
The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the Index Catalogues, describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use.

NGC 55, is a Magellanic type barred spiral galaxy located about 6.5 million light-years away in the constellation Sculptor. Along with its neighbor NGC 300, it is one of the closest galaxies to the Local Group, probably lying between the Milky Way and the Sculptor Group. It has an estimated mass of (2.0 ± 0.4) × 1010M☉.

NGC 634 is a spiral galaxy, lying at a distance of 217.1 megalight-years away from the Milky Way in the northern constellation of Triangulum. This object was discovered in the nineteenth century by French astronomer Édouard Stephan. It is inclined by an angle of 82.4° to the line of sight from the Earth, and thus is being viewed nearly edge on.

NGC 68 is a lenticular galaxy, and the central member of the NGC 68 group, in the constellation Andromeda. The galaxy was discovered on September 11, 1784, by William Herschel, who observed the NGC 68 group as a single object and described it as "extremely faint, large, 3 or 4 stars plus nebulosity". As such, his reported location is between NGC 68, NGC 70, and NGC 71. By the time Dreyer looked at the galaxies to add to the NGC catalog, however, he was able to tell that the single galaxy observed by Herschel was in fact 3 adjacent galaxies, and cataloged them as NGC 68, NGC 70, and NGC 71.

VV 166, sometimes also called the NGC 70 galaxy group or Arp 113, is a cluster of galaxies in Andromeda. The main group was discovered in 1784 by William Herschel, who listed the galaxies as a single object. Later, in the 1880s, John Louis Emil Dreyer managed to discern some of the galaxies in this region and cataloged them. The prominent elliptical galaxy in the region, NGC 68, is probably not a member of the group.

NGC 1077 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Perseus. It was discovered on 16 August 1886 by Lewis A. Swift. It was described as "very faint, pretty large, extended" by John Louis Emil Dreyer, the compiler of the New General Catalogue.
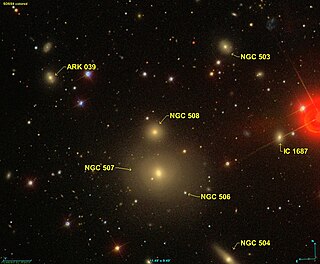
NGC 508, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5099 or UGC 939, is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 247 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 12 September 1784 by British astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 511, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5103 or UGC 936, is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is located approximately 499 million light-years from the Solar System and was discovered on 26 October 1876 by French astronomer Édouard Stephan.

NGC 519, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5182, is an elliptical galaxy located approximately 242 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Cetus. It was discovered on 20 November 1886 by astronomer Lewis Swift.

NGC 4212 is a flocculent spiral galaxy with LINER activity located about 53 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 8, 1784, and was listed in the NGC catalog as NGC 4208. He then observed the same galaxy and listed it as NGC 4212. Astronomer John Louis Emil Dreyer later concluded that NGC 4208 was identical to NGC 4212. NGC 4212 is a member of the Virgo Cluster.

NGC 714 is a lenticular galaxy located 190 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer Bindon Blood Stoney on October 28, 1850 and is a member of Abell 262.

NGC 717 is a lenticular galaxy located 210 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer Bindon Blood Stoney on October 28, 1850 and is a member of Abell 262.

NGC 739 is a spiral galaxy approximately 193 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Triangulum.












