Epsilon Eridani, proper name Ran, is a star in the southern constellation of Eridanus. At a declination of −9.46°, it is visible from most of Earth's surface. Located at a distance 10.5 light-years from the Sun, it has an apparent magnitude of 3.73, making it the third-closest individual star visible to the naked eye.

Achernar is the brightest star in the constellation of Eridanus and the ninth-brightest in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Eridani, which is Latinized from α Eridani and abbreviated Alpha Eri or α Eri. The name Achernar applies to the primary component of a binary system. The two components are designated Alpha Eridani A and B, with the latter known informally as Achernar B. As determined by the Hipparcos astrometry satellite, this system is located at a distance of approximately 139 light-years from the Sun.

40 Eridani is a triple star system in the constellation of Eridanus, abbreviated 40 Eri. It has the Bayer designation Omicron2 Eridani, which is Latinized from ο2 Eridani and abbreviated Omicron2 Eri or ο2 Eri. Based on parallax measurements taken by the Gaia mission, it is about 16.3 light-years from the Sun.

82 G. Eridani is a star 19.7 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Eridanus. It is a main-sequence star with a stellar classification of G6 V, and it hosts a system of at least three planets and a dust disk.

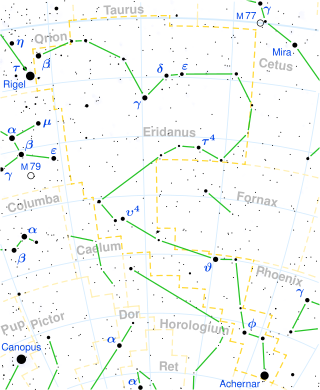
Eridanus is a constellation which stretches along the southern celestial hemisphere. It is represented as a river. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is the sixth largest of the modern constellations. The same name was later taken as a Latin name for the real Po River and also for the name of a minor river in Athens.

EF Eridani is a variable star of the type known as polars, AM Herculis stars, or magnetic cataclysmic variable stars. Historically it has varied between apparent magnitudes 14.5 and 17.3, although since 1995 it has generally remained at the lower limit. The star system consists of a white dwarf with a substellar-mass former star in orbit.

HD 10647 is a 6th-magnitude yellow-white dwarf star, 57 light-years away in the constellation of Eridanus. The star is visible to the unaided eye under very dark skies. It is slightly hotter and more luminous than the Sun, and at 1.75 billion years old, it is also younger. An extrasolar planet was discovered orbiting this star in 2003.

A K-type main-sequence star, also referred to as a K-type dwarf, or orange dwarf, is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type K and luminosity class V. These stars are intermediate in size between red M-type main-sequence stars and yellow/white G-type main-sequence stars. They have masses between 0.6 and 0.9 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 3,900 and 5,300 K. These stars are of particular interest in the search for extraterrestrial life due to their stability and long lifespan. Many of these stars have not left the main sequence as their low masses mean they stay on the main sequence for up to 70 billion years, a length of time much larger than the time the universe has existed. Well-known examples include Toliman and Epsilon Indi.
53 Eridani, also designated l Eridani, is a binary star in the constellation of Eridanus. The system has a combined apparent magnitude of 3.87. Parallax estimates made by the Hipparcos spacecraft put it at a distance of about 110 light-years, or 33.7 parsecs, from the Sun.
HD 11964 b is an extrasolar planet, a gas giant like Jupiter approximately 110 light-years away in the constellation of Cetus. The planet orbits the yellow subgiant star HD 11964 in a nearly-circular orbit, taking over 5 years to complete a revolution around the star at a distance of 3.34 astronomical units.

Epsilon Eridani b, also known as AEgir [sic], is an exoplanet approximately 10.5 light-years away orbiting the star Epsilon Eridani, in the constellation of Eridanus. The planet was discovered in 2000, and as of 2024 remains the only confirmed planet in its planetary system. It orbits at around 3.5 AU with a period of around 7.6 years, and has a mass around 0.6 times that of Jupiter. As of 2023, both the Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia and the NASA Exoplanet Archive list the planet as 'confirmed'.
Gliese 86 is a K-type main-sequence star approximately 35 light-years away in the constellation of Eridanus. It has been confirmed that a white dwarf orbits the primary star. In 1998 the European Southern Observatory announced that an extrasolar planet was orbiting the star.

Stephen Thorndike is a high school teacher. He is known for discovering, along with astrophysicist Alice C. Quillen, Epsilon Eridani c, a hypothetical planet orbiting the star Epsilon Eridani. After working at the University of Rochester, he now works as a science instructional specialist at Monroe 2 Boces in Spencerport, New York.
HD 196050 b is an exoplanet with a 1378-day period and a minimum mass of 2.90 Jupiter masses. The average orbital distance is 2.54 astronomical units and the orbital eccentricity is 22.8%. The periastron (closest) distance is 1.96 AU and the apastron (farthest) distance is 3.12 AU. The average orbital velocity is 20.1 km/s and the semi-amplitude is 49.7 m/s. The longitude of periastron is 187° and the time of periastron is 2,450,843 JD.
HD 114729 b is an extrasolar planet approximately 114 light years away in the constellation of Centaurus. This planet is probably slightly less massive than Jupiter. It is an "eccentric Jupiter" meaning that it does not orbit very near the star like the famous 51 Pegasi b but further out and its orbit is very oval-shaped. The mean distance from the star is 2.11 AU, about twice the Earth's distance from the Sun. At periastron, the planet is only 1.43 AU from the star, and at apoastron, the orbital distance is 2.72 AU.
HD 102117 b, formally named Leklsullun, is a planet that orbits the star HD 102117. The planet is a small gas giant a fifth the size of Jupiter. It orbits very close to its star, but not in a "torch orbit" like the famous 51 Pegasi b. It was one of the smallest extrasolar planets discovered as of 2006.

PSR J1719−1438 b is an extrasolar planet that was discovered on August 25, 2011, in orbit around PSR J1719−1438, a millisecond pulsar. The pulsar planet is most likely composed largely of crystalline carbon but with a density far greater than diamond. PSR J1719-1438 b orbits so closely to its host star that its orbit would fit inside the Sun. The existence of such carbon planets had been theoretically postulated.
Zeta Eridani is a binary star in the constellation of Eridanus. With an apparent visual magnitude of 4.80, it is visible to the naked eye on a clear dark night. Based on parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 110 light-years from the Sun.

51 Eridani is a star in the constellation Eridanus. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.22, meaning it is just visible to the unaided eye in suburban and rural skies. The primary star's absolute magnitude is 2.87. There is also a binary star named GJ 3305 which shares the same proper motion through space with it, making it overall a triple star system.

51 Eridani b is a "Jupiter-like" planet that orbits the young F0 V star 51 Eridani, in the constellation Eridanus. It is 96 light years away from the solar system, and it is approximately 20 million years old.








