SM U-32 was a German Type U 31 U-boat of the Imperial German Navy.

SM U-35 was a German U 31-class U-boat which operated in the Mediterranean Sea during World War I. It ended up being the most successful U-boat participating in the war, sinking 220 merchant ships for a total of 505,121 gross register tons (GRT).
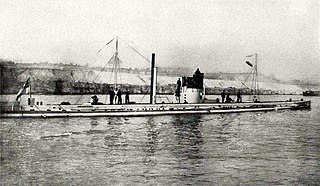
SM U-9 was a German Type U 9 U-boat. She was one of 329 submarines serving in the Imperial German Navy, and engaged in commerce raiding (Handelskrieg) during World War I.

HMS E1 was a British E-class submarine that was built by Chatham Dockyard and cost £101,700. E1 was laid down on 14 February 1911. She was launched on 9 November 1912 and was commissioned on 6 May 1913. During World War I she was part of the British submarine flotilla in the Baltic.
SM U-68 was a Type U 66 submarine or U-boat for the German Imperial Navy during the First World War. She had been laid down in December 1913 as U-9 of the U-7 class for the Austro-Hungarian Navy but was sold to Germany, along with the others in her class, in November 1914. Under German control, the class became known as the U 66 type and the boats were renumbered; U-9 became U-68, and was redesigned and reconstructed to German specifications. She was launched in June 1915 and commissioned in August.
SM U-40 was a German Type U 31 U-boat of the German Imperial Navy during World War I.

SM U-38 was a German Type U 31 U-boat which operated in the Mediterranean Sea during World War I. It ended up being the third most successful U-boat participating in the war, sinking 134 merchant ships sunk for a total of 287,811 GRT.
HMS E21 was a British E class submarine built by Vickers, Barrow-in-Furness. She was launched on 24 July 1915 and commissioned on 1 October 1915. E21 was sold on 14 December 1921.

HMS E50 was a British E-class submarine built by John Brown, Clydebank. She was launched on 13 November 1916 and was commissioned on 23 January 1917. E50 was damaged in a collision with the Imperial German Navy submarine UC-62 while submerged in the North Sea off the North Hinder Light Vessel on 19 March 1917. E 50 was lost on 1 February 1918, and it was earlier believed that she struck a mine in the North Sea off the South Dogger Light Vessel. In 2011 the wreck was found by a Danish Expedition much closer to the Danish coast, 65 NM west of Nymindegab.

HMS E49 was an E-class submarine built by Swan Hunter, Wallsend for the Royal Navy. She was laid down on 15 February 1915 and was commissioned on 14 December 1916. E49 was mined off the Shetland Islands on 12 March 1917. The minefield was laid by the German U-boat UC-76 on 10 March 1917. There were no survivors. E49 lies 96 ft (29 m) down with her bows blown off.

HMS E48 was a British E-class submarine launched by Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company, Govan in 1916 and was completed by William Beardmore and Company, Dalmuir. She was launched on 2 August 1916 and was commissioned in February 1917.

HMS E34 was a British E-class submarine built by John Thornycroft, Woolston, Hampshire. She was launched on 27 January 1917 and commissioned in March 1917. HMS E34 sank the U-boat UB-16 off Harwich in the North Sea on 10 May 1918. E34 was mined near the Eijerlandse Gronden, the sands between the Frisian islands Texel and Vlieland on 20 July 1918. There were no survivors.
HMS E35 was a British E-class submarine built by John Brown, Clydebank. She was launched on 20 May 1916 and commissioned on 14 July 1917. E35 sank U-154 off the island of Madeira on 11 May 1918. This sinking was helped by British intelligence who had learned of a planned rendezvous between two U-boats off Cape St Vincent. E35 was sold in Newcastle on 6 September 1922.
HMS E38 was a British E-class submarine built by Fairfield, Govan, Clyde. She was launched on 13 June 1916 and commissioned on 10 July 1917. E38 was sold for scrap in Newport on 6 September 1922.
HMS E44 was a British E-class submarine built by Swan Hunter, Wallsend. She was laid down on 8 January 1916 and was commissioned on 18 July 1916. E44 was sold for scrap in South Wales on 13 October 1921.
HMS E45 was a British E-class submarine built by Cammell Laird, Birkenhead. She was launched on 25 January 1916 and was commissioned in August 1916. E45 torpedoed U-boat UC-62 in the North Sea on 15 October 1917. E45 was sold in South Wales on 6 September 1922.
SM U-67 was a Type U 66 submarine or U-boat for the German Imperial Navy during the First World War. She had been laid down in November 1913 as U-8 the second boat of the U-7 class for the Austro-Hungarian Navy but was sold to Germany, along with the others in her class, in November 1914.
SM U-33 was a German Type U 31 U-boat of the Imperial German Navy.
SM U-92 was one of 329 submarines serving in the Imperial German Navy in World War I. She was engaged in the commerce warfare in the First Battle of the Atlantic.
SM U-96 was a Type U 93 submarine and one of the 329 submarines serving in the Imperial German Navy in World War I. U-96 was engaged in the naval warfare and took part in the First Battle of the Atlantic. She was launched in 1917. On 6 December 1917, she collided with the submarine SM UC-69 at Barfleur, France ; UC-69 sank with the loss of eleven of her crew. U-96 survived the war.








