is relatively far at a distance of 790 light years but is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity −18.3 km/s.
HD 27274, also known as Gliese 167, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern constellation Dorado. It has an apparent magnitude of 7.63, making it readily visible in binoculars, but not to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the star is known to be located 42.5 light-years away from the Solar System However, it is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −23 km/s. At its current distance, HD 27274 is dimmed down by 0.05 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.
HD 173791 is a solitary yellow hued star located in the southern constellation Telescopium. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.80, allowing it to be viewed with the naked eye under suitable viewing conditions. Parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 364 light years, and it is currently receding from the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of 9.7 km/s.
HD 85951, formally named Felis, is a solitary orange hued star in the constellation Hydra. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.94, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Based on parallax measurements, the object is about 570 light-years away from the Sun and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 50 km/s.

Q Scorpii, also designated as HD 159433, is an astrometric binary located in the southern zodiac constellation Scorpius. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.27, making it readily visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. It lies in the tail of Scorpius, between the stars λ Scorpii and μ Scorpii and is located 7′ away from the faint globular cluster Tonantzintla 2. Based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, the system is estimated to be 158 light years distant, but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −49 km/s.
HD 63399 is an orange hued star located in the southern constellation Puppis, the poop deck. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.45, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. Based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, the object is estimated to be 445 light years distant. It appears to be receding with a spectroscopic radial velocity of 28.5 km/s. At its current distance, HD 63399 is diminished by 0.29 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.
HD 96146 is a binary star located in the southern constellation Antlia. The system has a combined apparent magnitude of 5.41, making it visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft place the pair at a distance of 710 light years with a large margin of error. It is currently receding with a poorly constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 4.7 km/s.
HD 121439, also known as HR 5240, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Apus. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.08, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The object is located relatively far at a distance of 774 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements but is receding with a fairly constrained radial velocity of 4 km/s. At its current distance, HD 121439's brightness is diminished by 0.57 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.
HD 39901 is an orange hued star located in the constellation Columba. It is also called HR 2069, which is the star's Bright Star Catalog designation. Eggen (1989) lists it as a member of the old disk population.
HD 30080, also known as HR 1509, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern constellation Caelum, the chisel. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.66, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements from Gaia DR3 place the object at a distance of 612 light years. It appears to be approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −3.8 km/s. Eggen (1989) lists it as a member of the thick disk population.
HD 37289, also known as HR 1916, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.61, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is estimated to be 308 light years distant. It appears to be approaching the Sun, having a heliocentric radial velocity of −20.7 km/s.

WZ Columbae, also known as HD 38170, is a solitary, bluish-white hued star located in the southern constellation Columba, the dove. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.28, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is about 365 light years distant. It appears to be receding from the Solar System, having a heliocentric radial velocity of 36.3 km/s.
HD 167714, also known as HR 6837, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has apparent magnitude of 5.95, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from Gaia, the object is estimated to be 359 light years distant. With a heliocentric radial velocity of −13.9 km/s, it is approaching the Solar System.
HD 58425, also known as HR 2830, is an astrometric binary located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It is faintly visible to the naked eye as an orang point of light at an apparent magnitude of 5.64. Based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, the system is estimated to be 470 light years away from Earth. It appears to be rapidly receding from the Sun, having a heliocentric radial velocity of 58.6 km/s. HD 58425 is listed as 54 Ursae Majoris in Johann Hevelius' catalogue, but this was dropped after the official IAU's official constellation borders were drawn.

CW Octantis, also known as HD 148542, is a solitary, white hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.03, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements from Gaia DR3 place the object at a distance of 629 light years. It appears to be receding from the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of 7.1 km/s.
HD 191220, also known as HR 7698, is a solitary white hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.14, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 245 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements but is slowly receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 0.1 km/s. At its current distance, HD 191220's brightness is diminished by 0.22 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 198716, also known as HR 7987 or 33 G. Microscopii, is a solitary star located in the southern constellation Microscopium. Eggen (1993) lists it as a member of the Milky Way's old disk population.

HD 196737, also designated as HR 7893, is a solitary orange hued star located in the southern constellation Microscopium. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.47, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The object is located relatively close at a distance of 241 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 14.2 km/s. At its current distance, HD 196737's brightness is diminished by 0.14 magnitudes due to interstellar dust. It has an absolute magnitude of 1.17.
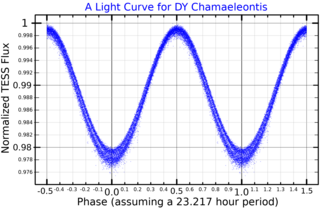
HD 118285, also known as HR 5115, is a variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon. DY Chamaeleontis is its variable star designation. It has an average apparent magnitude of 6.32, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. The object is located relatively far at a distance of 864 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 18 km/s. At its current distance, HD 118285's brightness is diminished by 0.58 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.







