
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) found in many animals.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB1 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRB1 gene. DRB1 encodes the most prevalent beta subunit of HLA-DR. DRB1 alleles, especially those encoding amino acid sequence changes at positions 11 and 13, are associated risk of rheumatoid arthritis.
HLA DR3-DQ2 is double serotype that specifically recognizes cells from individuals who carry a multigene HLA DR, DQ haplotype. Certain HLA DR and DQ genes have known involvement in autoimmune diseases. DR3-DQ2, a multigene haplotype, stands out in prominence because it is a factor in several prominent diseases, namely coeliac disease and juvenile diabetes. In coeliac disease, the DR3-DQ2 haplotype is associated with highest risk for disease in first degree relatives, highest risk is conferred by DQA1*0501:DQB1*0201 homozygotes and semihomozygotes of DQ2, and represents the overwhelming majority of risk. HLA DR3-DQ2 encodes DQ2.5cis isoform of HLA-DQ, this isoform is described frequently as 'the DQ2 isoform', but in actuality there are two major DQ2 isoform. The DQ2.5 isoform, however, is many times more frequently associated with autoimmune disease, and as a result to contribution of DQ2.2 is often ignored.

HLA-DQ8 (DQ8) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within the HLA-DQ (DQ) serotype group. DQ8 is a split antigen of the DQ3 broad antigen. DQ8 is determined by the antibody recognition of β8 and this generally detects the gene product of DQB1*0302.

HLA-DQ4 (DQ4) is a serotype subgroup within HLA-DQ(DQ) serotypes. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β4 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ is encoded by HLA-DQB1 locus and DQ4 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*04 allele group. This group currently contains 2 common alleles, DQB1*0401 and DQB1*0402. HLA-DQ4 and HLA-DQB1*04 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ4 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1 alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. These isoforms, nicknamed DQ4.3 and DQ4.4, are also encoded by the DQA1*0303 and DQA1*0401 genes, respectively.

HLA-DQ6 (DQ6) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-DQ (DQ) serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β6 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ isoforms are encoded by HLA-DQB1 locus and DQ6 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*06 allele group. This group currently contains many common alleles, DQB1*0602 is the most common. HLA-DQ6 and DQB1*06 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ6 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1 alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. For DQ6, however, cis-isoform pairing only occurs with DQ1 α-chains. There are many haplotypes of DQ6.

HLA-DQ1 is a serotype that covers a broad range of HLA-DQ haplotypes. Historically it was identified as a DR-like alpha chain called DC1; later, it was among 3 types DQw1, DQw2 and DQw3. Of these three serotyping specificities only DQw1 recognized DQ alpha chain. The serotype is positive in individuals who bear the DQA1*01 alleles. The most frequently found within this group are: DQA1*0101, *0102, *0103, and *0104. In the illustration on the right, DQ1 serotyping antibodies recognizes the DQ α (magenta), where antibodies to DQA1* gene products bind variable regions close to the peptide binding pocket.

HLA-DR53 is an HLA-DR serotype that recognizes gene products of HLA-DRB4 locus. There are 13 alleles at this locus that encode 7 proteins.

HLA-DR17 (DR17) is an HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*0301 and *0304 gene products. DR17 is found at high frequency in Western Europe. DR17 is part of the broader antigen group HLA-DR3 and is very similar to the group HLA-DR18.

HLA-DR16(DR16) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1601, *1602 and *1604 gene products. DR16 is found in the Mediterranean at modest frequencies. DR16 is part of the older HLA-DR2 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR15 antigens.

HLA-DR15 (DR15) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1501 to *1505 and *1507 gene products. DR15 is found at high levels from Ireland to Central Asia. DR15 is part of the older HLA-DR2 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR16 antigens.

HLA-DR14(DR14) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1401 to *1408, *1410 to *1418, and other *14 gene products. DR14 serotype is a split antigen of the older HLA-DR6 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR13 antigens.

HLA-DR11 (DR11) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1101 to *1110. DR11 serotype is a split antigen of the older HLA-DR5 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR12 antigens.

HLA-DR12(DR12) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1201 to *1203, *1206. DR12 serotype is a split antigen of the older HLA-DR5 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR11 antigens.

HLA-DR5 (DR5) is a broad-antigen serotype that is further split into HLA-DR11 and HLA-DR12 antigen serotypes.

HLA-DR3 is composed of the HLA-DR17 and HLA-DR18 split 'antigens' serotypes. DR3 is a component gene-allele of the AH8.1 haplotype in Northern and Western Europeans. Genes between B8 and DR3 on this haplotype are frequently associated with autoimmune disease. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is associated with HLA-DR3 or HLA-DR4. Nearly half the US population has either DR3 or DR4, yet only a small percentage of these individuals will develop type 1 diabetes.

HLA-DR4 (DR4) is an HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*04 gene products. The DR4 serogroup is large and has a number of moderate frequency alleles spread over large regions of the world.

HLA-DR1 (DR1) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*01 gene products. It has been observed to be common among centenarians.
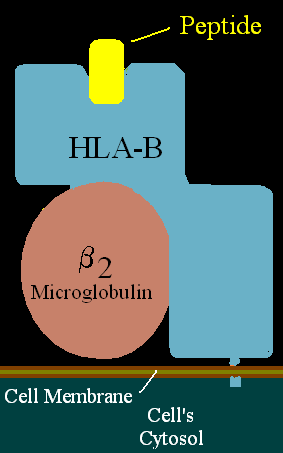
HLA-B7 (B7) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*07 gene products. B7, previously HL-A7, was one of the first 'HL-A' antigens recognized, largely because of the frequency of B*0702 in Northern and Western Europe and the United States. B7 is found in two major haplotypes in Europe, where it reaches peak frequency in Ireland. One haplotype A3-B7-DR15-DQ1 can be found over a vast region and is in apparent selective disequilibrium. B7 is a risk factor for cervical cancer, sarcoidosis, and early-onset spondylarthropathies.
HLA B7-DR15-DQ6 is a multigene haplotype that covers a majority of the human major histocompatibility complex on chromosome 6. A multigene haplotype is set of inherited alleles covering several genes, or gene-alleles, common multigene haplotypes are generally the result of descent by common ancestry. Chromosomal recombination fragments multigene haplotypes as the distance to that ancestor increases in number of generations.




