
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.

The Rosette Nebula is an H II region located near one end of a giant molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy. The open cluster NGC 2244 is closely associated with the nebulosity, the stars of the cluster having been formed from the nebula's matter.

The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786. It was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by the English amateur astronomer William Huggins, demonstrating that planetary nebulae were gaseous and not stellar in nature. Structurally, the object has had high-resolution images by the Hubble Space Telescope revealing knots, jets, bubbles and complex arcs, being illuminated by the central hot planetary nebula nucleus (PNN). It is a well-studied object that has been observed from radio to X-ray wavelengths.

The Eskimo Nebula, also known as the Clown-faced Nebula, Lion Nebula, or Caldwell 39, is a bipolar double-shell planetary nebula (PN). It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The formation resembles a person's head surrounded by a parka hood. It is surrounded by gas that composed the outer layers of a Sun-like star. The visible inner filaments are ejected by a strong wind of particles from the central star. The outer disk contains unusual, light-year-long filaments.

The Owl Nebula is a planetary nebula approximately 2,030 light years away in the constellation Ursa Major. Estimated to be about 8,000 years old, it is approximately circular in cross-section with a faint internal structure. It was formed from the outflow of material from the stellar wind of the central star as it evolved along the asymptotic giant branch. The nebula is arranged in three concentric shells, with the outermost shell being about 20–30% larger than the inner shell. The owl-like appearance of the nebula is the result of an inner shell that is not circularly symmetric, but instead forms a barrel-like structure aligned at an angle of 45° to the line of sight.

NGC 2438 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Puppis. Parallax measurements by Gaia put the central star at a distance of roughly 1,370 light years. It was discovered by William Herschel on March 19, 1786. NGC 2438 appears to lie within the cluster M46, but it is most likely unrelated since it does not share the cluster's radial velocity.

NGC 7027, also known as the Jewel Bug Nebula or the Magic Carpet Nebula, is a very young and dense planetary nebula located around 3,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cygnus. Discovered in 1878 by Édouard Stephan using the 800 mm (31 in) reflector at Marseille Observatory, it is one of the smallest planetary nebulae and by far the most extensively studied.

NGC 1514, also known as the Crystal Ball Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the zodiac constellation of Taurus, positioned to the north of the star Psi Tauri along the constellation border with Perseus. Distance to the nebula is 466 pc, according to GAIA DR2 data.
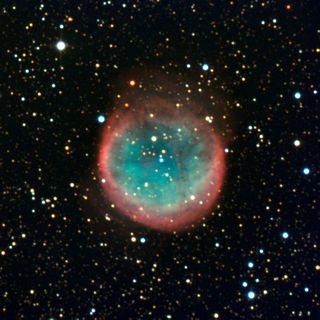
NGC 6781, also known as the Snowglobe Nebula, is a planetary nebula located in the equatorial constellation of Aquila, about 2.5° east-northeast of the 5th magnitude star 19 Aquilae. It was discovered July 30, 1788 by the Anglo-German astronomer William Herschel. The nebula lies at a distance of 1,500 ly from the Sun. It has a visual magnitude of 11.4 and spans an angular size of 1.9 × 1.8 arcminutes.

NGC 2022 is a planetary nebula in the equatorial constellation of Orion, located at a distance of 8.21 kilolight-years from the Sun. It was first observed by William Herschel on December 28, 1785, who described it as: considerably bright, nearly round, like a star with a large diameter, like an ill-defined planetary nebula. In medium-sized amateur telescopes it looks like a small grayish patch of light. It is not very bright but it is still easy to spot it in the eyepiece. Even in a telescope as small as 80mm it can just be seen using a narrowband filter such as an OIII filter as a 'fuzzy' star. The object has the shape of a prolate spheroid with a major to minor axis ratio of 1.2, an apparent size of 28″, and a halo extending out to 40″, which is about the angular diameter of Jupiter as seen from Earth.

NGC 5307 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Centaurus, positioned less than 3° to the northeast of the star Epsilon Centauri. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on April 15, 1836. The nebula is located at a distance of approximately 10.6 kilolight-years from the Sun. The central star, designated PNG 312.3+10.5, is a weak emission-line star, superficially similar to the WC subtype of Wolf–Rayet stars. It has a spectral class of O(H)3.5 V.
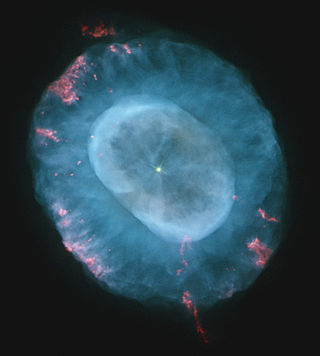
NGC 7662 is a planetary nebula located in the northern constellation Andromeda. It is known as the Blue Snowball Nebula, Snowball Nebula, and Caldwell 22. This nebula was discovered October 6, 1784 by the German-born English astronomer William Herschel. In the New General Catalogue it is described as a "magnificent planetary or annular nebula, very bright, pretty small in angular size, round, blue, variable nucleus". The object has an apparent visual magnitude of 8.3 and spans an angular size of 32″ × 28″. Parallax measurements give a distance estimate of 5,730 ± 340 ly (1,757 ± 103 pc).

NGC 2867 is an elliptical Type II planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Carina, just over a degree to the NNW of the star Iota Carinae. It was discovered by John Herschel on April 1, 1834. Herschel initially thought he might have found a new planet, but on the following night he checked again and discovered it had not moved. The nebula is located at a distance of 7,270 light-years from the Sun.

NGC 1360, also known as the Robin's Egg Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation of Fornax. It was identified as a planetary nebula due to its strong radiation in the OIII (oxygen) bands. Reddish matter, believed to have been ejected from the original star before its final collapse, is visible in images. It is slightly fainter than IC 2003.

NGC 2899 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Vela. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on February 27, 1835. This nebula can be viewed with a moderate-sized amateur telescope, but requires a larger telescope to resolve details. NGC 2899 is located at a distance of 3,350 ± 670 light-years (1,026 ± 205 pc) from the Sun and 25,894 ± 3 light-years (7,939 ± 1 pc) from the Galactic Center.

Little Ghost Nebula, also known as NGC 6369, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Ophiuchus. It was discovered by William Herschel.

NGC 1501 is a complex planetary nebula located in the constellation of Camelopardalis, it was discovered on 27 August 1787 by William Herschel.

NGC 4361 is a planetary nebula in the constellation of Corvus. It is included in the Astronomical League's Herschel 400 Observing Program.

NGC 6905, also known as the Blue Flash Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Delphinus. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1784. The central star is 14.0 mag. The distance of the nebula, as with most planetary nebulae, is not well determined and estimates range between 1.7 and 2.6 kpc.

NGC 6445, also known as the Little Gem Nebula or Box Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by William Herschel on May 28, 1786. The distance of NGC 6445 is estimated to be slightly more than 1,000 parsecs based on the parallax measured by Gaia, which was measured at 0.9740±0.3151 mas.




















