
Coma Berenices is an ancient asterism in the northern sky, which has been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is in the direction of the fourth galactic quadrant, between Leo and Boötes, and it is visible in both hemispheres. Its name means "Berenice's Hair" in Latin and refers to Queen Berenice II of Egypt, who sacrificed her long hair as a votive offering. It was introduced to Western astronomy during the third century BC by Conon of Samos and was further corroborated as a constellation by Gerardus Mercator and Tycho Brahe. It is the only modern constellation named after a historic person.
NGC 1 is an intermediate spiral galaxy of the morphological type Sbc, located in the constellation of Pegasus. It was discovered on 30 September 1861 by Heinrich d'Arrest.

NGC 6946, sometimes referred to as the Fireworks Galaxy, is a face-on intermediate spiral galaxy with a small bright nucleus, whose location in the sky straddles the boundary between the northern constellations of Cepheus and Cygnus. Its distance from Earth is about 25.2 million light-years or 7.72 megaparsecs, similar to the distance of M101 in the constellation Ursa Major. Both were once considered to be part of the Local Group, but are now known to be among the dozen bright spiral galaxies near the Milky Way but beyond the confines of the Local Group. NGC 6946 lies within the Virgo Supercluster.

NGC 891 is an edge-on unbarred spiral galaxy about 30 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. It was discovered by William Herschel on October 6, 1784. The galaxy is a member of the NGC 1023 group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster. It has an H II nucleus.

NGC 1512 is a barred spiral galaxy approximately 38 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Horologium. The galaxy displays a double ring structure, with a (nuclear) ring around the galactic nucleus and an (inner) further out in the main disk. The galaxy hosts an extended UV disc with at least 200 clusters with recent star formation activity. NGC 1512 is a member of the Dorado Group.

NGC 70 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Andromeda. It was discovered on October 7, 1855, by R. J. Mitchell and was also observed on December 19, 1897 by Guillaume Bigourdan from France who described it as "extremely faint, very small, round, between 2 faint stars".

NGC 101 is a spiral galaxy estimated to be about 150 million light-years away in the constellation of Sculptor. It was discovered by John Herschel in 1834 and its magnitude is 12.8. It is a member of the Southern Supercluster the closest galaxy supercluster to the Local Supercluster.

NGC 596 is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Cetus. The galaxy lies 65 million light years away from Earth, which means, given its apparent dimensions, that NGC 596 is approximately 60,000 light years across. The galaxy shows an outer envelope and is a merger remnant. The surface brightness profile is smooth and featureless. The galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole, whose mass is estimated to be 170 million (108.24) .

NGC 4473 is an elliptical galaxy located about 50 million light-years away in the constellation of Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 8, 1784. NGC 4473 has an inclination of about 71°. NGC 4473 is a member of a chain of galaxies called Markarian's Chain which is part of the larger Virgo Cluster of galaxies.

NGC 4647 is an intermediate spiral galaxy estimated to be around 63 million light-years away in the constellation of Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on March 15, 1784. NGC 4647 is listed along with Messier 60 as being part of a pair of galaxies called Arp 116; their designation in Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies. The galaxy is located on the outskirts of the Virgo Cluster.

NGC 4907 is a barred spiral galaxy located about 270 million light-years away in the constellation of Coma Berenices. It is also classified as a LINER galaxy. NGC 4907 was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on May 5, 1864. The galaxy is a member of the Coma Cluster, located equidistant between NGC 4928 and NGC 4829.

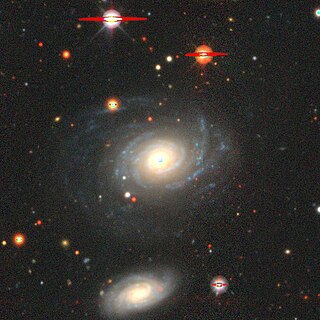
NGC 4689 is a spiral galaxy located about 54 million light-years away in the constellation of Coma Berenices. NGC 4689 is also classified as a LINER galaxy. NGC 4689 is inclined at an angle of about 36° which means that the galaxy is seen almost face-on to the Earth's line of sight. NGC 4689 was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 12, 1784. The galaxy is a member of the Virgo Cluster.

NGC 4492 is a spiral galaxy located about 90 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. NGC 4492 was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on December 28, 1785. It was rediscovered by astronomer Arnold Schwassmann on January 23, 1900, and was listed as IC 3438. NGC 4492 lies in the direction of the Virgo Cluster. However, it is not considered to be a member of that cluster.

NGC 6670 is a pair of interacting galaxies within the Draco constellation, which lie around 401 million light-years from Earth. Its shape resembles a leaping dolphin. NGC 6670 was discovered by Lewis A. Swift on July 31, 1886. NGC 6670 is a combination of two colliding disc galaxies which are known as NGC 6670E and NGC 6670W. The galaxy is 100 billion times brighter than the Sun. The galaxies have already collided once before and they are now moving towards each other again nearing a second collision. Its apparent magnitude is 14.3, its size is 1.0 arc minutes.

NGC 1993 is a lenticular galaxy located in the Lepus constellation. It was discovered by John Herschel on February 6, 1835. It is about 143 million light years from the Milky Way. Its apparent magnitude is 13.39 and its size is 1.5 arc minutes.

NGC 1510 is a dwarf lenticular galaxy approximately 38 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Horologium. It was discovered by John Herschel on December 4, 1836.

NGC 1979 is a lenticular galaxy in the Lepus constellation. It is about 78 million light-years from the Milky Way. It was discovered by William Herschel on 20 November, 1784 and its size is 1.8 by 1.8 arc minutes.

NGC 931 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Triangulum. It is located at a distance of circa 200 million light-years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 931 is about 200,000 light years across. It was discovered by Heinrich d'Arrest on September 26, 1865. It is classified as a Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 1142 is a distorted spiral galaxy in the constellation of Cetus. It is located about 370 million light years away from Earth, which means, given its apparent dimensions, that NGC 1142 is approximately 170,000 light years across. It is a type 2 Seyfert galaxy. It interacts with the elliptical galaxy NGC 1141.

NGC 1332 is an almost edge-on elliptical galaxy located in constellation of Eridanus. Situated about 70 million light years away, it is a member of the Eridanus cluster of galaxies, a cluster of about 200 galaxies. It is also the brightest member of the NGC 1332 Group. It was discovered by William Herschel on 9 December 1784.




















